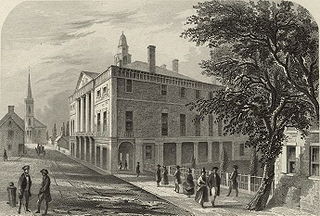Presidential elections were first held in the United States from December 15, 1788 to January 7, 1789, under the new Constitution ratified in 1788. George Washington was unanimously elected for the first of his two terms as president and John Adams became the first vice president. This was the only U.S. presidential election that spanned two calendar years without a contingent election and the first national presidential election in American history.
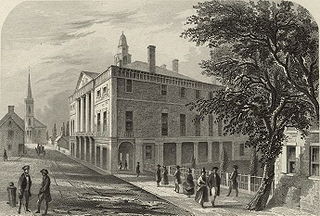
The 1st United States Congress, comprising the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in New York City and later at Congress Hall in Philadelphia. With the initial meeting of the First Congress, the United States federal government officially began operations under the new frame of government established by the 1787 Constitution. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3, of the Constitution. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority. Twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution were passed by this Congress and sent to the states for ratification; the ten ratified as additions to the Constitution on December 15, 1791, are collectively known as the Bill of Rights, with an additional amendment ratified more than two centuries later to become the Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution.

The 1920 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 67th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 2, 1920, while Maine held its on September 13. They coincided with the election of President Warren G. Harding, the first time that women in all states were allowed to vote in federal elections after the passage of the 19th Amendment.

1914 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 64th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1914, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They were held in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's first term.
The 1906 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1906, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's second term. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 60th United States Congress.

The 1904 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1904, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election to a full term of President Theodore Roosevelt. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 59th United States Congress.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 31 states for all 234 seats between August 4, 1854, and November 6, 1855, during President Franklin Pierce's term. Each state legislature separately set a date to elect representatives to the House of Representatives before the 34th Congress convened its first session on December 3, 1855.
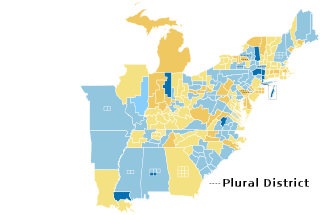
The 1840–41 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 6, 1840, and November 2, 1841. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, before or after the first session of the 27th United States Congress convened on May 31, 1841. Elections were held for all 242 seats, representing 26 states.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1794–95 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 25, 1794, and September 5, 1795 (Kentucky). Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 4th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1795. They were held during President George Washington's second term. Elections were held for all 105 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1792–93 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 27, 1792, and September 6, 1793. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 3rd United States Congress convened on December 2, 1793. With the addition of the new state of Kentucky's representatives, and the congressional reapportionment based on the 1790 United States census, the size of the House increased to 105 seats.

The 1788–89 United States House of Representatives elections were the first U.S. House of Representatives elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. Each state set its own date for its congressional elections, ranging from November 24, 1788, to March 5, 1789, before or after the first session of the 1st United States Congress convened on March 4, 1789. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States.

The 1870–71 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1870 and 1871, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1864–65 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They occurred during the American Civil War and Abraham Lincoln's re-election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1864 and 1865, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The United States elections of 1788–1789 were the first federal elections in the United States following the ratification of the United States Constitution in 1788. In the elections, George Washington was elected as the first president and the members of the 1st United States Congress were selected.

The 1862 United States elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Abraham Lincoln's first term, during the Third Party System and the Civil War. Members of the 38th United States Congress were chosen in this election. West Virginia and Nevada joined the union during the 38th Congress, but several states were in rebellion, reducing the size of both chambers of Congress. The Republican Party kept control of Congress, although it was reduced to a plurality in the House.

The 1788–89 United States presidential election in Virginia took place on January 7, 1789, as part of the 1788–1789 United States presidential election to elect the first President. Voters chose 12 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for President and Vice President. However, one elector did not vote and another elector was not chosen because an election district failed to submit returns, resulting in only 10 electoral votes being submitted.