Related Research Articles

Niger-Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over nearly the entirety of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger-Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.

Benue–Congo is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa.
The Adamawa languages are a putative family of 80–90 languages scattered across the Adamawa Plateau in central Africa, in Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, and Chad, spoken altogether by only one and a half million people. Joseph Greenberg classified them as one branch of the Adamawa–Ubangi family of Niger–Congo languages. They are among the least studied languages in Africa, and include many endangered languages; by far the largest is Mumuye, with 400,000 speakers. A couple of unclassified languages—notably Laal and Jalaa—are found along the fringes of the Adamawa area.
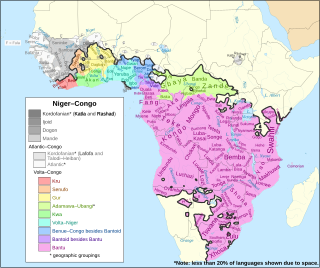
Volta–Congo is a major branch of the Atlantic–Congo family. It includes all the Niger-Congo languages and subfamilies except the families of the erstwhile Atlantic and Kordofanian branches, Mande, Dogon, and Ijo. It thus only differs from Atlantic–Congo in that it excludes the Atlantic languages and, in some conceptions, Kru and Senufo.

The Languages of Africa is a 1963 book of essays by the linguist Joseph Greenberg, in which the author sets forth a genetic classification of African languages that, with some changes, continues to be the most commonly used one today. It is an expanded and extensively revised version of his 1955 work Studies in African Linguistic Classification, which was itself a compilation of eight articles which Greenberg had published in the Southwestern Journal of Anthropology between 1949 and 1954. It was first published in 1963 as Part II of the International Journal of American Linguistics, Vol. 29, No. 1; however, its second edition of 1966, in which it was published as an independent work, is more commonly cited.

Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and to which Bantoid is named after.

Taraba is a state in North Eastern Nigeria, named after the Taraba River which traverses the southern part of the state. Taraba's capital is Jalingo. The inhabitants are mainly the Fulani, Jukun, Chamba,Kuteb and the Ichen who are found predominantly in the southern part of the state while Wurkum, Mumuye, and Kona tribes are predominantly located in the northern part of the state. The central region is mainly occupied by the Mambila people, Chamba,Fulani and Jibawa. There are over 40 different tribes and their languages in Taraba State.
Ijoid is a proposed but undemonstrated group of languages linking the Ijaw languages (Ịjọ) with the endangered Defaka language. The similarities, however, may be due to Ijaw influence on Defaka.
Fali may refer to:
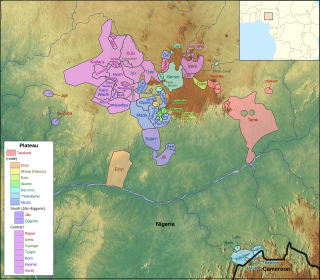
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau Southern Kaduna, Nassarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.
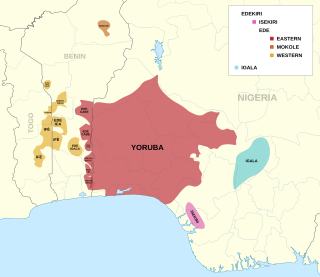
Yoruboid is a 'megagroup' of 14 related language clades, composed of the Igala group of dialects spoken in south central Nigeria, and the Edekiri group spoken in a band across Togo, Ghana, Benin and southern Nigeria, including the Itsekiri of Warri Kingdom.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language of Nigeria is English, the language of former colonial British Nigeria. As reported in 2003, Nigerian English and Nigerian Pidgin were spoken as a second language by 100 million people in Nigeria. Communication in the English language is much more popular in the country's urban communities than it is in the rural areas, due to globalization.
The Gbaya languages, also known as Gbaya–Manza–Ngbaka, are a family of perhaps a dozen languages spoken mainly in the western Central African Republic and across the border in Cameroon, with one language (Ngbaka) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, with a few small languages in the Republic of the Congo. Many of the languages go by the ethnic name Gbaya, though the largest, with over a million speakers, is called Ngbaka, a name shared with the Ngbaka languages of the Ubangian family.
The Savannas languages, also known as Gur–Adamawa or Adamawa–Gur, is a branch of the Niger–Congo languages that includes Greenberg's Gur and Adamawa–Ubangui families.

Volta–Niger is a proposed but undemonstrated family of languages, also known as West Benue–Congo or East Kwa. Among these are the most spoken languages of southern Nigeria, Benin, Togo, and southeast Ghana: Yoruba, Igbo, Bini, Fon, and Ewe.
Ebira is a Niger-Congo language. It is spoken by around 3 million people in North central Nigeria. It is the most divergent Nupoid language.
Ukaan is a poorly described Niger–Congo language or dialect cluster of uncertain affiliation. Roger Blench suspects, based on wordlists, that it might be closest to the (East) Benue–Congo languages. Blench (2012) states that "noun-classes and concord make it look Benue-Congo, but evidence is weak."
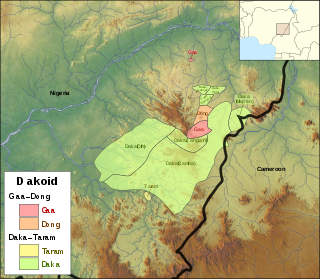
The Dakoid languages are a branch of the Northern Bantoid languages spoken in Taraba and Adamawa states of eastern Nigeria.
The Itsekiri language is a major branch of the Yoruboid group of languages, which as a group, is a key member of the Volta–Niger sub-family of the Niger–Congo family of African languages. Itsekiri is spoken by nearly 900,000 people in Nigeria as a first language and by many others as an additional language notably in the Niger Delta and in parts of Edo and Ondo states of Nigeria. The other key members of the Yoruboid group are Yoruba and Igala along with the various Yoruba dialects spoken in Benin and Togo.

The Hausa–Gwandara languages of the Afro-Asiatic family are spoken principally in Niger and Nigeria. They include Gwandara and Hausa, the most populous Chadic language and a major language of West Africa.
References
- ↑ Fali at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Williamson, Kay (1989) 'Benue–Congo Overview', pp. 248–274 in Bendor-Samuel, John & Rhonda L. Hartell (eds.) The Niger–Congo Languages – A classification and description of Africa's largest language family. Lanham, Maryland: University Press of America.