| Elections in Alabama |
|---|
 |
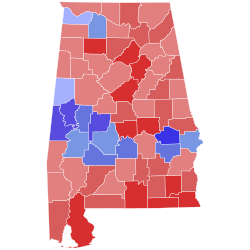
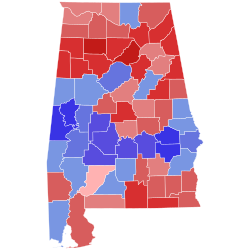
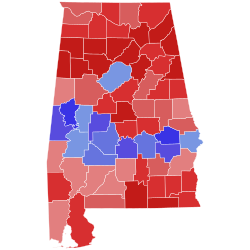
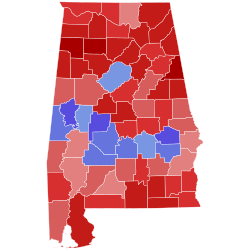
United States Senate elections in Alabama occur when voters in the U.S. state of Alabama select an individual to represent the state in the United States Senate in either of the state's two seats allotted by the Constitution. Regularly scheduled general elections occur on Election Day, coinciding with various other federal, statewide, and local races.
Contents
Each state is allotted two U.S. Senators elected to staggered six-year terms, which were originally selected by the state legislature. The Senate is divided into three classes to stagger the terms of its members such that one-third of the Senate would be up for re-election every two years. Upon Alabama's admission to the Union in 1819, the state was assigned a Class 2 seat and a Class 3 seat, first elected in 1819. Since the passage of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, U.S. Senators are elected directly by the voters of each state. Special elections may be held to fill mid-term vacancies to elect an individual to serve the remainder of the unexpired term.
The list below contains results from all U.S. Senate elections held in Alabama after the passage of the Seventeenth Amendment, sorted by year. The next scheduled election for the Class 2 seat is in 2026, while the Class 3 seat will hold its next election in 2028.