The "Republican Revolution", "Revolution of '94", or "Gingrich Revolution" are political slogans that refer to the Republican Party's (GOP) success in the 1994 U.S. mid-term elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of Representatives, and a pick-up of eight seats in the Senate. It was led by Newt Gingrich.

Claude Augustus Swanson was an American lawyer and Democratic politician from Virginia. He served as U.S. Representative (1893–1906), Governor of Virginia (1906–1910), and U.S. Senator from Virginia (1910–1933), before becoming U.S. Secretary of the Navy under President Franklin D. Roosevelt from 1933 until his death. Swanson and fellow U.S. Senator Thomas Staples Martin led a Democratic political machine in Virginia for decades in the late 19th and early 20th century, which later became known as the Byrd Organization for Swanson's successor as U.S. Senator, Harry Flood Byrd.

The 72nd United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1931, to March 4, 1933, during the last two years of Herbert Hoover's presidency. The apportionment of seats in this House of Representatives was based on the 1910 United States census. The Senate had a Republican majority. The House started with a very slim Republican majority, but by the time it first met in December 1931, the Democrats had gained a majority through special elections.

The 1934 United States Senate elections were held in the middle of Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt's first term. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. During the Great Depression, voters strongly backed Roosevelt's New Deal and his allies in the Senate, with Democrats picking up a net of nine seats, giving them a supermajority. Republicans later lost three more seats due to mid-term vacancies ; however, a Democrat in Iowa died and the seat remained vacant until the next election. The Democrats entered the next election with a 70-22-2-1 majority.

The 1932 United States Senate elections coincided with Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide victory over incumbent Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.
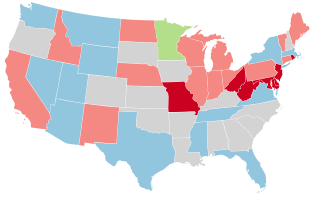
The 1928 United States Senate elections were elections that coincided with the presidential election of Republican Herbert Hoover. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The strong economy helped the Republicans to gain seven seats from the Democrats.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

Vincent Francis Harrington was a Democratic U.S. Representative from Iowa. Harrington was commissioned in the United States Army Air Forces after the Pearl Harbor attack, resigned from Congress when President Franklin D. Roosevelt disallowed members of Congress from serving in the military at the same time, and died of natural causes while on active duty in England. A Liberty Ship was named in his honor.

The 1822–23 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1822 and 1823, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1932 United States Senate election in Vermont took place on November 8, 1932. Republican Porter H. Dale successfully ran for re-election to another term in the United States Senate, defeating Democratic candidate Fred C. Martin. Dale died in October 1933, vacating the seat until a special election was held in January 1934.

The 1928 United States Senate election in Virginia was held on November 6, 1928. Incumbent Senator Claude A. Swanson was re-elected to a fourth term. This is the most recent U.S. Senate election in Virginia history when a candidate ran completely unopposed.

The 1922 United States Senate election in Virginia was held on November 7, 1922. Incumbent Senator Claude A. Swanson was re-elected to a third term after defeating Republican J. W. McGavock. Swanson and fellow Senator Carter Glass were the first U.S. Senators to be elected by popular vote following the passage of the 17th Amendment.

The 1920 United States Senate special election in Virginia was held on Tuesday November 2. Appointed Senator Carter Glass defeated Republican J. R. Pollard and was elected to finish the term of Democrat Thomas S. Martin, who died the previous year. Glass and fellow Senator Claude A. Swanson were the first U.S. senators to be elected by popular vote following the passage of the 17th Amendment.

The 1946 United States Senate elections in Ohio was held on November 5, 1946, alongside a concurrent special election to the same seat.

The 1942 United States Senate election in Minnesota took place on November 3, 1942. Incumbent Republican Joseph H. Ball, who had been temporarily appointed by Governor Harold Stassen in 1940 to fill the seat of the deceased Farmer–Labor U.S. Senator Ernest Lundeen, defeated Farmer–Labor former U.S. Senator and former Governor Elmer Benson, independent candidate Martin A. Nelson, and Democratic nominee Ed Murphy, to win election to the full six-year term beginning in January 1943. A special election held on the same date elected Republican nominee Arthur E. Nelson to serve the remainder of Lundeen's unexpired term.
A general election was held in the U.S. state of Minnesota on November 6, 2018. All of Minnesota's executive officers were up for election as well as all the seats in the Minnesota House of Representatives, several judicial seats, two United States Senate seats, Minnesota's eight seats in the United States House of Representatives, and several seats for local offices. Special elections were also held for a Minnesota Senate seat and Minnesota's Class 2 U.S. Senate seat. A primary election to nominate Republican and Democratic–Farmer–Labor (DFL) candidates and several judicial and local primary elections were held on August 14, 2018.

United States gubernatorial elections were held in 1913, in four states. Massachusetts at this time held gubernatorial elections every year. It would abandon this practice in 1920. New Jersey at this time held gubernatorial elections every 3 years. It would abandon this practice in 1949. Virginia holds its gubernatorial elections in odd numbered years, every 4 years, following the United States presidential election year.
















