
Khentkaus II was a royal woman who lived in ancient Egypt. She was a wife of Egyptian king Neferirkare Kakai of the Fifth Dynasty. She was the mother of two kings, Neferefre and Nyuserre Ini.
Iput I was a queen of ancient Egypt, a daughter of King Unas, the last king of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She married Teti, the first Pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Their son was Pepi I Meryre. She possibly ruled as regent for her son Pepi I.

Ankhesenpepi II or Ankhesenmeryre II was a queen consort during the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the wife of Kings Pepi I and Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, and the mother of Pepi II. She likely served as regent during the minority of her son. She was buried in a pyramid in Saqqara.
Neith was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, one of the principal queens of the Old Kingdom pharaoh Pepi II Neferkare, who ruled. Queen Neith was named after goddess Neith.
Iput was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the Sixth Dynasty, a sister and wife of Pepi II.

Ankhesenpepi IV was an ancient Egyptian queen, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi II of the Sixth Dynasty. She was the mother of a crown prince Neferkare. Pepi II also had several other wives.
Nubwenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi I of the 6th dynasty.
Inenek, also called Inti, was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi I of the 6th Dynasty.
Khuit II was a wife of King Teti, the first pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt.

Khentetka or Khentetenka was a queen consort of Egypt; the wife of King Djedefre during the 4th Dynasty.
Meritites IV was a queen consort from the Sixth Dynasty. She was believed to be a wife of Pepi I Meryre, but her title of King's Daughter of his body of Pepy-Mennefer (s3t-niswt-nt-kht.f-ppy-mn-nfr) is now understood to indicate that she was a daughter of Pepi I Meryre and wife of a king Neferkare, presumably Pepi II. One more evidence for that theory is that her name means "Beloved of her father".
Hekenuhedjet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the 4th Dynasty, a wife of pharaoh Khafre. She is depicted in the tomb of her son, the vizier Sekhemkare.
Persenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the 4th Dynasty. She may have been a daughter of Pharaoh Khufu and a wife of Pharaoh Khafre. She is mainly known from her tomb at Giza.
Khenut was the queen consort of Egypt as the wife of King Unas. She lived during the time of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She was a suspected mother of Queen Iput.
Tem was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the 11th Dynasty, a wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II and the mother of Mentuhotep III. She was buried in Tomb DBXI.15 in Deir el-Bahari, in her husband's mortuary complex. She outlived her husband and was buried during her son's reign. It is likely that she was of commoner origin, as there is no evidence in her grave that points to a royal origin. She is only named on her sarcophagus and on an offering table. Her titles are "King's beloved wife" (ḥmt-nỉswt mrỉỉ.t=f), King's Mother" (mwt-nỉswt), Mother of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt (mwt-nỉswt-bỉt), and Great of Sceptre (wr.t-ḥt=s).

Ashayet or Ashait was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Mentuhotep II in the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.17) and small decorated chapel were found in Mentuhotep II's Deir el-Bahari temple complex. The shrine and burial to Ashayet was found along with the tombs of four other women in their twenties and a young girl, Henhenet, Kawit, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. However, it is likely that there were three other additional shrines that were destroyed in the expansions of Mentuhotep II's burial complex. The nine shrines were built in the First Intermediate Period, prior to Mentuhotep II's reunification of Egypt. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were Priestesses of Hathor. The location of their burial is significant to their titles as Priestesses of Hathor as the cliffs of Deir el-Bahri were sacred to Hathor from the Old Kingdom onwards.

Henhenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.11) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Kawit, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. Most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.
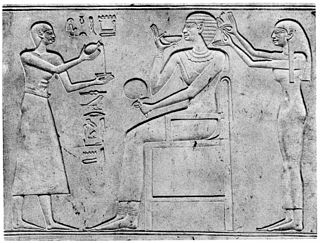
Kawit was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.9) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.

Kemsit was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, the wife of pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (TT308) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kawit, Sadeh and Mayet. Most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.

Sadeh or Sadhe was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.7) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other women, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kawit, Kemsit and Mayet. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.








