
Alabama is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama is the 30th largest by area and the 24th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states.

Scouting in Alabama has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live.
Alabama has played a central role in the development of both blues and country music. Appalachian folk music, fiddle music, gospel, spirituals, and polka have had local scenes in parts of Alabama. The Tuskegee Institute's School of Music, especially the Tuskegee Choir, is an internationally renowned institution. There are three major modern orchestras, the Mobile Symphony, the Alabama Symphony Orchestra and the Huntsville Symphony Orchestra; the last is the oldest continuously operating professional orchestra in the state, giving its first performance in 1955.

The Alabama–Auburn football rivalry, better known as the Iron Bowl, is an American college football rivalry game between the University of Alabama Crimson Tide and the Auburn University Tigers, both charter members of the Southeastern Conference (SEC) and both teams are located in the state of Alabama. The series is considered one of the most important football rivalries in American sports. The rivalry, which started in 1893, was played for many years at Legion Field in Birmingham, Alabama. In the early 20th Century, Birmingham was the leading industrial city of the South, rivaling Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania in the production of pig iron, coke, coal and the manufacture of steel. Thus, the term "Iron Bowl" came to represent the rivalry. Auburn Coach Ralph "Shug" Jordan is credited with actually coining it—when asked by reporters in 1964 how he would deal with the disappointment of not taking his team to a bowl game, he responded, "We've got our bowl game. We have it every year. It's the Iron Bowl in Birmingham."

The 2002 Alabama gubernatorial election was held on November 5. With 669,105 votes or 48.95%, incumbent Democrat Don Siegelman lost re-election to Republican Bob Riley, a margin of 3,120 votes or 0.22%. The close and controversial election was marked by high turnout. This was the third consecutive Alabama gubernatorial election where the incumbent was defeated. Riley was sworn in on January 20, 2003, marking what is to date the last time the Alabama Governor’s office changed partisan control.
Alabama's 7th congressional district is a United States congressional district in Alabama that elects a representative to the United States House of Representatives. The district encompasses Choctaw, Dallas, Greene, Hale, Lowndes, Marengo, Pickens, Perry, Sumter and Wilcox counties, and portions of Clarke, Jefferson, Montgomery and Tuscaloosa counties. The district encompasses portions of the Birmingham, Montgomery and Tuscaloosa/Northport urban areas. The largest city entirely within the district is Selma.
The 1893 Alabama Crimson White football team represented the University of Alabama in the 1893 college football season. The team was led by head coach Eli Abbott and played their home games at Lakeview Park in Birmingham and The Quad in Tuscaloosa, Alabama. In what was the second season of Alabama football, the team finished with a record of zero wins and four losses (0–4).
The 1902 Alabama Crimson White football team represented the University of Alabama in the 1902 college football season. The team was led by head coach Eli Abbott, in his only season of his second stint, and played their home games at The Quad in Tuscaloosa and at West End Park in Birmingham, Alabama. James O. Heyworth served as a co-head coach with Abbott for the season. In what was the tenth season of Alabama football, the team finished with a record of four wins and four losses.
The 1907 Alabama Crimson Tide football team represented the University of Alabama in the 1907 Southern Intercollegiate Athletic Association football season. It was the Crimson Tide's 15th overall and 12th season as a member of the Southern Intercollegiate Athletic Association (SIAA). The team was led by head coach J. W. H. Pollard, in his second year, and played their home games at the University of Alabama Quad in Tuscaloosa, the Birmingham Fairgrounds in Birmingham, Highland Park in Montgomery and at Monroe Park in Mobile, Alabama. They finished the season with a record of five wins, one loss and two ties.
The Alabama Independent School Association is an organization of private schools in Alabama, formed in 1966 as the Alabama Private School Association. Originally a group of eight segregation academies, the membership grew to 60 by the 1971–72 school year. In 1990, the group voted to change its name to the Alabama Independent School Association. In 2008, an all-black school, Restoration Academy joined the AISA with no serious incidents. Today, the AISA serves 70 member schools. Most member schools are located in the state of Alabama, but one member school is located in Meridian, MS and one affiliate member is located in Smyrna, TN
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Mobile, Alabama, USA.

Alabama Heritage is a nonprofit educational quarterly history magazine first published during the summer of 1986. It is published by the University of Alabama, the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and the Alabama Department of Archives and History. The magazine was conceived with a broad conception of "heritage," incorporating more than traditional history. Issues include articles about archaeology, architecture, anthropology, religion, folk arts, literature, and music. Alabama Heritage, through support from Blue Cross and Blue Shield, is available in every school in the state of Alabama.

John Harold Merrill is an American politician who served as the 53rd secretary of state of Alabama from 2015 to 2023. He served in the Alabama House of Representatives from 2010 to 2014. Merrill is a member of the Republican Party.

The 2018 Alabama gubernatorial election took place on November 6, 2018, to elect the governor of Alabama. Incumbent Governor Kay Ivey (R), who took office on April 10, 2017, upon the resignation of Robert Bentley (R) ran for election to a full term and won over Tuscaloosa mayor Walt Maddox. Ivey was sworn in for her first full term on January 14, 2019. This was the first time since 1966 that a woman was elected Governor of Alabama.
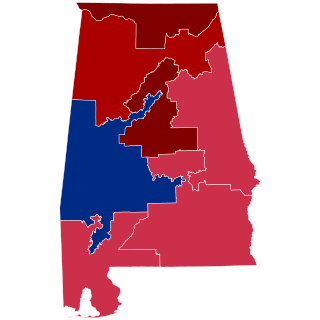
The 2020 United States House of Representatives elections in Alabama were held on November 3, 2020, to elect the seven U.S. representatives from the state of Alabama, one from each of the state's seven congressional districts. The elections coincided with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the House of Representatives, elections to the United States Senate, and various state and local elections.

Early women's suffrage work in Alabama started in the 1860s. Priscilla Holmes Drake was the driving force behind suffrage work until the 1890s. Several suffrage groups were formed, including a state suffrage group, the Alabama Woman Suffrage Organization (AWSO). The Alabama Constitution had a convention in 1901 and suffragists spoke and lobbied for women's rights provisions. However, the final constitution continued to exclude women. Women's suffrage efforts were mainly dormant until the 1910s when new suffrage groups were formed. Suffragists in Alabama worked to get a state amendment ratified and when this failed, got behind the push for a federal amendment. Alabama did not ratify the Nineteenth Amendment until 1953. For many years, both white women and African American women were disenfranchised by poll taxes. Black women had other barriers to voting including literacy tests and intimidation. Black women would not be able to fully access their right to vote until the passage of the Voting Rights Act of 1965.









