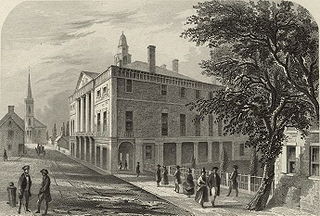The Seventeenth Amendment to the United States Constitution established the direct election of United States senators in each state. The amendment supersedes Article I, Section 3, Clauses 1 and 2 of the Constitution, under which senators were elected by state legislatures. It also alters the procedure for filling vacancies in the Senate, allowing for state legislatures to permit their governors to make temporary appointments until a special election can be held.

The Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution extends the right to participate in presidential elections to the District of Columbia. The amendment grants to the district electors in the Electoral College, as though it were a state, though the district can never have more electors than the least-populous state. How the electors are appointed is to be determined by Congress. The Twenty-third Amendment was proposed by the 86th Congress on June 16, 1960; it was ratified by the requisite number of states on March 29, 1961.
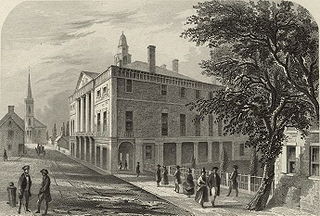
The 1st United States Congress, comprising the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives, met from March 4, 1789, to March 4, 1791, during the first two years of George Washington's presidency, first at Federal Hall in New York City and later at Congress Hall in Philadelphia. With the initial meeting of the First Congress, the United States federal government officially began operations under the new frame of government established by the 1787 Constitution. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the provisions of Article I, Section 2, Clause 3, of the Constitution. Both chambers had a Pro-Administration majority. Twelve articles of amendment to the Constitution were passed by this Congress and sent to the states for ratification; the ten ratified as additions to the Constitution on December 15, 1791, are collectively known as the Bill of Rights, with an additional amendment ratified more than two centuries later to become the Twenty-seventh Amendment to the United States Constitution.
The 100 seats in the United States Senate are divided into three classes for the purpose of determining which seats will be up for election in any two-year cycle, with only one class being up for election at a time. With senators being elected to fixed terms of six years, the classes allow about a third of the seats to be up for election in any presidential or midterm election year instead of having all 100 be up for election at the same time every six years. The seats are also divided in such a way that any given state's two senators are in different classes so that each seat's term ends in different years. Class 1 and class 2 consist of 33 seats each, while class 3 consists of 34 seats. Elections for class 1 seats took place in 2024, and elections for classes 2 and 3 will take place in 2026 and 2028, respectively.

The Vermont General Assembly is the legislative body of the state of Vermont, in the United States. The Legislature is formally known as the "General Assembly", but the style of "Legislature" is commonly used, including by the body itself. The General Assembly is a bicameral legislature, consisting of the 150-member Vermont House of Representatives and the 30-member Vermont Senate. Members of the House are elected by single and two-member districts. 68 districts choose one member, and 41 choose two, with the term of service being two years. The Senate includes 30 Senators, elected by seven single-member and nine multi-member districts with two or three members each. It is the only state legislative body in the United States in which a third party has had continuous representation and been consecutively elected alongside Democrats and Republicans.
Since Arkansas became a U.S. state in 1836, it has sent congressional delegations to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives, beginning with the 25th United States Congress in 1837. Before becoming a state, the Arkansas Territory elected a non-voting delegate at-large to Congress, beginning with the 16th United States Congress in 1819. Each state elects two senators to serve for six years in general elections, with their re-election staggered. Prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were elected by the Arkansas General Assembly. Each state elects varying numbers of members of the House, depending on population, to two-year terms.
Elections in the United States are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages; as well as for special districts and school districts which may transcend county and municipal boundaries.

Midterm elections in the United States are the general elections that are held near the midpoint of a president's four-year term of office, on Election Day on the Tuesday after the first Monday in November. Federal offices that are up for election during the midterms include all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives, and 33 or 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate.

The Florida Senate is the upper house of the Florida Legislature, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Florida, the Florida House of Representatives being the lower house. Article III, Section 1 of the Constitution of Florida, adopted in 1968, defines the role of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted. The Senate is composed of 40 members, each elected from a single-member district with a population of approximately 540,000 residents. The Senate Chamber is located in the State Capitol building.

An off-year election in the United States typically refers to a general election held in an odd-numbered year when neither a presidential election nor a midterm election takes place. At times, the term "off-year" may also be used to refer to midterm election years, while the term "off-cycle" can also refer to any election held on another date than Election Day of an even-numbered year.

Elections in California are held to fill various local, state and federal seats. In California, regular elections are held every even year ; however, some seats have terms of office that are longer than two years, so not every seat is on the ballot in every election. Special elections may be held to fill vacancies at other points in time. Recall elections can also be held. Additionally, statewide initiatives, legislative referrals and referendums may be on the ballot.

Various kinds of elections in Connecticut occurs annually in each of the state's cities and towns, the exact type of which is dependent on the year. Elections for federal and statewide offices occur in even-numbered years, while municipal elections occur in odd-numbered ones. The office of the Connecticut Secretary of State oversees the election process, including voting and vote counting. In a 2020 study, Connecticut was ranked as the 20th easiest state for citizens to vote in.

The 1900–01 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with President William McKinley's re-election as well as the 1900 House of Representatives elections. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1900 and 1901, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1884–85 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with the presidential election of 1884. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1884 and 1885, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1888–89 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with Benjamin Harrison's victory over incumbent President Grover Cleveland. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1888 and 1889, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1792–93 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states, coinciding with President George Washington's unanimous re-election. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1792 and 1793, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the ten senators in Class 2.

Some type of election in Idaho occurs annually in each of the state's cities and towns, the exact type of which is dependent on the year. Elections for federal and statewide offices occur in even-numbered years, while municipal elections occur in odd-numbered years.

Kentucky state elections in 2018 were held on Tuesday, November 6, 2018, with the primary elections being held on May 22, 2018. These midterm elections occurred during the presidency of Republican Donald Trump and the governorship of Republican Matt Bevin, alongside other elections in the United States. All six of Kentucky's seats in the United States House of Representatives, nineteen of the 38 seats in the Kentucky State Senate, all 100 seats in the Kentucky House of Representatives, and one of the seven seats on the Kentucky Supreme Court were contested. Numerous county and local elections were also contested within the state.