
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Collectively they are referred to as strepsirrhines. Also belonging to the suborder are the extinct adapiform primates which thrived during the Eocene in Europe, North America, and Asia, but disappeared from most of the Northern Hemisphere as the climate cooled. Adapiforms are sometimes referred to as being "lemur-like", although the diversity of both lemurs and adapiforms does not support this comparison.

Omomyidae is a group of early primates that radiated during the Eocene epoch between about 55 to 34 million years ago (mya). Fossil omomyids are found in North America, Europe & Asia, making it one of two groups of Eocene primates with a geographic distribution spanning holarctic continents, the other being the adapids. Early representatives of the Omomyidae and Adapidae appear suddenly at the beginning of the Eocene in North America, Europe, and Asia, and are the earliest known crown primates.

Plesiadapis is one of the oldest known primate-like mammal genera which existed about 58–55 million years ago in North America and Europe. Plesiadapis means "near-Adapis", which is a reference to the adapiform primate of the Eocene period, Adapis. Plesiadapis tricuspidens, the type specimen, is named after the three cusps present on its upper incisors.

Eosimias is a genus of early primates, first discovered and identified in 1999 from fossils collected in the Shanghuang fissure-fillings of Liyang, the southern city of Jiangsu Province, China. It is a part of the family Eosimiidae, and includes three known species: Eosimias sinensis, Eosimias centennicus, and Eosimias dawsonae. It provides us with a glimpse of a primate skeleton similar to that of the common ancestor of the Haplorhini. The name Eosimias is designed to mean "dawn monkey", from Greek eos "dawn" and Latin simius "monkey".

Miacis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to middle Eocene.

Necrolemur is a small bodied omomyid with body mass estimations ranging from 114–346 g (4.0–12.2 oz). Necrolemur’s teeth feature broad basins and blunt cusps, suggesting their diet consisted of mostly soft fruit, though examination of microwear patterns suggests that populations from lower latitudes also consumed insects and gums.

Smilodectes is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in North America during the middle Eocene. It possesses a post-orbital bar and grasping thumbs and toes. Smilodectes has a small cranium size and the foramen magnum was located at the back of the skull, on the occipital bone.
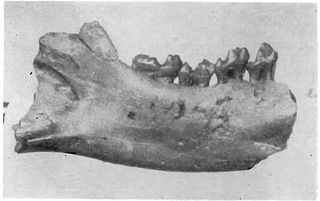
Altanius is a genus of extinct primates found in the early Eocene of Mongolia. Though its phylogenetic relationship is questionable, many have placed it as either a primitive omomyid or as a member of the sister group to both adapoids and omomyids. The genus is represented by one species, Altanius orlovi, estimated to weigh about 10–30 g (0.35–1.1 oz) from relatively well-known and complete dental and facial characteristics.

Pelycodus is an extinct genus of adapiform primate that lived during the early Eocene (Wasatchian) period in Europe and North America, particularly Wyoming and New Mexico. It is very closely related to Cantius and may even be its subgenus. It may also have given rise to the Middle Eocene Uintan primate Hesperolemur, although this is controversial. From mass estimates based on the first molar, the two species, P. jarrovii and P. danielsae, weighed 4.5 kg and 6.3 kg respectively and were frugivores with an arboreal, quadrupedal locomotion.

Miocyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America from the early to late Eocene.

Tritemnodon was an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived in North America during the early Eocene. Fossils of Tritemnodon agilis have been found in Utah and Wyoming. It was the size of a wolf.
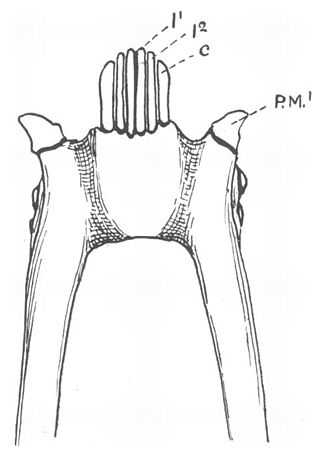
A toothcomb is a dental structure found in some mammals, comprising a group of front teeth arranged in a manner that facilitates grooming, similar to a hair comb. The toothcomb occurs in lemuriform primates, treeshrews, colugos, hyraxes, and some African antelopes. The structures evolved independently in different types of mammals through convergent evolution and vary both in dental composition and structure. In most mammals the comb is formed by a group of teeth with fine spaces between them. The toothcombs in most mammals include incisors only, while in lemuriform primates they include incisors and canine teeth that tilt forward at the front of the lower jaw, followed by a canine-shaped first premolar. The toothcombs of colugos and hyraxes take a different form with the individual incisors being serrated, providing multiple tines per tooth.

Dinopithecus is an extinct genus of very large primates closely related to baboons, that lived during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs in South Africa and Ethiopia. It was named by British paleontologist Robert Broom in 1937. The only species currently recognized is Dinopithecus ingens, as D. quadratirostris has been reassigned to the genus Soromandrillus. It is known from several infilled cave sites in South Africa, all of early Pleistocene age, including Skurweberg, Swartkrans, and Sterkfontein.

Cantius is a genus of adapiform primates from the early Eocene of North America and Europe. It is extremely well represented in the fossil record in North America and has been hypothesized to be the direct ancestor of Notharctus in North America. The evolution of Cantius is characterized by a significant increase in body mass that nearly tripled in size. The earliest species were considered small-sized and weighed in around 1 kg (2.2 lb), while the later occurring species were considered medium-sized and likely weighed in around 3 kg (6.6 lb). Though significantly smaller, the fossil remains discovered of the various species of Cantius have striking similarities to that of Notharctus and Smilodectes. It is likely Cantius relied on arboreal quadrupedal locomotion, primarily running and leaping. This locomotor pattern comparable to that of extant lemurs, which has fostered the hypothesis that Cantius and other strepsirrhine adapiforms may have a close phylogenetic affinity to living lemurs.

Sinopa is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct family Sinopidae within extinct order Hyaenodonta, that lived in North America and Asia from the early to middle Eocene.

Anaptomorphinae is a pre-historic group of primates known from Eocene fossils in North America and Europe and later periods of Paleocene Asia, and are a sub-family of omomyids. The anaptomorphines is a paraphyletic group consisting of the two tribes Trogolemurini and Anaptomorphini. Anaptomorphine radiation in Wyoming, one of the most detailed records of changes within populations and between species in the fossil record, has provided remarkable evidence of transitional fossils.

Afrotarsius is a primate found in the Paleogene of Africa.

The Wasatch Formation (Tw) is an extensive highly fossiliferous geologic formation stretching across several basins in Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, Utah and western Colorado. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Eocene period. The formation defines the Wasatchian or Lostcabinian, a period of time used within the NALMA classification, but the formation ranges in age from the Clarkforkian to Bridgerian.

David Tab Rasmussen, also known as D. Tab Rasmussen, was an American biological anthropologist. Specializing in both paleontology and behavioral ecology with interests in Paleogene mammals, early primate evolution, prosimians, and birds, he synthesized multiple fields of study in order to better understand evolutionary processes. His field research spanned the western United States as well as internationally in Africa and the Neotropics. He published over 85 research articles.

Uintaceras is an extinct genus of medium-sized early rhinocerotoids that lived in North America during the Middle Eocene, with only the type species U. radinskyi, named in 1997, currently contained within the genus. Traditionally considered the oldest and most primitive species of the Rhinocerotidae, it may instead have been a close relative of the Asian Paraceratheriidae. The dubious species Forstercooperia (Hyrachyus) grandis is also possibly the same animal as Uintaceras, although the Asian material of F. grandis was assignable to Forstercooperia confluens.






















