
Hesse or Hessia, officially the State of Hesse, is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major historic cities are Darmstadt and Kassel. With an area of 21,114.73 square kilometers and a population of over six million, it ranks seventh and fifth, respectively, among the sixteen German states. Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Germany's second-largest metropolitan area, is mainly located in Hesse.

A Regierungsbezirk means "governmental district" and is a type of administrative division in Germany. Currently, four of sixteen Bundesländer are split into Regierungsbezirke. Beneath these are rural and urban districts.
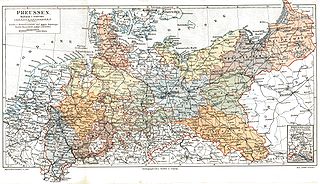
The Provinces of Prussia were the main administrative divisions of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. Prussia's province system was introduced in the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, and were mostly organized from duchies and historical regions. Provinces were divided into several Regierungsbezirke, sub-divided into Kreise (districts), and then into Gemeinden (townships) at the lowest level. Provinces constituted the highest level of administration in the Kingdom of Prussia and Free State of Prussia until 1933, when Nazi Germany established de facto direct rule over provincial politics, and were formally abolished in 1946 following World War II. The Prussian provinces became the basis for many federal states of Germany, and the states of Brandenburg, Lower Saxony, and Schleswig-Holstein are direct successors of provinces.

Battenberg is a small town in the district of Waldeck-Frankenberg in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is located on the river Eder, a tributary of the Fulda, which flows into the Weser, and lies at the southeastern edges of the Rothaar Mountains. The closest larger cities are Marburg, Siegen, and Kassel, and the town is approximately equally far away from Frankfurt am Main, Cologne, and Dortmund.
Toussaint von Charpentier was a German geologist and entomologist.

Mining law is the branch of law relating to the legal requirements affecting minerals and mining. Mining law covers several basic topics, including the ownership of the mineral resource and who can work them. Mining is also affected by various regulations regarding the health and safety of miners, as well as the environmental impact of mining.

The approximately 5,400 railway stations in Germany that are owned and operated by the Deutsche Bahn subsidiary DB Station&Service are divided into seven categories, denoting the service level available at the station.
The Bundesfinanzdirektionen were the German federal funding agencies with responsibility to the Federal Ministry of Finance that operated between 2008-2015. On January 1, 2016 it was replaced by the newly established German federal government's General Directorate Generalzolldirektion.

The Gesellschaft für deutsche Sprache, or GfdS, is Germany's most important government-sponsored language society. Its headquarters are in Wiesbaden. Re-founded shortly after the Second World War in 1947, the GfdS is politically independent and the declared successor of the Allgemeiner Deutscher Sprachverein, the General Association for the German Language, which had been founded in 1885 in Brunswick. Its aim is to research and cultivate the German language; to critically evaluate the current German language change; and to give recommendations concerning the current usage of German.

Gießen railway station is the main railway station in Gießen, Hesse, Germany. The station is a Category 2 station is used by 20,000 passengers daily. The station was opened on 25 August 1850 and is located on the Main-Weser Railway and Dill railway. The current station reception building was built between 1904 and 1911. The main original station building is a historic landmark and has been protected. Outside the station is a bus station and a taxi rank. Parking garages are located nearby.

The Döhlen Basin is a landscape unit in the German federal state of Saxony, southwest of Dresden. The Döhlen Basin has a length of 22 km and a width of 6 km and lies within the district of Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge.

The Saxon Mining Office is the executive authority for mining rights in the German state of Saxony. It is also responsible for all non-metallic mineral resources on the terrain of the former East Germany.

The Bergregal was the historic right of ownership of untapped mineral resources in parts of German-speaking Europe; ownership of the Bergregal meant entitlement to the rights and royalties from mining. Historically, it was one of those privileges that constituted the original sovereign rights of the king.
The 2013–14 DFB-Pokal was the 71st season of the annual German football cup competition. It began on 2 August 2013 with the first of six rounds and ended on 17 May 2014 with the final at the Olympiastadion in Berlin. Bayern Munich went on to win the competition for the second season running, defeating Borussia Dortmund 2–0 in the final.

The Schauinsland Pit was a silver and lead mine east of Freiburg im Breisgau. From the 19th century zinc was also mined. The mine operated from the 13th century until 1954. Since 1997 Schauinsland Pit has been a show mine.

The Caroline Pit in the Eberbächle, a side valley of the Brettenbach, is an old silver mine in Sexau in the Black Forest in Germany which is open to the public as a show mine. In 1987, volunteers began to uncover the pit and maintain it. It lies within the mining region of Sexau and Freiamt.

The Silbergründle Pit near Seebach in the Black Forest in Germany was a lead and silver mine.

The list of German municipal flags lists the flags of municipalities of Germany. Most municipalities of Germany have unique flags. Like state flags, most of them are with either a bicolor or tricolor stipes with or without the emblem ("wappen"). Therefore, the list will also discuss the emblems. Please note that some of the flags listed are either de facto flags, flags that are flown for local purposes or flags that are not yet approved by state interior ministries.
Stadttheater may refer to:














