
The 1800 United States presidential election was the fourth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from October 31 to December 3, 1800. In what is sometimes called the "Revolution of 1800", the Democratic-Republican Party candidate, Vice President Thomas Jefferson, defeated the Federalist Party candidate and incumbent, President John Adams. The election was a political realignment that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican leadership. This was the first presidential election in American history to be a rematch.

The 1820 United States presidential election was the ninth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Wednesday, November 1, to Wednesday, December 6, 1820. Taking place at the height of the Era of Good Feelings, the election saw incumbent Democratic-Republican President James Monroe win re-election without a major opponent. It was the third and the most recent United States presidential election in which a presidential candidate ran effectively unopposed. As of 2024, this is the most recent presidential election where an incumbent president was re-elected who was neither a Democrat nor a Republican, before the Democratic-Republican party split into separate parties. This election and the 2012 election are the only ones in U.S. history, to date, in which a third consecutive president was elected to a second consecutive term.

The 1822–23 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 1, 1822, and August 14, 1823. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 18th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1823. They occurred during President James Monroe's second term.
The 1820–21 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 3, 1820, and August 10, 1821. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 17th United States Congress convened on December 3, 1821. They coincided with President James Monroe winning reelection unopposed.
The 1818–19 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1818 and August 12, 1819. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 16th United States Congress convened on December 6, 1819. They occurred during President James Monroe's first term. Also, newly admitted Alabama elected its first representatives in September 1819, increasing the size of the House to 186 seats.
The 1816–17 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 30, 1816 and August 14, 1817. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 15th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1817. The size of the House increased to 184 after Indiana and Mississippi achieved statehood.
The 1814–15 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1814 and August 10, 1815. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 14th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1815. They occurred during President James Madison's second term. Elections were held for all 182 seats, representing 18 states.

The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810 and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
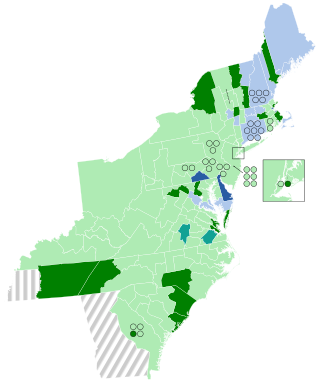
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1802–03 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1802 and December 14, 1803. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, either before or after the first session of the 8th United States Congress convened on October 17, 1803. They occurred during President Thomas Jefferson's first term in office.
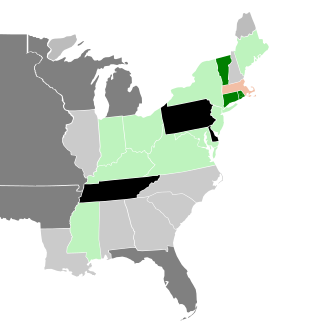
The 1820–21 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, corresponding with James Monroe's landslide re-election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1820 and 1821, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1802–03 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1802 and 1803, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1822–23 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1822 and 1823, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

Alabama elected its member August 5–6, 1821.

New Jersey elected its members November 7, 1820. There were an unusually large number of candidates, 119 candidates according to one contemporary newspaper. Some candidates ran under an "Anti-Caucus" ticket. Only 1 of the 6 six incumbents would serve in the next term, as 4 retired and 1 died after re-election.

On December 20, 1820, Jesse Slocumb (DR) of North Carolina's 4th district died. A special election was held to fill the resulting vacancy

John Condit (Democratic-Republican) of New Jersey's at-large congressional district resigned to become assistant collector of the Port of New York.

Rhode Island elected its members August 29, 1820.














