
Piye was an ancient Kushite king and founder of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled Egypt from 744–714 BC. He ruled from the city of Napata, located deep in Nubia, modern-day Sudan.

Neferkare Shabaka, or Shabako was the third Kushite pharaoh of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, who reigned from 705 to 690 BC. The Greek sources called him Sabacon (Σαβακῶν) and is mentioned by both Herodotus and Manetho.

Kashta was an 8th century BCE king of the Kushite Dynasty in ancient Nubia and the successor of Alara. His nomen k3š-t3 "of the land of Kush" is often translated directly as "The Kushite". He was succeeded by Piye, who would go on to conquer ancient Egypt and establish the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty there.

Amenirdis I was a God's Wife of Amun during the 25th Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Originating from the Kingdom of Kush, she was the daughter of Pharaoh Kashta and Queen Pebatjma, and was later adopted by Shepenupet I. She went on to rule as high priestess, and has been shown in several artifacts from the period.

Alara was a King of Kush, who is generally regarded as the founder of the Napatan royal dynasty by his 25th Dynasty Kushite successors and was the first recorded prince of Kush. He unified all of Upper Nubia from Meroë to the Third Cataract and is possibly attested at the Temple of Amun at Kawa. Alara also established Napata as the religious capital of Kush. Alara himself was not a 25th dynasty Kushite king since he never controlled any region of Egypt during his reign compared to his two immediate successors: Kashta and Piye respectively. Nubian literature credits him with a substantial reign since future Nubian kings requested that they might enjoy a reign as long as Alara's. His memory was also central to the origin myth of the Kushite kingdom, which was embellished with new elements over time. Alara was a deeply revered figure in Nubian culture and the first Kushite king whose name came down to scholars.

The Sphinx of Taharqo is a granite gneiss statue of a sphinx with the face of Taharqo. He was a Nubian king, who was one of the 25th Egyptian Dynasty rulers of the Kingdom of Kush. It is now in the British Museum in London.
Tabiry was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
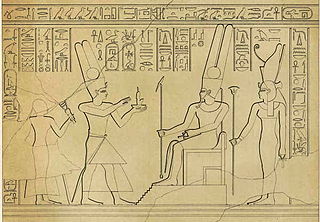
Abar was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is known from a series of stela found in Sudan and Egypt. Her appearances mark her as the niece of King Alara of Nubia, married to King Piye and the mother of King Taharqa.

Takahatenamun was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
Khensa (Khenensaiuw) was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.

El-Kurru was the first of the three royal cemeteries used by the Kushite royals of Napata, also referred to as Egypt's 25th Dynasty, and is home to some of the royal Nubian Pyramids. It is located between the 3rd and 4th cataracts of the Nile about 1 mile (1.6 km) west of the river in what is now Northern state, Sudan. El-Kurru was first excavated by George Reisner in 1918 and 1919 and after his death his assistant Dows Dunham took over his work and published the excavation report on El-Kurru in 1950. The El Kurru cemetery was primarily used from about 860 BC until 650 BC. The first tomb with a name attached to it is that of King Piye dating to about 750 BC, the sixteen earlier tombs possibly belong to Piye's royal predecessors. The last 25th dynasty king, Tantamani, was buried at El Kurru around 650 BC. The subsequent Napatan rulers chose to be buried at the royal cemetery at Nuri instead. However, in the mid-4th century the 20th king, whose name is unknown, chose to have his tomb, as well as that of his queen, built at El Kurru.

Naparaye was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
Tabekenamun (Tabakenamun) was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
Qalhata was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.

Pebatjma was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the wife of King Kashta. She is mentioned on a statue of her daughter Amenirdis I, now in Cairo (42198). She is also mentioned on a doorjamb from Abydos.
Arty was a Nubian King's wife dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.

Nasalsa was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush. She is known from a shabti, some inscriptions on tablets and cups, text on the stela of Khaliut, a dedication inscription and a text from Kawa. Dodson mentions that Nasalsa is named on the Enthronement Stela of Atlanersa and on the Election and Adoption Stelae of Aspelta. These stelae were from Gebel Barkal.

Amanimalel was a Kushite queen of the Napatan kingdom of Nubia, likely a spouse of king Senkamanisken living in the second half of the 7th century BC. She is mostly known from one or possibly two statues of her of very high quality.
Madiqen was a Nubian queen with the Egyptian titles king's wife, king's wife of the living and king's sister. Her mother was queen Nasalsa. Her father was most likely king Senkamanisken. Her royal husband is not known for sure, but Aspelta and Anlamani are most likely options. Madiqen is known from her burial at Nuri. Her burial consisted of a pyramid with a small chapel in front of it. There is a staircase going down to the two burial chambers that were found looted. Gold foil and alabaster vessels were found. There were also 80 shabtis providing her name and title. On a stela of Aspelta is mentioned that she was promoted by the king to the position of a songtress of Amun at Napata. This position was then given to her daughter Henuttakhebit.
Henuttakhebit was a Nubian queen with the Egyptian titles king's wife, king's daughter and king's sister. Her royal husband is not known for sure. Perhaps she was the wife of Aspelta and daughter of Senkamanisken, as proposed by Dows Dunham and M. F. Laming Macadam. This is not certain. She was the daughter or adopted daughter of queen Madiqen and followed her as songstress of Amun in Napata.












