The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Copper and Bronze Ages. It has also been considered as the final Age of the three-age division starting with prehistory and progressing to protohistory. In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but they now include other parts of the Old World.

Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.

Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water.

A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called a bloom. The mix of slag and iron in the bloom, termed sponge iron, is usually consolidated and further forged into wrought iron. Blast furnaces, which produce pig iron, have largely superseded bloomeries.

The Great Dyke or Dike is a linear geological feature that trends nearly north-south through the centre of Zimbabwe passing just to the west of the capital, Harare. It consists of a band of short, narrow ridges and hills spanning for approximately 550 kilometres (340 mi). The hills become taller as the range goes north, and reach up to 460 metres (1,510 ft) above the Mvurwi Range. The range is host to vast ore deposits, including gold, silver, chromium, platinum, nickel and asbestos.
There are several classification systems for the economic evaluation of mineral deposits worldwide. The most commonly used schemes base on the International Reporting Template, developed by the CRIRSCO - Committee for Mineral Reserves International Reporting Standards, like the Australian Joint Ore Reserves Committee - JORC Code 2012, the Pan-European Reserves & Resources Reporting Committee' – PERC Reporting Standard from 2021, the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum - CIM classification and the South African Code for the Reporting of Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (SAMREC). A more detailed description of the historical development concerning reporting about mineral deposits can be found on the PERC web site.

The Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum (CIM) is a not-for-profit technical society of professionals in the Canadian minerals, metals, materials and energy industries. CIM's members are convened from industry, academia and government.
OneMine is non-profit entity and searchable online global mining and minerals library.
Blyvooruitzicht is a gold mine and gold-mining village in Gauteng, South Africa. It is situated about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) south of the centre of Carletonville and 80 kilometres (50 mi) westwards from Johannesburg.

Metals and metal working had been known to the people of modern Italy since the Bronze Age. By 53 BC, Rome had expanded to control an immense expanse of the Mediterranean. This included Italy and its islands, Spain, Macedonia, Africa, Asia Minor, Syria and Greece; by the end of the Emperor Trajan's reign, the Roman Empire had grown further to encompass parts of Britain, Egypt, all of modern Germany west of the Rhine, Dacia, Noricum, Judea, Armenia, Illyria, and Thrace. As the empire grew, so did its need for metals.

Tarì was the Christian designation of a type of gold coin of Islamic origin minted in Sicily, Malta and Southern Italy from about 913 to the 13th century.
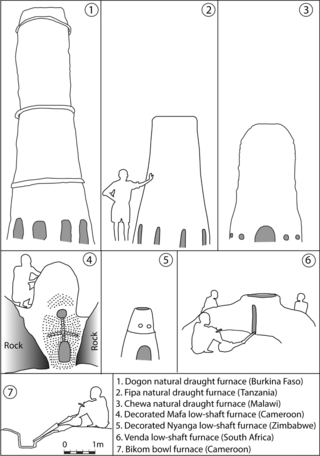
Copper metallurgy in Africa encompasses the study of copper production across the continent and an understanding of how it influenced aspects of African archaeology.

Kraku Lu Jordan is archeological site in Serbia. It is situated at the confluence of the Brodica river into Pek, near Kučevo. Represents the most explored metallurgical center in eastern Serbia. The metallurgic occupation of the site lasted for about 100 years, beginning around 280 AD and ending in 380 AD. Kraku Lu Jordan is precisely dated by discovered coins from Diocletian time. This metallurgical complex was then destroyed in a fire in the late 4th century. Archaeological excavations began in 1971, and with few interruptions, lasted until 1987.
Potholes are frequently encountered during mining operations in the Bushveld Igneous Complex in South Africa. Two orebodies, the Upper Group 2 (UG2) and the Merensky Reef, host about 70% of the world's platinum group metals (PGM), and pose major extraction problems for the mining industry in their faults, dykes, joints, domes, iron-rich ultramafic pegmatoids, rolls and dunite pipes. The greatest mining problems, though, are presented by potholes.

William Bleloch was a South African metallurgist noted for developing smelting techniques for the processing of chrome ores. At a 1975 ceremony when the University of the Witwatersrand conferred upon him an honorary doctorate of Science and Engineering, the citation read "William Bleloch can truly be called the father of our electrochemical and electrometallurgical industries".

The School of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering is one of seven schools in the University of the Witwatersrand's Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment. The School offers 4-year undergraduate degrees and post-graduate degrees in chemical and metallurgical engineering.

The Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit is one of several research entities based in the School of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. It provides research as well as supervision to masters and doctorate students within the University, as well as consulting to industry.

South32 is a mining and metals company headquartered in Perth, Western Australia. It was spun out of BHP Billiton on 18 May 2015. It is listed on the Australian Securities Exchange with secondary listings on the Johannesburg and London Stock Exchanges.
The following lists events that happened during 2008 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The South African Mineral Reporting Codes (SAMCODES) are codified sets of standards and guidelines applicable to the South African Minerals and Petroleum Industries, drafted and overseen by the SAMCODES Standards Committee (SSC), a professional and non-governmental body. Specifically, the standards and guidelines are applicable to public reports compiled on behalf of South African Minerals and Petroleum companies for the benefit of investors. The Codes are incorporated into Section 12 of the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE) Listings Rules, which detail "the criteria for the listing of, and the additional disclosure requirements for Mineral Companies and, in certain circumstances, substantial mineral assets of non-Mineral Companies" in South Africa. As such, the SSC acts in an advisory capacity to the JSE, ensuring that reports submitted for listings consideration are compliant with the SAMCODES.













