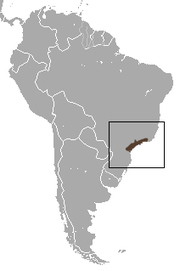
| Muriquis [1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Northern muriqui, Brachyteles hypoxanthus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Family: | Atelidae |
| Subfamily: | Atelinae |
| Genus: | Brachyteles Spix, 1823 |
| Type species | |
| Brachyteles macrotarsus | |
| Species | |
The muriquis, also known as woolly spider monkeys, are the monkeys of the genus Brachyteles. [1] They are closely related to both the spider monkeys and the woolly monkeys. [1]