
State Route 14 (SR 14) is a north–south state highway in the U.S. state of California that connects Los Angeles to the northern Mojave Desert. The southern portion of the highway is signed as the Antelope Valley Freeway. Its southern terminus is at Interstate 5 in the Los Angeles neighborhoods of Granada Hills and Sylmar just immediately to the south of the border of the city of Santa Clarita. SR 14's northern terminus is at U.S. Route 395 (US 395) near Inyokern. Legislatively, the route extends south of I-5 to SR 1 in the Pacific Palisades area of Los Angeles; however, the portion south of the junction with I-5 has not been constructed. The southern part of the constructed route is a busy commuter freeway serving and connecting the cities of Santa Clarita, Palmdale, and Lancaster to the rest of the Greater Los Angeles area. The northern portion, from Vincent to US 395, is legislatively named the Aerospace Highway, as the highway serves Edwards Air Force Base, once one of the primary landing strips for NASA's Space Shuttle, as well as the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake that supports military aerospace research, development and testing. This section is rural, following the line between the hot Mojave desert and the forming Sierra Nevada mountain range. Most of SR 14 is loosely paralleled by a rail line originally built by the Southern Pacific Railroad, and was once the primary rail link between Los Angeles and Northern California. While no longer a primary rail line, the southern half of this line is now used for the Antelope Valley Line of the Metrolink commuter rail system.

The Mohave Valley is a valley located mostly on the east shore of the south-flowing Colorado River in northwest Arizona. The valley extends into California's San Bernardino County; the northern side of the valley extends into extreme southeast Clark County, Nevada. The main part of the valley lies in southwest Mohave County, Arizona and is at the intersection of the southeast Mojave and northwest Sonoran deserts.

The Dead Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern Mojave Desert, in San Bernardino County, California. The range borders the tri-state intersection of Nevada, Arizona and California, and the Mohave Valley, with the Fort Mojave Indian Reservation bordering the range foothills on the east and northeast, in the three states.
The Piute Mountains are a mountain range located in the Eastern Mojave Desert and within Mojave Trails National Monument, in San Bernardino County, California.

The Sacramento Mountains are a mountain range in the Eastern Mojave Desert and within Mojave Trails National Monument, in San Bernardino County, California.

The Piute Range is located in the Mojave Desert, primarily in northeast San Bernardino County, California, United States, with a north portion in Nevada. Most of the range is the eastern border of the Mojave National Preserve, a National Park Service natural area and park.

Lanfair Valley is located in the Mojave Desert in southeastern California near the Nevada state line. It is bounded on the north by the New York Mountains and Castle Mountains, on the east by the Piute Range, and on the south by the Woods Mountains and Vontrigger Hills. Joshua Trees can be found in most of the valley. Elevation is 4,045 feet.

The Midland Trail, also called the Roosevelt Midland Trail, was a national auto trail spanning the United States from Washington, D.C., west to Los Angeles, California and San Francisco, California. First road signed in 1913, it was one of the first, if not the first, marked transcontinental auto trails in America.
Ludlow is an unincorporated community in the Mojave Desert on Interstate 40, located in San Bernardino County, California, United States. The older remains of the ghost town are along historic Route 66.

The Mojave Road, also known as Old Government Road, is a historic route and present day dirt road across what is now the Mojave National Preserve in the Mojave Desert in the United States. This rough road stretched 147 miles (237 km) from Beale's Crossing, to Fork of the Road location along the north bank of the Mojave River where the old Mojave Road split off from the route of the Old Spanish Trail/Mormon Road.

U.S. Route 395 (US 395) is a United States Numbered Highway, stretching from Hesperia, California to the Canadian border in Laurier, Washington. The California portion of US 395 is a 557-mile (896 km) route which traverses from Interstate 15 (I-15) in Hesperia, north to the Oregon state line in Modoc County near Goose Lake. The route clips into Nevada, serving the cities Carson City and Reno, before returning to California.

The Sacramento Wash is a major drainage of northwest Arizona in Mohave County. The wash is east of the Black Canyon of the Colorado and drains into the south-flowing Colorado River 45 mi south of Lake Mohave, and 90 mi south of Hoover Dam at Lake Mead. The wash outfall is in the center-south of the Havasu-Mohave Lakes Watershed. An equivalent wash drains to the west of the Colorado River and the Black Canyon, draining southeast Nevada and a small part of California, the Piute Wash of the Piute Valley. The Piute Wash outfall is upstream of the Sacramento's outfall by about 15 miles.

Eldorado Valley, or El Dorado Valley, is a Great Basin valley in the Mojave Desert southeast of Las Vegas and southwest of Boulder City, Nevada. The valley is endorheic, containing the Eldorado Dry Lake. The Great Basin Divide, transects ridgelines and saddles, on the north, northeast, east, and south around the valley, as the valley sits on the east of the McCullough Range, a Great Basin massif, on the Great Basin Divide at its north terminus and its south terminus. Much of the valley is protected as part of Avi Kwa Ame National Monument.

Mount Manchester is the highest peak in the Dead Mountains of extreme northeastern San Bernardino County, California, in the Mojave Desert.

The Piute Wash of extreme southeastern Nevada and northeast San Bernardino County California is the south-flowing drainage of the Piute Valley. The wash and valley are located northwest of Needles, California.

The Piute Valley is a 45-mile-long (72 km) north–south valley southeast of Las Vegas, Nevada, and northwest of Needles. The north of the valley is at Searchlight, with some of the valley extending northwest from Searchlight. At the center-north lies Cal-Nev-Ari, Nevada.
Barnwell, originally a rail camp named Summit, then Manvel, was a former railhead serving local mining camps, now a ghost town, in San Bernardino County, California. It lies at an elevation 4806 feet in the New York Mountains.
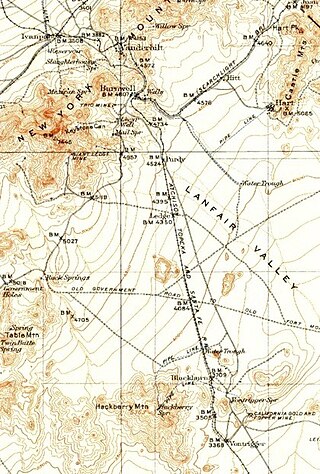
California Eastern Railway, is a defunct 45-mile (72 km) short-line railroad that operated from 1902 to 1911. The railroad ran from Goffs, California, to Ivanpah. It was first a private line operated by a mining company that was acquired by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.
The Sacramento Wash (California) is the drainage southward, then east from the Lanfair Valley of extreme eastern San Bernardino County, California. The drainage combines with the Piute Wash-(mostly of Nevada) at the south terminus of the Dead Mountains, and immediately enters the Colorado River, just north of Needles, California. Another Sacramento Wash occurs across the Colorado, as an eastern drainage from northwest Arizona, also at Needles, CA.

The Camp Goffs was a sub camp of the US Army Desert Training Center in Riverside County, California. The main headquarters for the Desert Training Center was Camp Young, this is where General Patton's 3rd Armored Division was stationed. Camp Goffs was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.985). The site of the Camp Goffs just north at the former Santa Fe Railroad station at Goffs, California. Goffs, California is on U.S. Route 66 5 miles north of the current Interstate 40, 25 miles (40 km) west of Needles in San Bernardino County, California. Currently at the south east end of the Mojave National Preserve. Camp Goffs was 20 miles southeast of Camp Essex and Camp Clipper.

















