Since Montana became a U.S. state in 1889, it has sent congressional delegations to the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. Each state elects two senators to serve for six years. Before the Seventeenth Amendment took effect in 1913, senators were elected by the Montana State Legislature. Members of the House of Representatives are elected to two-year terms, one from Montana's at-large congressional district. Before becoming a state, the Territory of Montana elected a non-voting delegate at-large to Congress from 1864 to 1889.
The 1816–17 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 30, 1816 and August 14, 1817. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 15th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1817. The size of the House increased to 184 after Indiana and Mississippi achieved statehood.
The 1814–15 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1814 and August 10, 1815. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 14th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1815. They occurred during President James Madison's second term. Elections were held for all 182 seats, representing 18 states.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812 and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.
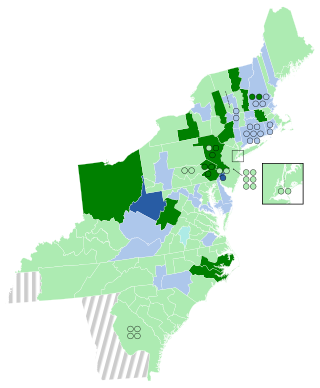
The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810 and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
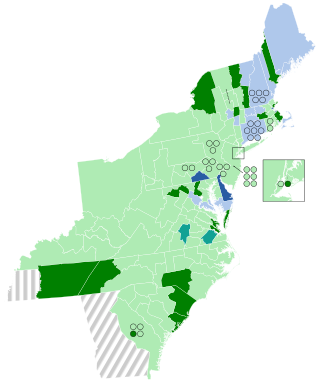
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800 and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 105 seats, representing 15 states.

The 1798–99 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1798 in New York and August 1, 1799 in Tennessee. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, with some after the official start of the 6th United States Congress on March 4, 1799, but before the start of the first session of this Congress in Philadelphia on December 2, 1799. These elections were held during President John Adams term. It was the last congressional session before the move to the new capital at Washington, D.C. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 16 states.

The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The number of elections in Alaska varies by year, but typically municipal elections occur every year, plus primary and general elections for federal and state offices occur during even-numbered years. Alaska has a gubernatorial election every four years. Members of the state's United States congressional delegation run for election or re-election at the times set out in the United States Constitution. Primary elections assist in choosing political parties' nominees for various positions. On a regional basis, elections also cover municipal issues. In addition, a special election can occur at any time.

The United States House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together, they comprise the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
This is a complete list of current members of the United States House of Representatives based on seniority. For the most part, representatives are ranked by the beginning of their terms in office. Representatives whose terms begin the same day are ranked alphabetically by last name.

This is a list of past elections in the U.S. state of Tennessee. Tennessee's politics are currently dominated by the Republican Party. Republicans currently hold both of the state's U.S. Senate seats, a majority of Congressional seats, and the state legislature. Democratic strength is largely concentrated in Nashville, Memphis, and parts of Knoxville, Chattanooga, and Clarksville. Several sunburn areas of Nashville and Memphis also contain significant Democratic minorities. Tennessee is one of thirteen states which holds its presidential primaries on Super Tuesday. Tennessee does not require voters to declare a party affiliation when registering. The state is one of eight states which require voters to present a form of photo identification.

This is a list of elections in the U.S. state of Nevada. Nevada is a swing state in state and federal elections, with margins that typically are under five percent. Unique to the state is the "None of These Candidates" voting option for all statewide and presidential and vice-presidential election ballots. This option is listed along with the names of individuals running for the position and is often described as "none of the above". The option first appeared on the Nevada ballot in 1975.












