The Callitrichidae are a family of New World monkeys, including marmosets, tamarins, and lion tamarins. At times, this group of animals has been regarded as a subfamily, called the Callitrichinae, of the family Cebidae.

The golden lion tamarin, also known as the golden marmoset, is a small New World monkey of the family Callitrichidae. Endemic to the Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil, the golden lion tamarin is an endangered species. The range for wild individuals is spread across four places along southeastern Brazil, with a recent census estimating 3,200 individuals left in the wild and a captive population maintaining about 490 individuals among 150 zoos.

The pied tamarin, sometimes referred to as the Brazilian bare-faced tamarin, is a critically endangered species of primate found in a restricted area of the Brazilian Amazon Rainforest. It was named the mascot of Manaus, Brazil in 2005. The species is endangered due to the increasing size of the city of Manaus which is encroaching on their native habitat.

Geoffroy's tamarin, also known as the Panamanian, red-crested or rufous-naped tamarin, is a tamarin, a type of small monkey, found in Panama and Colombia. It is predominantly black and white, with a reddish nape. Diurnal, Geoffroy's tamarin spends most of its time in trees, but does come down to the ground occasionally. It lives in groups that most often number between three and five individuals, and generally include one or more adults of each sex. It eats a variety of foods, including insects, plant exudates, fruits and other plant parts. Insects and fruits account for the majority of its diet, but exudates are also important. But since its teeth are not adapted for gouging trees to get to the sap, it can only eat exudates when they are easily available.

Dublin Zoo, in Phoenix Park, is a zoo in Dublin, Ireland, and one of Dublin's most popular attractions. Established and designed in 1830 by Decimus Burton, it opened the following year. Today it focuses on conservation projects, breeding programmes, and growing awareness for animals. Its stated mission is to "work in partnership with zoos worldwide to make a significant contribution to the conservation of the endangered species on Earth".

The lion-tailed macaque, also known as the wanderoo, is an Old World monkey endemic to the Western Ghats of South India.

The tamarins are squirrel-sized New World monkeys from the family Callitrichidae in the genus Saguinus. They are the first offshoot in the Callitrichidae tree, and therefore are the sister group of a clade formed by the lion tamarins, Goeldi's monkeys and marmosets.

The cotton-top tamarin is a small New World monkey weighing less than 0.5 kg (1.1 lb). This New World monkey can live up to 24 years, but most of them die by 13 years. One of the smallest primates, the cotton-top tamarin is easily recognized by the long, white sagittal crest extending from its forehead to its shoulders. The species is found in tropical forest edges and secondary forests in northwestern Colombia, where it is arboreal and diurnal. Its diet includes insects and plant exudates, and it is an important seed disperser in the tropical ecosystem.

The black-faced lion tamarin or Superagüi lion tamarin is a small New World monkey of the family Callitrichidae. It is endangered and endemic to coastal forests in southeastern Brazil. There are several conservation projects and the total populations is unlikely to exceed 400 individuals. It is overall golden-orange with contrasting black head, legs and tail.

The golden-headed lion tamarin, also the golden-headed tamarin, is a lion tamarin endemic to Brazil. It is found only in the lowland and premontane tropical forest fragments in the state of Bahia, and therefore is considered to be an endangered species. It lives at heights of 3–10 metres (9.8–32.8 ft). Its preferred habitat is within mature forest, but with habitat destruction this is not always the case. Several sources seem to have different information on the number of individuals within a group, and the type of social system that may be apparent. The golden-headed lion tamarin lives within group sizes ranging from 2 to 11 individuals, with the average size ranging from 4 to 7. According to various sources, the group may consist of two adult males, one adult female, and any immature individuals, one male and one female and any immature individuals, or there may be one producing pair and a varying number of other group members, usually offspring from previous generations. There is not much known on its mating system, but according to different sources, and information on the possible social groups, it can be assumed that some may practice monogamous mating systems, and some may practice polyandrous mating systems. Both males and females invest energy in caring for the young, and all members of the group also help with juvenile care.

The black lion tamarin, also known as the golden-rumped lion tamarin, is a lion tamarin endemic to the Brazilian state of São Paulo, almost exclusively at the Morro do Diabo State Park. Its limited geographical range makes it the rarest of the New World monkeys, with little known about it. It was thought to be extinct for 65 years until its rediscovery in 1970. In 2016 an adult couple was found to the east, in the Caetetus Ecological Station, after six years with no sightings.

The black tamarin or western black-handed tamarin is a species of tamarin endemic to Brazil.

The Serra do Mar coastal forests is an ecoregion of the tropical moist forests biome. It is part of the Atlantic Forest of eastern South America. This ecoregion has an outstanding biodiversity consisting of flora, mammals, birds, and herpetofauna.

The greater bamboo lemur, also known as the broad-nosed bamboo lemur and the broad-nosed gentle lemur, is a species of lemur endemic to the island of Madagascar.

The black-shanked douc is an endangered species of douc found mostly in the forests of Eastern Cambodia, with some smaller populations in Southern Vietnam. The region they are mostly found in is called the Annamite Range, a mountainous area that passes through Cambodia and Vietnam. Its habitat is mostly characterized by evergreen forest in the mountains, in the middle to upper canopy. They move around quadrupedally and by brachiation up in the trees. This species is unique with its coloration among the doucs as it has a bluish face with yellow rings around its eyes a blue scrotum and a pink penis. Like other doucs, this species has a tail as long as its body and head length. Black-shanked douc have been observed in groups ranging from 3 to 30 individuals, depending on their habitat. Group tend to have a fission-fusion dynamic that changes with food availability. Their diet varies from dry to wet season. Regardless of the season, their diet consists mostly of leaves, but they have also been found to consume considerable amounts of fruits and flowers during wet season. The species changed conservation status in 2015 from endangered to critically endangered in the IUCN Red List of Endangered Species. This reassessment is due to an increase of the rate of population decline. No global population estimate exists. The majority of the population can be found in Cambodia, with smaller populations in Vietnam. In fact, the Wildlife Conservation Society reports almost 25,000 individuals in Cambodia's Keo Seima Wildlife Sanctuary, a population that has remained stable over the last decade. The largest populations estimated to be in Vietnam is around 500-600 individuals. The biggest challenges that the black-shanked douc faces in terms of conservation are habitat loss and illegal poaching. Conservation efforts are being made to control illegal poaching and trade in Vietnam by putting laws against hunting and trading threatened species.
Manilkara rufula is a species of tree in the Sapodilla family. It is endemic to the northeastern submontane forests of Bahia, Sergipe, Pernambuco, Paraíba, Ceará and Piauí states of Brazil. Although this species exists in many places, where it occurs it is either not numerous, or its numbers are declining due to loss of habitat.

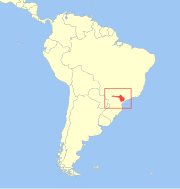
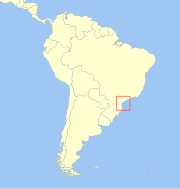
Poço das Antas Biological Reserve is a biological reserve located in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil.

The Roloway monkey is an endangered species of Old World monkey endemic to tropical West Africa. It was previously considered a subspecies of the Diana monkey. The species is classified as Critically Endangered due to habitat loss and their continued hunting because of the bushmeat trade. The Roloway monkey is mainly an arboreal species, for the most part inhabiting forests in Ghana and some reserves in South-Eastern Côte-D'Ivoire. More specifically, studies have shown that C. roloway is primarily concentrated in the Tanoé forest of the Côte-D'Ivoire because of their heavy threats to extinction and lack of habitat. It is still difficult to gather data on wild subjects, as they have low populations in a vast forest, but they are a unique and vanishing species.

The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates is a list of highly endangered primate species selected and published by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Species Survival Commission (SSC) Primate Specialist Group (PSG), the International Primatological Society (IPS), Global Wildlife Conservation (GWC), and Bristol Zoological Society (BZS). The IUCN/SSC PSG worked with Conservation International (CI) to start the list in 2000, but in 2002, during the 19th Congress of the International Primatological Society, primatologists reviewed and debated the list, resulting in the 2002–2004 revision and the endorsement of the IPS. The publication was a joint project between the three conservation organizations until the 2012–2014 list when BZS was added as a publisher. The 2018–2020 list was the first time Conservation International was not among the publishers, replaced instead by GWC. The list has been revised every two years following the biannual Congress of the IPS. Starting with the 2004–2006 report, the title changed to "Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates". That same year, the list began to provide information about each species, including their conservation status and the threats they face in the wild. The species text is written in collaboration with experts from the field, with 60 people contributing to the 2006–2008 report and 85 people contributing to the 2008–2010 report. The 2004–2006 and 2006–2008 reports were published in the IUCN/SSC PSG journal Primate Conservation,, since then they have been published as independent publications.

The western pygmy marmoset is a marmoset species, a very small New World monkey found in the northwestern Amazon rainforest in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. It was formerly regarded as conspecific with the similar eastern pygmy marmoset, which has whitish underparts. Although the western pygmy marmoset occurs further west than the eastern pygmy marmoset, the primary separators of their ranges are the Amazon River and Marañón River, with the western occurring to the north of them and the eastern to the south.