
Pepi II Neferkare was a pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty in Egypt's Old Kingdom who reigned from c. 2278 BC. His second name, Neferkare (Nefer-ka-Re), means "Beautiful is the Ka of Re". He succeeded to the throne at age six, after the death of Merenre I.
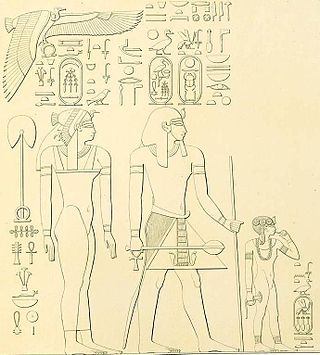
Ahmose was an Ancient Egyptian queen in the Eighteenth Dynasty. She was the Great Royal Wife of the dynasty's third pharaoh, Thutmose I, and the mother of the queen and pharaoh Hatshepsut. Her name means "Born of the Moon".

Pepi I Meryre was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, third king of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, who ruled for over 40 years at the turn of the 24th and 23rd centuries BC, toward the end of the Old Kingdom period. He was the son of Teti, the founder of the dynasty, and ascended the throne only after the brief intervening reign of the shadowy Userkare. His mother was Iput, who may have been a daughter of Unas, the final ruler of the preceding Fifth Dynasty. Pepi I, who had at least six consorts, was succeeded by his son Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, with whom he may have shared power in a coregency at the very end of his reign. Pepi II Neferkare, who might also have been Pepi I's son, succeeded Merenre.

Sitre or Tia-Sitre, was the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Ramesses I of Egypt and mother of Seti I.

Bintanath was the firstborn daughter and later Great Royal Wife of the Egyptian Pharaoh Ramesses II.
Iput I was a queen of ancient Egypt, a daughter of King Unas, the last king of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She married Teti, the first Pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Their son was Pepi I Meryre. She possibly ruled as regent for her son Pepi I.

Ankhesenpepi II or Ankhesenmeryre II was a queen consort during the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the wife of Kings Pepi I and Merenre Nemtyemsaf I, and the mother of Pepi II. She likely served as regent during the minority of her son. She was buried in a pyramid in Saqqara.
Neith was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, one of the principal queens of the Old Kingdom pharaoh Pepi II Neferkare, who ruled. Queen Neith was named after goddess Neith.
The pyramid of Pepi I is the pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Pepi I of the Sixth Dynasty in the 24th or 23rd century BC. The complex gave its name to the capital city of Egypt, Memphis. As in the pyramids of his predecessors, Pepi I's substructure was filled with vertical columns of hieroglyphic texts, Pyramid Texts. It was in Pepi I's pyramid that these texts were initially discovered in 1880 by Gaston Maspero, though they originated in the pyramid of Unas. The corpus of Pepi I's texts is also the largest from the Old Kingdom, comprising 2,263 columns and lines of hieroglyphs.
Iput was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the Sixth Dynasty, a sister and wife of Pepi II.
Ankhesenpepi III was an ancient Egyptian queen of the Sixth Dynasty as a consort of Pepi II, who was probably her uncle. She was a daughter of Merenre Nemtyemsaf I and was named after her grandmother, Ankhesenpepi I.

Ankhesenpepi IV was an ancient Egyptian queen, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi II of the Sixth Dynasty. She was the mother of a crown prince Neferkare. Pepi II also had several other wives.
Udjebten or Wedjebten was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi II of the Sixth Dynasty.
Nubwenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi I of the 6th dynasty.
Nedjeftet is a queen mentioned on reliefs discovered near the pyramid complex of Pepi I. She was a wife of Pepi. Her name was also that of the 20th nome, later known as the Herakleopolis nome, in Upper Egypt; it is possible her family came from there and the marriage was to strengthen the king's position as opposed to the local lords.
Khuit II was a wife of King Teti, the first pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt.
Meritites IV was a queen consort from the Sixth Dynasty. She was believed to be a wife of Pepi I Meryre, but her title of King's Daughter of his body of Pepy-Mennefer (s3t-niswt-nt-kht.f-ppy-mn-nfr) is now understood to indicate that she was a daughter of Pepi I Meryre and wife of a king Neferkare, presumably Pepi II. One more evidence for that theory is that her name means "Beloved of her father".

Takahatenamun was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
Khensa (Khenensaiuw) was a Nubian queen dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt.
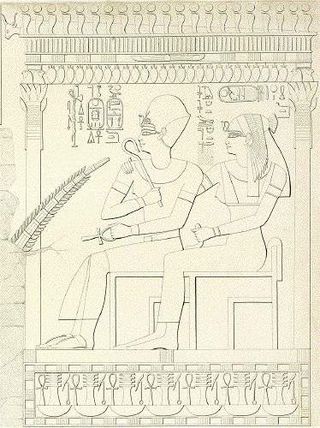
Merytre-Hatshepsut was the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Thutmose III after the death of Queen Satiah. She was the mother of Pharaoh Amenhotep II.








