Related Research Articles

Transcription is the first of several steps of DNA based gene expression in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme RNA polymerase.

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.

A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction

DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the primary enzyme complex involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg and Malcolm Gefter in 1970. The complex has high processivity and, specifically referring to the replication of the E.coli genome, works in conjunction with four other DNA polymerases. Being the primary holoenzyme involved in replication activity, the DNA Pol III holoenzyme also has proofreading capabilities that corrects replication mistakes by means of exonuclease activity reading 3'→5' and synthesizing 5'→3'. DNA Pol III is a component of the replisome, which is located at the replication fork.
dnaQ is the gene encoding the ε subunit of DNA polymerase III in Escherichia coli. The ε subunit is one of three core proteins in the DNA polymerase complex. It functions as a 3’→5’ DNA directed proofreading exonuclease that removes incorrectly incorporated bases during replication. dnaQ may also be referred to as mutD.
RNA polymerase 1 is, in higher eukaryotes, the polymerase that only transcribes ribosomal RNA, a type of RNA that accounts for over 50% of the total RNA synthesized in a cell.

RNA polymerase II is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.

DNA polymerase II is a prokaryotic DNA-Dependent DNA polymerase encoded by the PolB gene.

RNA-dependent RNA polymerase or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyses synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription of RNA from a DNA template.
Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid is chromosomal DNA, in contrast to extra-chromosomal DNAs like plasmids. It is also then abbreviated as gDNA. Most organisms have the same genomic DNA in every cell; however, only certain genes are active in each cell to allow for cell function and differentiation within the body.
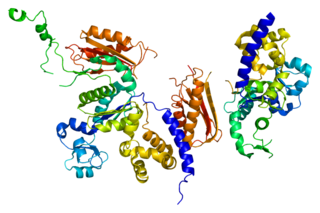
DNA polymerase kappa is an DNA polymerase that in humans is encoded by the POLK gene. It is involved in translesion synthesis.

DNA polymerase subunit gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLG gene. Mitochondrial DNA polymerase is heterotrimeric, consisting of a homodimer of accessory subunits plus a catalytic subunit. The protein encoded by this gene is the catalytic subunit of mitochondrial DNA polymerase. Defects in this gene are a cause of progressive external ophthalmoplegia with mitochondrial DNA deletions 1 (PEOA1), sensory ataxic neuropathy dysarthria and ophthalmoparesis (SANDO), Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome (AHS), and mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy syndrome (MNGIE).

Protein reversionless 3-like (REV3L) also known as DNA polymerase zeta catalytic subunit (POLZ) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the REV3L gene.

DNA polymerase eta, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POLH gene.

DNA-directed RNA polymerase III subunit RPC4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLR3D gene.

In molecular biology, the δ (delta) subunit of DNA polymerase III is encoded by the holA gene in E. coli and other bacteria. Along with the γ, δ', χ, and ψ subunits that make up the core polymerase, and the β accessory proteins, the δ subunit is responsible for the high speed and processivity of polIII.
In E. coli and other bacteria, holB is a gene that encodes the delta prime subunit of DNA polymerase III.

In E. coli and other bacteria, holC is a gene that encodes the chi subunit of DNA polymerase III.
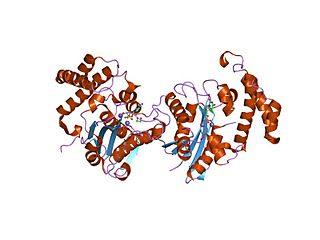
In E. coli and other bacteria, holE is a gene that encodes the theta subunit of DNA polymerase III.

DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLE gene. It is the central catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase epsilon.
References
| This molecular biology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |