This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics.

Climate change has been a critical issue in Australia since the beginning of the 21st century. Australia is becoming hotter and more prone to extreme heat, bushfires, droughts, floods, and longer fire seasons because of climate change. Climate issues include wildfires, heatwaves, cyclones, rising sea levels, and erosion.

Climate change in the US state of Washington is a subject of study and projection today. The major impacts of climate change in Washington State include increase in carbon dioxide levels, increase in temperatures, earlier annual snow melt, sea level rise, and others.

Climate change is an urgent and significant issue affecting Japan. In recent years, the country has observed notable changes in its climate patterns, with rising temperatures serving as a prominent indicator of this phenomenon. As an archipelago situated in northeastern Asia, Japan is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change due to its diverse geography and exposure to various weather systems. The nation experiences a broad range of climates, spanning from the frigid winters of Hokkaido to the subtropical climates of Okinawa. Changes in temperature patterns have the potential to disrupt ecosystems, impact agricultural productivity, modify water resources, and pose significant challenges to infrastructure and human settlements.

On a per-person basis, Wyoming emits more carbon dioxide than any other state or any other country: 276,000 pounds (125,000 kg) of it per capita a year, because of burning coal, which provides nearly all of the state's electrical power.

Climate change in Nevada has been measured over the last century, with the average temperature in Elko, Nevada increasing by 0.6 °F (0.33 °C), and precipitation increasing by up to 20% in many parts of the state. These past trends may or may not continue into the future.

Climate change has received significant scientific, public and political attention in Sweden. In 1896, Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius was the first scientist to quantify global heating. Sweden has a high energy consumtion per capita, but reducing the dependency on fossil energy has been on the agenda of cabinets of the Governments of Sweden since the 1970s oil crises. In 2014 and 2016, Sweden was ranked #1 in the Global Green Economy Index (GGEI), because the Swedish economy produces relatively low emissions. Sweden has had one of the highest usages of biofuel in Europe and aims at prohibiting new sales of fossil-cars, including hybrid cars, by 2035, and for an energy supply system with zero net atmospheric greenhouse gas emissions by 2045.

Climate change is greatly impacting Canada's environment and landscapes. These events are likely to become even more frequent and severe in the future due to the continued release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The number of climate change–related events, such as the 2021 British Columbia Floods and an increasing number of forest fires, has become an increasing concern over time. Canada's annual average temperature over land warmed by 1.7 degrees Celsius between 1948 and 2016. The rate of warming is highest in Canada's north, the Prairies, and northern British Columbia. The country's precipitation has increased in recent years and extreme weather events have become more common.

Turkey's climate is varied and generally temperate, with the regions bordering the Mediterranean and Black Sea heavily affected by the coasts, and the interior being drier and more continental.

Climate change has far reaching impacts on the natural environment and people of Finland. Finland was among the top five greenhouse gas emitters in 2001, on a per capita basis. Emissions increased to 58.8 million tonnes in 2016. Finland needs to triple its current cuts to emissions in order to be carbon neutral by 2035. Finland relies on coal and peat for its energy, but plans to phase out coal by 2029. Finland has a target of carbon neutrality by the year 2035 without carbon credits. The policies include nature conservation, more investments in trains, changes in taxation and more sustainable wood burning. After 2035 Finland will be carbon negative, meaning soaking more carbon than emitting.
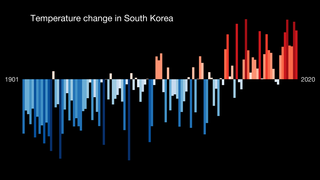
Climate change has led to extreme weather events in South Korea that affects: social, economy, industry, culture, and many other sectors. South Korea is experiencing changes in climate parameters. Such parameters include annual temperature, rainfall amounts, and precipitation.

Climate change in Alaska encompasses the effects of climate change in the U.S. state of Alaska.

Climate change in Nebraska encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Nebraska.

Climate change has had large impacts on the ecosystems and landscapes of the US territory Puerto Rico. According to a 2019 report by Germanwatch, Puerto Rico is the most affected by climate change. The territory's energy consumption is mainly derived from imported fossil fuels.

Climate change in Rhode Island encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Rhode Island.

Climate change in Vermont encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Vermont.

Climate change is affecting Austrian temperatures, weather, ecosystems and biodiversity. Since 1950 temperatures have risen by 1.8 °C, and in the past 150 years glaciers have melted, losing a significant amount of their volume. Changed precipitation patterns, increased temperatures, reduced snowfall, melting glaciers and more frequent extreme weather phenomenon, such as droughts, are expected effects from climate change. Ecosystems and biodiversity in Austria are facing changes due to increasing temperatures and the spread of thermophile species, heat and drought stress on animals and plants, an increase in alien and invasive species and an increase in pathogenic organisms and the spread of disease.

Climate change in New York encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases, in the U.S. state of New York. It is of concern due to its impact on the people, ecosystem, and economy of the state. Many parts of the state are already experiencing weather changes, and sea-level rise, and threatening local communities.

Climate change in South Dakota encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of South Dakota.

The climate in Texas is changing partially due to global warming and rising trends in greenhouse gas emissions. As of 2016, most area of Texas had already warmed by 1.5 °F (0.83 °C) since the previous century because of greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and other countries. Texas is expected to experience a wide range of environmental impacts from climate change in the United States, including rising sea levels, more frequent extreme weather events, and increasing pressure on water resources.



























