As with most ancient Egyptian royal dynasties, the family tree for the Twelfth Dynasty is complex and unclear.
As with most ancient Egyptian royal dynasties, the family tree for the Twelfth Dynasty is complex and unclear.

Ancient Egypt was a civilization in ancient Northeast Africa, situated in the Egyptian Nile Valley in the country Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes. The history of ancient Egypt occurred as a series of stable kingdoms, separated by periods of relative instability known as Intermediate Periods: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age and the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.

Pharaoh is the common title now used for the monarchs of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BCE, although the term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until Merneptah, c. 1210 BCE, during the Nineteenth dynasty, "king" being the term used most frequently until the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings used to have up to three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee, and the Two Ladies or Nebty name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later.

The Ptolemaic dynasty, sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty, was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Ancient Egypt during the Hellenistic period. Their rule lasted for 275 years, from 305 to 30 BC. The Ptolemaic was the last dynasty of ancient Egypt.
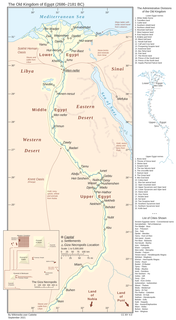
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynasty, such as King Sneferu, who perfected the art of pyramid-building, and the kings Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure, who constructed the pyramids at Giza. Egypt attained its first sustained peak of civilization during the Old Kingdom, the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley.

The First Dynasty of ancient Egypt covers the first series of Egyptian kings to rule over a unified Egypt. It immediately follows the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, possibly by Narmer, and marks the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, a time at which power was centered at Thinis.
The history of ancient Egypt spans the period from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern Nile valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC.
In ancient Egyptian history, dynasties are series of rulers sharing a common origin. They are usually, but not always, traditionally divided into 32 pharaonic dynasties; these dynasties are commonly grouped by modern scholars into "kingdoms" and "intermediate periods".

The Second Dynasty of ancient Egypt is the latter of the two dynasties of the Egyptian Archaic Period, when the seat of government was centred at Thinis. It is most known for its last ruler, Khasekhemwy, but is otherwise one of the most obscure periods in Egyptian history.

The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Sources cite at least 118 identified "Egyptian" pyramids. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. Of those located in modern Egypt, most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.

The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt is considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom by Egyptologists. It often is combined with the Eleventh, Thirteenth, and Fourteenth dynasties under the group title, Middle Kingdom. Some scholars only consider the 11th and 12th dynasties to be part of the Middle Kingdom.

The Eleventh Dynasty of ancient Egypt is a well-attested group of rulers. Its earlier members before Pharaoh Mentuhotep II are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, whereas the later members are considered part of the Middle Kingdom. They all ruled from Thebes in Upper Egypt.

The Fifth Dynasty of ancient Egypt is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and VI under the group title the Old Kingdom. The Fifth Dynasty pharaohs reigned for approximately 150 years, from the early 25th century BC until the mid 24th century BC.
The Early Dynastic Period or Archaic Period, also known as the Thinite Period, is the era of ancient Egypt that immediately follows the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt in c. 3150 BC. It is generally taken to include the First Dynasty and the Second Dynasty, lasting from the end of the archaeological culture of Naqada III until c. 2686 BC, or the beginning of the Old Kingdom. With the First Dynasty, the Egyptian capital moved from Thinis to Memphis, with the unified land being ruled by an Egyptian god-king. In the south, Abydos remained the major centre of ancient Egyptian religion; the hallmarks of ancient Egyptian civilization, such as Egyptian art, Egyptian architecture, and many aspects of Egyptian religion, took shape during the Early Dynastic Period.

The Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt is also known as the Bubastite Dynasty, since the pharaohs originally ruled from the city of Bubastis. It was founded by Shoshenq I.

The Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt was a dynasty of pharaohs that ruled in Upper Egypt during the late Second Intermediate Period, approximately from 1580 to 1550 BC. Its mainly Theban rulers are contemporary with the Hyksos of the Fifteenth Dynasty and succeed the Sixteenth Dynasty, which was also based in Thebes.
The Twenty-first, Twenty-second, and Twenty-third Dynasties ruled Egypt from the 10th century through the 8th century BC. The family tree of the Twenty-first dynasty was heavily interconnected with the family of the High Priests of Amun at Thebes. The Twenty-second dynasty and Twenty-third dynasty were also related by marriage to the family of the High Priests.

The following outline is provided as an overview of a topical guide to ancient Egypt:

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmosid Dynasty for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.

The Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt dynasty was the last native dynasty to rule Egypt before the Persian conquest in 525 BC. The dynasty's reign is also called the Saite Period after the city of Sais, where its pharaohs had their capital, and marks the beginning of the Late Period of ancient Egypt.