
Malabar Muslims or Muslim Mappilas are members of the Muslim community found predominantly in Kerala and the Lakshadweep islands in Southern India. The term Mappila (Maha-Pilla) means Greater Child in Malayalam, Which is used to describe Malabar Muslims in Northern Kerala. Muslims share the common language of Malayalam with the other religious communities of Kerala.
Beypore or Beypur is an ancient port town and a locality town in Kozhikode district in the state of Kerala, India. It is located opposite to Chaliyam, the estuary where the river Chaliyar empties into Arabian Sea. Beypore is part of Kozhikode Municipal Corporation. The place was formerly known as Vaypura / Vadaparappanad and also as Beydary. Tippu Sultan, ruler of Mysore, named the town "Sultan Pattanam". There is a marina and a beach while Beypore port is one of the oldest ports in Kerala, which historically traded with the Middle East. Beypore is noted for building wooden ships, known as dhows or urus in the Malayalam language. These ships were usually bought by Arab merchants for trading and fishing but are now used as tourist ships. According to Captain Iwata, founder member of the Association of Sumerian ships in Japan, Sumerian ships might have been built in Beypore. There is evidence to prove that Beypore had direct trade links with Mesopotamia and was a prominent link on the maritime silk route. The first railway line of Kerala was laid in 1861 from Tirur to Beypore (Chaliyam) passing through Tanur, Parappanangadi, Vallikkunnu, and Kadalundi.

Ezhimala, a hill reaching a height of 286 metres (938 ft), is located near Payyanur, in Kannur district of Kerala, South India. It is a part of a conspicuous and isolated cluster of hills, forming a promontory, 38 km (24 mi) north of Kannur (Cannanore). The Indian Naval Academy at Ezhimala is Asia's largest, and the world's third-largest, naval academy.

The term Kerala was first epigraphically recorded as Cheras (Keralaputra) in a 3rd-century BCE rock inscription by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka of Magadha. It was mentioned as one of four independent kingdoms in southern India during Ashoka's time, the others being the Cholas, Pandyas and Satyaputras. The Cheras transformed Kerala into an international trade centre by establishing trade relations across the Arabian Sea with all major Mediterranean and Red Sea ports as well those of Eastern Africa and the Far East. The dominion of Cheras was located in one of the key routes of the ancient Indian Ocean trade. The early Cheras collapsed after repeated attacks from the neighboring Cholas and Rashtrakutas.

Thrissur, anglicised as Trichur, is one of the 14 districts in the Indian state of Kerala. It is situated in the central region of the state. Spanning an area of about 3,032 km2 (1,171 sq mi), the district is home to over 9% of Kerala's population.

Koyilandy is a major town municipality and a taluk in Kozhikode district, Kerala on the Malabar Coast. The historical town is located right in the middle of the coast of Kozhikode district, between Kozhikode and Kannur, on National Highway 66.

Islam arrived in Kerala, the Malayalam-speaking region in the south-western tip of India, through Middle Eastern merchants. The Indian coast has an ancient relation with West Asia and the Middle East, even during the pre-Islamic period.

Barkur is an area in the Brahmavara taluk, Udupi district of Karnataka state in India, comprising three villages, Hosala, Hanehalli, and Kachoor. The area is located on the bank of River Seetha. It is also referred to as a "temple town".

Thrissur is the administrative capital of Thrissur District, in the central part of Kerala state, India. Thrissur district was formed on 1 July 1949. It is an important cultural centre, and is known as the Cultural Capital of Kerala. It is famous for the Thrissur Pooram festival, one of the most colourful and spectacular temple festival of Kerala. From ancient times, Thrissur has been politically, economically and culturally significant to the Indian subcontinent. It has opened the gates for Arabs, Romans, Portuguese, Dutch and English. According to tradition, Thrissur is where Christianity, Islam and Judaism entered the Indian subcontinent. Local Christian tradition holds that Thomas the Apostle arrived in 52 CE, and Muslim tradition states that Methala is the location of country's first mosque.

Vallikkunnu is a village in Tirurangadi Taluk of Malappuram district in the state of Kerala, India with an area of 25 km2. It is located 5 km north of Parappanangadi town and comes under the jurisdiction of Parappanangadi Police Station and Parappanangadi Judicial First Class Magistrate Court. Its latitude and longitude are 11'07" N and 7'51"E respectively. Vallikkunnu was awarded the best panchayath of Kerala in 1997. Vallikunnu is situated on Tirur-Kadalundi Road. Vallikkunnu is also a part of the Oldest Railway Line of Kerala laid in 1861 from Tirur to Chaliyam via Tanur, Parappanangadi, Vallikkunnu, and Kadalundi.

Religion in Kerala is diverse. According to 2011 census of India figures, 54.73% of Kerala's population are Hindus, 26.56% are Muslims, 18.38% are Christians, and the remaining 0.33% follow other religions or have no religion. As of 2020, Hindus, Muslims, Christians and others account for 41.5%, 43.9%, 13.9% and 0.7% of the total child births in the state, respectively.

Arakkal Kingdom was a Muslim kingdom in Kannur town in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, South India. The king was called Ali Raja and the ruling queen was called Arakkal Beevi. Arakkal kingdom included little more than the Cannanore town and the southern Laccadive Islands, originally leased from the Kolattiri. They owed allegiance to the Kolattiri rulers, whose ministers they had been at one time. The rulers followed the Marumakkathayam system of matrilineal inheritance, a system that is unique to a section of Hindus of Kerala. Under Marumakkathayam, the succession passes to the male offspring of its female members, in other words from a man to his sister's son and so forth. As the only Muslim rulers in Malabar, they saw the rise of Hyder Ali, de facto ruler of the Mysore Sultanate as the opportunity to increase their own power at the expense of Chirakkal, and invited him to invade Kerala. Ali Raja Arakkal Sultan Afsal Ashraf living in Konni Panchayat of Pathanamthitta district is the living heir of the Arakkal dynasty.
The Rulers of the Chera dynasty or Rulers of the Chera Perumals were the kings of Chera dynasty of Kerala. The first Chera Perumal was "brought" from a country east of the Ghats to Kerala by Nambudiri Brahmins.

Chaliyam is a village situated at the estuary of Chaliyar in Kozhikode district of Kerala, India. Chaliyam forms an island, bounded by the Chaliyar in the north, and River Kadalundi in south, and the Conolly Canal in the east. It is located just opposite to Beypore port. Chaliyam was the former terminus of the South-West Line of the Madras Railway. Chaliyam is also famous for the Guinness World Records holder Muhammed Adil, a P.M who covered around seven km in the Chaliyar River with his hand and legs tied with ropes.
Madayi Mosque is mosque at Pazhayangadi in Kannur district, northern Kerala, India. It is one of the oldest mosques in Kerala, with local legends dating back to the 7th century AD. It is believed to have been established by Malik ibn Dinar and contains a block of white marble said to have been brought from Mecca by ibn Dinar. It is one of the several mosques around Pazhayangadi/Payangadi. It is situated on the banks of Kuppam River, which joins Valapattanam River at its estuary.

Safa Mosque or Safa Shahouri Mosque is a mosque located at Ponda within Goa, India. It is a sixteenth century Islamic Monument. The mosque has a complex consisting of garden and fountains. The terracotta tile roof accommodates a rectangular prayer hall. It is an ASI protected Monument of National Importance in Goa.

The Zeenath Baksh Juma Masjid commonly known as Masjid Zeenath Baksh is the 3rd oldest mosque in India and the oldest in the state of Karnataka constructed during 644 AD. This masjid which is also known as Beliye Palli is located in the Bunder area in the city of Mangalore and is well known for its pure Indian architecture style.
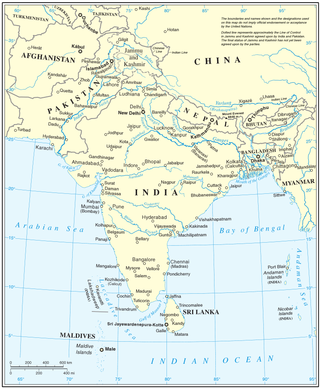
Islam is the second-largest religion in South Asia, with more than 650 million Muslims living there, forming about one-third of the region's population. Islam first spread along the coastal regions of the Indian subcontinent and Sri Lanka, almost as soon as it started in the Arabian Peninsula, as the Arab traders brought it to South Asia. South Asia has the largest population of Muslims in the world, with about one-third of all Muslims living here. Islam is the dominant religion in half of the South Asian countries. It is the second largest religion in India and third largest in Sri Lanka and Nepal.
Qissat Shakarwati Farmad is an Arabic manuscript of anonymous authorship. It is argued that the qissat is the oldest, most detailed, and comprehensive recorded version of the Cheraman Perumal legend.
Thajuddin, formerly known as the Tamil King Cheraman Perumal, played a significant role in history as the first Indian monarch to embrace Islam. After his conversion, the Siddhars gave him the title Makkahvukkupona Perumal. His conversion tale is steeped in intriguing events, with a pivotal moment revolving around the legendary splitting of the moon.
![Cheraman Juma Palli (ceermaa[?] jumaa plllli).jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/cf/Cheraman_Juma_Palli_%28%E0%B4%9A%E0%B5%87%E0%B4%B0%E0%B4%AE%E0%B4%BE%E0%B5%BB_%E0%B4%9C%E0%B5%81%E0%B4%AE%E0%B4%BE_%E0%B4%AA%E0%B4%B3%E0%B5%8D%E0%B4%B3%E0%B4%BF%29.jpg/220px-Cheraman_Juma_Palli_%28%E0%B4%9A%E0%B5%87%E0%B4%B0%E0%B4%AE%E0%B4%BE%E0%B5%BB_%E0%B4%9C%E0%B5%81%E0%B4%AE%E0%B4%BE_%E0%B4%AA%E0%B4%B3%E0%B5%8D%E0%B4%B3%E0%B4%BF%29.jpg)















