
Mentuhotep II, also known under his prenomen Nebhepetre, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Eleventh Dynasty. He is credited with reuniting Egypt, thus ending the turbulent First Intermediate Period and becoming the first pharaoh of the Middle Kingdom. He reigned for 51 years, according to the Turin King List. Mentuhotep II succeeded his father Intef III on the throne and was in turn succeeded by his son Mentuhotep III.
Intef III was the third pharaoh of the Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt during the late First Intermediate Period in the 21st century BC, at a time when Egypt was divided in two kingdoms. The son of his predecessor Intef II and father of his successor Mentuhotep II, Intef III reigned for 8 years over Upper Egypt and extended his domain North against the 10th Dynasty state, perhaps as far north as the 17th nome. He undertook some building activity on Elephantine. Intef III is buried in a large saff tomb at El-Tarif known as Saff el-Barqa.

Senusret I also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 BC to 1926 BC, and was one of the most powerful kings of this Dynasty. He was the son of Amenemhat I. Senusret I was known by his prenomen, Kheperkare, which means "the Ka of Re is created." He expanded the territory of Egypt allowing him to rule over an age of prosperity.

Khentkaus II was a royal woman who lived in ancient Egypt. She was a wife of Egyptian king Neferirkare Kakai of the Fifth Dynasty. She was the mother of two kings, Neferefre and Nyuserre Ini.

Tuya was the wife of Pharaoh Seti I of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and mother of Tia, Ramesses II, and possibly Henutmire.

The Theban Tomb TT319 is located in Deir el-Bahari, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to the king's wife Neferu II, wife of the ancient Egyptian king Mentuhotep II. Neferu was the daughter of Queen Iah and Intef III.

Mentuhotep was an ancient Egyptian queen of the Second Intermediate Period, wife of pharaoh Djehuti. Her main title was Great Royal Wife. Another title was Khenemetneferhedjet.

Ankhesenpepi IV was an ancient Egyptian queen, a wife of Pharaoh Pepi II of the Sixth Dynasty. She was the mother of a crown prince Neferkare. Pepi II also had several other wives.
Seshemetka was an ancient Egyptian queen from the First Dynasty of Egypt, a wife of pharaoh Den and the mother of Anedjib. Her royal titles were Great one of the hetes-sceptre , She who sees Horus , She who carries Seth .
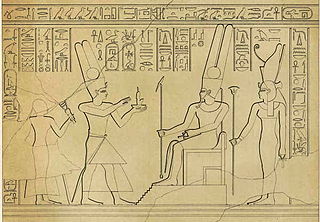
Abar was a Nubian queen of the Kingdom of Kush dated to the Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt. She is known from a series of stela found in Sudan and Egypt. Her appearances mark her as the niece of King Alara of Nubia, married to King Piye and the mother of King Taharqa.
Takhuit was the Great Royal Wife of Psamtik II. She dates to the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt.

Iah was a king's mother and queen of ancient Egypt c. 2060 BC, during the mid 11th Dynasty. Daughter of a pharaoh, possibly Intef II, and mother of pharaoh Mentuhotep II, she was the queen of Intef III.
Tem was an ancient Egyptian queen consort of the 11th Dynasty, a wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II and the mother of Mentuhotep III. She was buried in Tomb DBXI.15 in Deir el-Bahari, in her husband's mortuary complex. She outlived her husband and was buried during her son's reign. It is likely that she was of commoner origin, as there is no evidence in her grave that points to a royal origin. She is only named on her sarcophagus and on an offering table. Her titles are "King's beloved wife" (ḥmt-nỉswt mrỉỉ.t=f), King's Mother" (mwt-nỉswt), Mother of the King of Upper and Lower Egypt (mwt-nỉswt-bỉt), and Great of Sceptre (wr.t-ḥt=s).

Ashayet or Ashait was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a wife of Mentuhotep II in the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.17) and small decorated chapel were found in Mentuhotep II's Deir el-Bahari temple complex. The shrine and burial to Ashayet was found along with the tombs of four other women in their twenties and a young girl, Henhenet, Kawit, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. However, it is likely that there were three other additional shrines that were destroyed in the expansions of Mentuhotep II's burial complex. The nine shrines were built in the First Intermediate Period, prior to Mentuhotep II's reunification of Egypt. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were Priestesses of Hathor. The location of their burial is significant to their titles as Priestesses of Hathor as the cliffs of Deir el-Bahri were sacred to Hathor from the Old Kingdom onwards.

Henhenet was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.11) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Kawit, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. Most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.
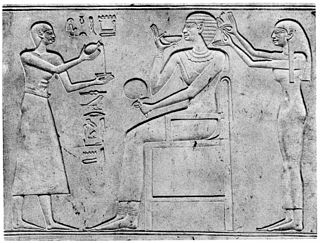
Kawit was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.9) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.

Kemsit was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, the wife of pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (TT308) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kawit, Sadeh and Mayet. Most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.

Sadeh or Sadhe was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th Dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.7) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex, behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other women, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kawit, Kemsit and Mayet. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.

Sobekemsaf(sbk-m-z3=f) was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 17th Dynasty. She was the wife of pharaoh Nubkheperre Intef and sister of an unidentified pharaoh, probably Sekhemre-Heruhirmaat Intef, Sobekemsaf II or Senakhtenre Ahmose.

Neferukayet was an ancient Egyptian princess and queen of the Eleventh Dynasty. Her name is only known from her steward Rediukhnum's stela, which was found in Dendera. She is possibly identical with the mother of Intef III, whose name was Neferu. Neferukayet also bore the titles "king's daughter" (z3.t-nỉsw.t), "king's beloved wife" (ḥm.t-nỉsw.t mrỉỉ.t=f) and "royal ornament" (ẖkr.t-nỉsw.t), based on this, she was likely the daughter of Intef I and the wife of Intef II. Furthermore, in the tomb of king Intef III was found a relief fragment naming a woman called Neferukau. Silke Roth argued that Neferukau is just a different writing for the name Neferukayet. Neferu would be just a short version of the name Neferukau/Neferukayet.

















