The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture.
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label such as 192.0.2.1 that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface identification, and location addressing.

A router is a computer and networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks, including internetworks such as the global Internet.

Wake-on-LAN is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened from sleep mode by a network message. It is based upon AMD's Magic Packet Technology, which was co-developed by AMD and Hewlett-Packard, following its proposal as a standard in 1995. The standard saw quick adoption thereafter through IBM, Intel and others.

Network address translation (NAT) is a method of mapping an IP address space into another by modifying network address information in the IP header of packets while they are in transit across a traffic routing device. The technique was initially used to bypass the need to assign a new address to every host when a network was moved, or when the upstream Internet service provider was replaced but could not route the network's address space. It has become a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. One Internet-routable IP address of a NAT gateway can be used for an entire private network.
The Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) is a computer networking protocol used in Internet Protocol networks to automatically assign an IP address to network devices from a configuration server. The BOOTP was originally defined in RFC 951 published in 1985.
Zero-configuration networking (zeroconf) is a set of technologies that automatically creates a usable computer network based on the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) when computers or network peripherals are interconnected. It does not require manual operator intervention or special configuration servers. Without zeroconf, a network administrator must set up network services, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS), or configure each computer's network settings manually.

ipconfig is a console application program of some computer operating systems that displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.
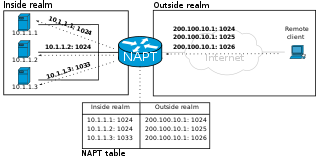
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
A default gateway is the node in a computer network using the Internet protocol suite that serves as the forwarding host (router) to other networks when no other route specification matches the destination IP address of a packet.
NetBIOS over TCP/IP is a networking protocol that allows legacy computer applications relying on the NetBIOS API to be used on modern TCP/IP networks.
Network address translation traversal is a computer networking technique of establishing and maintaining Internet Protocol connections across gateways that implement network address translation (NAT).
In computer networking, a host model is an option of designing the TCP/IP stack of a networking operating system like Microsoft Windows or Linux. When a unicast packet arrives at a host, IP must determine whether the packet is locally destined. If the IP stack is implemented with a weak host model, it accepts any locally destined packet regardless of the network interface on which the packet was received. If the IP stack is implemented with a strong host model, it only accepts locally destined packets if the destination IP address in the packet matches an IP address assigned to the network interface on which the packet was received.
A UDP Helper Address is a special router configuration used to forward broadcast network traffic from a client machine on one subnet to a server in another subnet.
The gateway address is a router interface connected to the local network that sends packets out of the local network. The gateway has a physical and a logical address.
A network host is a computer or other device connected to a computer network. A host may work as a server offering information resources, services, and applications to users or other hosts on the network. Hosts are assigned at least one network address.
A network socket is a software structure within a network node of a computer network that serves as an endpoint for sending and receiving data across the network. The structure and properties of a socket are defined by an application programming interface (API) for the networking architecture. Sockets are created only during the lifetime of a process of an application running in the node.
A rogue DHCP server is a DHCP server on a network which is not under the administrative control of the network staff. It is a network device such as a modem or a router connected to the network by a user who may be either unaware of the consequences of their actions or may be knowingly using it for network attacks such as man in the middle. Some kind of computer viruses or malicious software have been found to set up a rogue DHCP, especially for those classified in the category.
In computing, Microsoft's Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 introduced in 2007/2008 a new networking stack named Next Generation TCP/IP stack, to improve on the previous stack in several ways. The stack includes native implementation of IPv6, as well as a complete overhaul of IPv4. The new TCP/IP stack uses a new method to store configuration settings that enables more dynamic control and does not require a computer restart after a change in settings. The new stack, implemented as a dual-stack model, depends on a strong host-model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that one can dynamically insert and remove.

In computing, route is a command used to view and manipulate the IP routing table in Unix-like and Microsoft Windows operating systems and also in IBM OS/2 and ReactOS. Manual manipulation of the routing table is characteristic of static routing.





