
The simians, anthropoids, or higher primates are an infraorder of primates containing all animals traditionally called monkeys and apes. More precisely, they consist of the parvorders Platyrrhini and Catarrhini, the latter of which consists of the family Cercopithecidae and the superfamily Hominoidea.

Aegyptopithecus is an early fossil catarrhine that predates the divergence between hominoids (apes) and cercopithecids. It is known from a single species, Aegyptopithecus zeuxis, which lived around 38-29.5 million years ago in the early part of the Oligocene epoch. It likely resembled modern-day New World monkeys, and was about the same size as a modern howler monkey, which is about 56 to 92 cm long. Aegyptopithecus fossils have been found in the Jebel Qatrani Formation of modern-day Egypt. Aegyptopithecus is believed to be a stem-catarrhine, a crucial link between Eocene and Miocene fossils.
Oligopithecidae is an extinct basal Catarrhine family from the late Eocene of Egypt as sister of the rest of the Catarrhines. Its members were probably insectivorous, due to their simple molars and cusp arrangement.

Ptolemaiida is a taxon of wolf-sized afrothere mammals that lived in northern and eastern Africa during the Paleogene. The oldest fossils are from the latest Eocene strata of the Jebel Qatrani Formation, near the Fayum oasis in Egypt. A tooth is known from an Oligocene-aged stratum in Angola, and Miocene specimens are known from Kenya and Uganda.

Eosimiidae is the possible family of extinct primates believed to be the earliest simians.

Catopithecus is an early catarrhine fossil. It is known from more than 16 specimens of a single species, Catopithecus browni, found in the Jebel Qatrani Formation of the Faiyum Governorate, Egypt. The Jebel Qatrani Formation has been divided into two main faunal zones based on the fact that the fauna found in the lower portion of the quarry appear to be more primitive than those found in the upper section. The upper zone has been dated to older than 31 ± 1 myr based on the dating of a basalt layer that lies immediately above the formation and Nicolas Steno’s Law of Superposition. The lower zone contains the late Eocene green shale unit called Locality-41 (L-41) in which all the specimens of Catopithecus browni have been found. The relative dating of L-41 based on paleomagnetic correlations places it at 36 Myr according to Simons et al (1999), but Seiffert (2006) suggests this should be revised to 34.8-33.9 Myr.
Altiatlasius is an extinct genus of mammal, which may have been the oldest known primate, dating to the Late Paleocene from Morocco. The only species, Altiatlasius koulchii, was described in 1990.
Biretia is an extinct genus of Old World monkey belonging to the extinct family Parapithecidae. Fossils are found from Late Eocene strata in Egypt.

The Jebel Qatrani Formation is a geologic formation located in the Faiyum Governorate of central Egypt. It is exposed between the Jebel Qatrani escarpment and the Qasr el Sagha escarpment, north of Birket Qarun lake near Faiyum. The formation conformably overlies the Qasr el Sagha Formation and is topped by the Widan el Faras Basalt. The age of the formation has been subject to debate, but the most recent research indicates that it covers both the latest parts of the Eocene and the Early Oligocene, spanning over the boundary between these two time periods.

Saadanius is a genus of fossil primates dating to the Oligocene that is closely related to the common ancestor of the Old World monkeys and apes, collectively known as catarrhines. It is represented by a single species, Saadanius hijazensis, which is known only from a single partial skull tentatively dated between 29 and 28 million years ago. It was discovered in 2009 in western Saudi Arabia near Mecca and was first described in 2010 after comparison with both living and fossil catarrhines.
Parapithecidae is an now extinct family of primates which lived in the Eocene and Oligocene periods in Egypt. Eocene fossils from Myanmar are sometimes included in the family in addition. They showed certain similarities in dentition to Condylarthra, but had short faces and jaws shaped like those of tarsiers. They are part of the superfamily Parapithecoidea, perhaps equally related to Ceboidea and Cercopithecoidea plus Hominoidea - but the placement of Parapithecoidea is substantially uncertain.
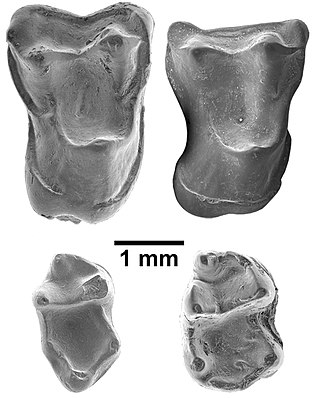
Afrasia djijidae is a fossil primate that lived in Myanmar approximately 37 million years ago, during the late middle Eocene. The only species in the genus Afrasia, it was a small primate, estimated to weigh around 100 grams (3.5 oz). Despite the significant geographic distance between them, Afrasia is thought to be closely related to Afrotarsius, an enigmatic fossil found in Libya and Egypt that dates to 38–39 million years ago. If this relationship is correct, it suggests that early simians dispersed from Asia to Africa during the middle Eocene and would add further support to the hypothesis that the first simians evolved in Asia, not Africa. Neither Afrasia nor Afrotarsius, which together form the family Afrotarsiidae, is considered ancestral to living simians, but they are part of a side branch or stem group known as eosimiiforms. Because they did not give rise to the stem simians that are known from the same deposits in Africa, early Asian simians are thought to have dispersed from Asia to Africa more than once prior to the late middle Eocene. Such dispersals from Asia to Africa also were seen around the same time in other mammalian groups, including hystricognathous rodents and anthracotheres.
Plesiopithecus is an extinct genus of early strepsirrhine primate from the late Eocene.
Afradapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived during the Late Eocene. The only known species, Afradapis longicristatus, was discovered in the Birket Qarun Formation in northern Egypt in 2009. While its geographic distribution is confined to Afro-Arabia, Afradapis belongs to the predominantly European adapiform family Caenopithecinae. This taxonomic placement is supported by recent phylogenetic analyses that recover a close evolutionary relationship between Afradapis and adapiforms, including Darwinius. While adapiforms have been noted for their strepsirrhine-like morphology, no adapiform fossil possesses the unique anatomical traits to establish an ancestor-descent relationship between caenopithecids and living strepsirrhines. It ate leaves and moved around slowly like lorises.
Widanelfarasia is an extinct genus of placental mammals known from the Late Eocene Jebel Qatrani Formation of Egypt. Two species are known: W. bowni and the smaller W. rasmusseni. Described in 2000 by E. R. Seiffert and Elwyn L. Simons, Widanelfarasia was initially classified as uncertain position within placentals, but was later placed within the afrosoricidan suborder Tenrecomorpha. The genus name derives from Widan el-Faras, two prominent hills in the area where the fossils were recovered.
Propliopithecoidea is a superfamily of catarrhine primates that inhabited Africa and the Arabian Peninsula during the Early Oligocene about 32 to 29 million years ago. Fossils have been found in Egypt, Oman and Angola. They are one of the earliest known families of catarrhines. They have a number of features in common with extant catarrhines, but also features that are primitive and not found in later catarrhine families.
Parapithecoidea is an extinct superfamily of primates which lived in the Eocene and Oligocene periods in Egypt. In some classifications all Parapithecoidea are placed within the family Parapithecidae. Seiffert et al. (2010) propose that Parapithecoidea arose during the Bartonian, with a split between Biretia and the Parapithecidae occurring early in the Priabonian.
Proteopithecidae is an extinct family of primates which lived in the Priabonian and probably early Oligocene periods. Fossils that have been found are in the Jebel Qatrani Formation in Egypt. Currently two genera are recognised, each with a single species, those being Proteopithecus sylviae and Serapia eocaena.

Hesham Sallam is an Egyptian paleontologist and the founder of the Mansoura University Vertebrate Paleontology Center (MUVP-C), the first vertebrate paleontology program in the Middle East. He works as an associate professor at the American University in Cairo and Mansoura University. Sallam led the discovery and description of Mansourasaurus shahinae, a species of sauropod dinosaur from Egypt, which has improved understanding of the prehistory of Africa during the latest Cretaceous period. His work has helped popularize paleontology in Egypt.

The Fayyum is a region and an important fossil Lagerstätte in northern Egypt. The region comprises the Fayyum Basin, which is intensively used for agriculture, and adjoining areas; the important areas of discovery are mostly north and west of Lake Qarun. The Wadi al-Hitan, known for its numerous whale fossils and since 2005 UNESCO World Natural Heritage Site, forms the south-western end. The deposits of the Fayyum belong to various geological formations. They are mainly composed of limestone, siltstone and sandstone. The lower sections consist of marine sediments, while the upper, continental sediments were formed in a coastal landscape. The formation period ranges from the Middle to the Upper Eocene to the Lower Oligocene, which corresponds to an age of around 41 to 28 million years ago. The entire sedimentary complex is overlain by basalt, which dates back to volcanic activity around 24 million years ago.














