
1916 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 65th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1916, while Maine held theirs on September 11. They coincided with the re-election of President Woodrow Wilson.
The 1908 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1908, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the 1908 United States presidential election, which William Howard Taft won. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to serve in the 61st United States Congress.
The 1906 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1906, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's second term. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 60th United States Congress.

The 1904 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1904, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election to a full term of President Theodore Roosevelt. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 59th United States Congress.
The 1902 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1902, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They occurred in the middle of President Theodore Roosevelt's first term, about a year after the assassination of William McKinley in September 1901. Elections were held for 386 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 58th United States Congress.

The 1900 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1900, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the re-election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 57th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
The 1898 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1898, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They were held during the middle of President William McKinley's first term. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 56th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1896 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 3, 1896, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of President William McKinley. Elections were held for 357 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 45 states, to serve in the 55th United States Congress. The size of the House increased by one seat after Utah gained statehood on January 4, 1896. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1894 United States House of Representatives elections were held from June 4, 1894, to November 6, 1894, with special elections throughout the year. Elections were held to elect representatives from all 356 congressional districts across each of the 44 U.S. states at the time, as well as non-voting delegates from the inhabited U.S. territories. The winners of this election served in the 54th Congress, with seats apportioned among the states based on the 1890 United States census.
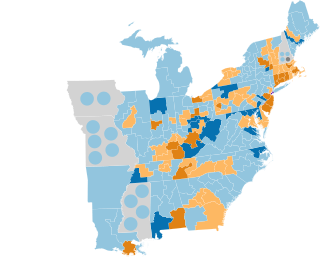
The 1844–45 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1844, and November 4, 1845. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 224 elected members representing 27 states took their seats when the first session of the 29th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1845. The new state of Florida elected its first representative during this election cycle, while one vacancy in New Hampshire's delegation remained unfilled for the duration of the 29th Congress.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 105 seats, representing 15 states.
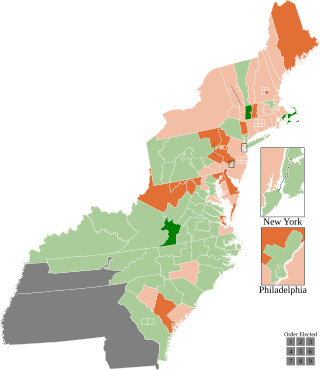
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

The 1998 United States Senate election in Maryland was held November 3, 1998. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Barbara Mikulski won re-election to a third term.

The 1992 United States Senate election in Maryland was held on November 3, 1992. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Barbara Mikulski won re-election to a second term.

The 1788–1789 United States Senate elections were the first U.S. Senate elections following the adoption of the Constitution of the United States. They coincided with the election of George Washington as the first president of the United States. As these elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures.

The 1952 United States Senate election in Maryland was held on November 4, 1952.

The 1968 United States Senate election in Maryland was held on November 5, 1968. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Daniel Brewster ran for re-election to a second term in office but was defeated by Republican U.S. Representative Charles Mathias. This is the last time a Senator from Maryland lost re-election.

The 1956 United States Senate election in Maryland was held on November 6, 1956. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator John Marshall Butler was re-elected to a second term in office, defeating Democratic businessman George P. Mahoney.
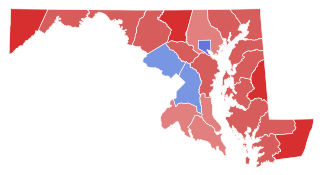
The 1970 United States Senate election in Maryland took place on November 3, 1970. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Joseph Tydings ran for re-election to a second term, but was narrowly defeated by Republican U.S. Representative J. Glenn Beall Jr.

The 1962 United States Senate election in Maryland was held on November 6, 1962. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator John Marshall Butler did not run for re-election to a third term in office. Democratic U.S. Representative Daniel Brewster won the re-election to succeed him easily over Republican U.S. Representative Edward Tylor Miller.
















