
Traffic lights, traffic signals or stoplights – known also as robots in South Africa are signalling devices positioned at road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order to control flows of traffic.

A bus stop is a place where buses stop for passengers to get on and off the bus. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage, where stops at busy locations may have shelters, seating, and possibly electronic passenger information systems; less busy stops may use a simple pole and flag to mark the location. Bus stops are, in some locations, clustered together into transport hubs allowing interchange between routes from nearby stops and with other public transport modes to maximise convenience.

Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have better capacity and reliability than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes roadways that are dedicated to buses, and gives priority to buses at intersections where buses may interact with other traffic; alongside design features to reduce delays caused by passengers boarding or leaving buses, or paying fares. BRT aims to combine the capacity and speed of a metro with the claimed flexibility, lower cost and simplicity of a bus system.

A curb extension is a traffic calming measure which widens the sidewalk for a short distance. This reduces the crossing distance and allows pedestrians and drivers to see each other when parked vehicles would otherwise block visibility.

A shoulder, hard shoulder or breakdown lane, is an emergency stopping lane by the verge of a road or motorway, on the right side in countries which drive on the right, and on the left side in countries which drive on the left. Many wider (U.S.) freeways, or expressways elsewhere have shoulders on both sides of each directional carriageway — in the median, as well as at the outer edges of the road, for additional safety. Shoulders are not intended for use by through traffic, although there are exceptions.

The Silver Line is a system of bus routes in Boston and Chelsea, Massachusetts, operated by the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA). It is operated as part of the MBTA bus system, but branded as bus rapid transit (BRT) as part of the MBTA subway system. Six routes are operated as part of two disconnected corridors. As of 2019, weekday ridership on the Silver Line was 39,000.

A single-track road or one-lane road is a road that permits two-way travel but is not wide enough in most places to allow vehicles to pass one another. This kind of road is common in rural areas across the United Kingdom and elsewhere. To accommodate two-way traffic, many single-track roads, especially those officially designated as such, are provided with passing places or pullouts or turnouts, or simply wide spots in the road, which may be scarcely longer than a typical car using the road. The distance between passing places varies considerably, depending on the terrain and the volume of traffic on the road. The railway equivalent for passing places are passing loops.

A bus bulb, also called a bus boarder, bus border, bumpout, bus cape, or a kerb outstand is an arrangement by which a sidewalk or pavement is extended outwards for a bus stop; typically the bus bulb replaces roadway that would otherwise be part of a parking lane. With bus bulbs or boarders, a bus can stay in its traffic lane to discharge and pick up passengers, instead of having to pull over to the curb.

The city of Glasgow, Scotland has a transport system encompassing air, rail, road, and an underground light metro line. Prior to 1962, the city was also served by trams. Commuters travelling into Glasgow from the neighbouring local authorities of North and South Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire, East Renfrewshire, and East and West Dunbartonshire have a major influence on travel patterns, with tens of thousands of residents commuting into the city each day. The most popular mode of transport in the city is the car, used by two thirds of people for journeys around the city.

The lighting system of a motor vehicle consists of lighting and signalling devices mounted or integrated at the front, rear, sides, and in some cases the top of a motor vehicle. They illuminate the roadway ahead for the driver and increase the vehicle's visibility, allowing other drivers and pedestrians to see its presence, position, size, and direction of travel, and its driver's intentions. Emergency vehicles usually have distinctive lighting equipment to warn drivers and indicate priority of movement in traffic.

Road signs in the United Kingdom and in its associated Crown dependencies and overseas territories conform broadly to European design norms, though a number of signs are unique: direction signs omit European route numbers and road signs generally use the Imperial System of units, unlike the rest of Europe. Signs in Wales and parts of Scotland are bilingual.

The 98 B-Line was a bus rapid transit line in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It linked Richmond to Downtown Vancouver, with a connection to Vancouver International Airport. It travelled mainly along Granville Street in Vancouver and a dedicated bus lane on No. 3 Road in Richmond. It was operated by Coast Mountain Bus Company and was funded by TransLink. The route was 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) long. The line carried over 18,000 passengers daily. It was discontinued on September 7, 2009, two and a half weeks after the opening of the Canada Line, which replaced it.

The B44 is a public transit line in Brooklyn, New York City, running mostly along Nostrand Avenue, as well as northbound on Rogers Avenue or New York Avenue and Bedford Avenue, between Sheepshead Bay and Williamsburg. Originally a streetcar line, it is now the B44 bus route, operated by the New York City Transit Authority.

A queue jump is a type of roadway geometry used to provide preference to buses at intersections, often found in bus rapid transit systems. It consists of an additional travel lane on the approach to a signalised intersection. This lane is often restricted to transit vehicles only. A queue jump lane is usually accompanied by a signal which provides a phase specifically for vehicles within the queue jump. Vehicles in the queue jump lane get a "head-start" over other queued vehicles and can therefore merge into the regular travel lanes immediately beyond the signal. The intent of the lane is to allow the higher-capacity vehicles to cut to the front of the queue, reducing the delay caused by the signal and improving the operational efficiency of the transit system.

The B82 bus route constitutes a public transit line in central Brooklyn, New York City. It connects Starrett City in southeast Brooklyn with Coney Island on Brooklyn's southwestern coast. The B82 operates primarily via Kings Highway and Flatlands Avenue in southern Brooklyn. The route is operated by MTA Regional Bus Operations, under the New York City Bus and Select Bus Service brands.

The Geary Bus Rapid Transit project added bus rapid transit features to San Francisco Municipal Railway lines along Geary Boulevard. The corridor serves routes 38, 38R, 38AX, 38BX which combined to serve 52,900 daily riders in 2019, the most of any corridor in the city. The project added transit-only lanes, painted red, along many sections of Geary between the Transbay Transit Center and 33rd Avenue. As part of the project, over 75% of Geary corridor has transit lanes.
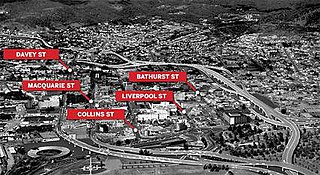
The Hobart Bypass is a proposed concept to bypass the Central Business District of Hobart, Tasmania. Currently, through traffic travels from the Tasman/Brooker Highways down the one-way Davey/Macquarie couplet to the Southern Outlet. As well as traffic concerns, there is also a call to build the bypass on the grounds that the current traffic arrangement cuts the central business district off from Hobart's waterfront.

Utah Valley Express, also known as UVX, is a bus rapid transit (BRT) line in central Utah County, Utah, United States. The line is operated by the Utah Transit Authority (UTA) and runs between southwest Orem to south central Provo by way of Utah Valley University (UVU) and Brigham Young University (BYU). It began service with a soft opening on August 13, 2018 while the station platforms were being finished and was formally opened on January 9, 2019. It is the second of several BRT lines that UTA has or is planning in Utah County and the Salt Lake Valley.

Terminology related to road transport—the transport of passengers or goods on paved routes between places—is diverse, with variation between dialects of English. There may also be regional differences within a single country, and some terms differ based on the side of the road traffic drives on. This glossary is an alphabetical listing of road transport terms.
Road signs in Mongolia are similar to the Russian UK road sign system. They ensure that transport vehicles move safely and in an orderly manner, and inform the participants of traffic built-in graphic icons. These icons are governed by the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic and Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.




















