The Inter-American Division of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which oversees the Church's work in Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and Northern South America.

The United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean is a United Nations regional commission to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 46 member States, and 14 associate members which are various non-independent territories, associated island countries and a commonwealth in the Caribbean. ECLAC publishes statistics covering the countries of the region and makes cooperative agreements with nonprofit institutions. The headquarters of ECLAC is in Santiago, Chile.

The Association of Caribbean States is an advisory association of nations centered on the Caribbean Basin. It was formed with the aim of promoting consultation, cooperation, and concerted action among all the countries of the Caribbean coastal area. The primary purpose of the ACS is to promote greater trade between the nations, enhance transportation, develop sustainable tourism, and facilitate greater and more effective responses to local natural disasters.

Petrocaribe was a regional oil procurement agreement between Venezuela and Caribbean member states. The trade organization was founded on 29 June 2005 in Puerto La Cruz, Venezuela during Hugo Chavez' presidency. Venezuela offered member states oil supplies on a concessionary financial agreement. Petrocaribe has been part of the "pink tide" in Latin America seeking to achieve post-neoliberal development in the region. In 2013 Petrocaribe established links with the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA) aiming to go beyond oil trade and promoting economic cooperation. The deal fell apart by 2019 after dwindling oil production, corruption, and oil price fluctuations took their toll.

ALBA or ALBA–TCP, formally the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America or the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America – Peoples' Trade Treaty, is an intergovernmental organization based on the idea of political and economic integration of Latin American and Caribbean countries.

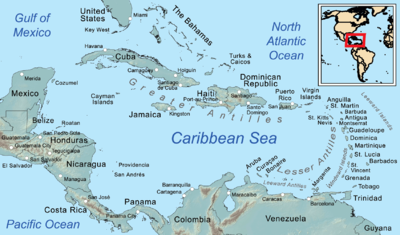
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island countries and 19 dependencies in three archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

The United Nations geoscheme for the Americas is an internal tool created and used by the UN's Statistics Division (UNSD) for the specific purpose of UN statistics.

The athletics competition at the 2006 Central American and Caribbean Games took place at the Estadio Pedro de Heredia in Cartagena, Colombia and lasted from July 25 to July 29. There were 23 events for men and 21 for women. A total of ten Games records were broken at the competition, in addition to a number of national records.

The track and field competition at the 1990 Central American and Caribbean Games was held at the Estadio Olímpico Universitario in Mexico City, Mexico, between 28 November and 2 December.

The track and field competition at the 1993 Central American and Caribbean Games was held in November at the Estadio Francisco Montaner in Ponce, Puerto Rico.

The track and field competition in the 1998 Central American and Caribbean Games was held in Maracaibo, Venezuela. It was the first edition to feature women's hammer throw and pole vault.
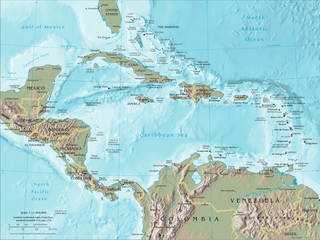
The Caribbean is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.

This is a timeline of the territorial evolution of the Caribbean and nearby areas of North, Central, and South America, listing each change to the internal and external borders of the various countries that make up the region.
The western Caribbean zone is a region consisting of the Caribbean coasts of Central America and Colombia, from the Yucatán Peninsula in southern Mexico to the Caribbean region in northern Colombia, and the islands west of Jamaica are also included. The zone emerged in the late sixteenth century as the Spanish failed to completely conquer many sections of the coast, and northern European powers supported opposition to Spain, sometimes through alliances with local powers.

The term Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) is an English-language acronym referring to the Latin American and the Caribbean region. The term LAC covers an extensive region, extending from The Bahamas and Mexico to Argentina and Chile. The region has over 670,230,000 people as of 2016, and spanned for 21,951,000 square kilometres (8,475,000 sq mi).