Related Research Articles

Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.

Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and the rectum.

Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine (colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
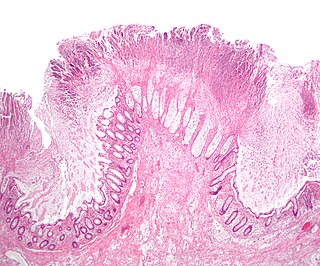
Toxic megacolon is an acute form of colonic distension. It is characterized by a very dilated colon (megacolon), accompanied by abdominal distension (bloating), and sometimes fever, abdominal pain, or shock.
In medicine, the ileal pouch–anal anastomosis (IPAA), also known as restorative proctocolectomy (RPC), ileal-anal reservoir (IAR), an ileo-anal pouch, ileal-anal pullthrough, or sometimes referred to as a J-pouch, S-pouch, W-pouch, or a pelvic pouch, is an anastomosis of a reservoir pouch made from ileum to the anus, bypassing the former site of the colon in cases where the colon and rectum have been removed. The pouch retains and restores functionality of the anus, with stools passed under voluntary control of the person, preventing fecal incontinence and serving as an alternative to a total proctocolectomy with ileostomy.
Leukapheresis is a laboratory procedure in which white blood cells are separated from a sample of blood. It is a specific type of apheresis, the more general term for separating out one particular constituent of blood and returning the remainder to the circulation.

Megacolon is an abnormal dilation of the colon. This leads to hypertrophy of the colon. The dilation is often accompanied by a paralysis of the peristaltic movements of the bowel. In more extreme cases, the feces consolidate into hard masses inside the colon, called fecalomas, which can require surgery to be removed.
Pouchitis is an umbrella term for inflammation of the ileal pouch, an artificial rectum surgically created out of ileum in patients who have undergone a proctocolectomy or total colectomy. The ileal pouch-anal anastomosis is created in the management of patients with ulcerative colitis, indeterminate colitis, familial adenomatous polyposis, cancer, or rarely, other colitides.

Neutropenic enterocolitis is inflammation of the cecum that may be associated with infection. It is particularly associated with neutropenia, a low level of neutrophil granulocytes in the blood.
Management of ulcerative colitis involves first treating the acute symptoms of the disease, then maintaining remission. Ulcerative colitis is a form of colitis, a disease of the intestine, specifically the large intestine or colon, that includes characteristic ulcers, or open sores, in the colon. The main symptom of active disease is usually diarrhea mixed with blood, of gradual onset which often leads to anaemia. Ulcerative colitis is, however, a systemic disease that affects many parts of the body outside the intestine.

Pancolitis, in its most general sense, refers to inflammation of the entire colon. This can be caused by a variety of things. Pancolitis or universal colitis is frequently used in a more specific fashion to denote a very severe form of ulcerative colitis. This form of ulcerative colitis is spread throughout the entire large intestine including the right colon, the left colon, the transverse colon, descending colon, and the rectum. A diagnosis can be made using a number of techniques but the most accurate method is direct visualization via a colonoscopy. Symptoms are similar to those of ulcerative colitis but more severe and affect the entire large intestine. Patients with ulcerative colitis generally exhibit symptoms including rectal bleeding as a result of ulcers, pain in the abdominal region, inflammation in varying degrees, and diarrhea. Pancolitis patients exhibit these symptoms and may also experience fatigue, fever, and night sweats. Due to the loss of function in the large intestine patients may lose large amounts of weight from being unable to procure nutrients from food. In other cases the blood loss from ulcers can result in anemia which can be treated with iron supplements. Additionally, due to the chronic nature of most cases of pancolitis, patients have a higher chance of developing colon cancer.
Vedolizumab, sold under the brand name Entyvio, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It binds to integrin α4β7. Blocking the α4β7 integrin results in gut-selective anti-inflammatory activity.
Faecal calprotectin is a biochemical measurement of the protein calprotectin in the stool. Elevated faecal calprotectin indicates the migration of neutrophils to the intestinal mucosa, which occurs during intestinal inflammation, including inflammation caused by inflammatory bowel disease. Under a specific clinical scenario, the test may eliminate the need for invasive colonoscopy or radio-labelled white cell scanning.
Calprotectin is a complex of the mammalian proteins S100A8 and S100A9. Other names for calprotectin include MRP8-MRP14, calgranulin A and B, cystic fibrosis antigen, L1, 60BB antigen, and 27E10 antigen. The proteins exist as homodimers but preferentially exist as S100A8/A9 heterodimers or heterotetramers (calprotectin) with antimicrobial, proinflammatory and prothrombotic properties. In the presence of calcium, calprotectin is capable of sequestering the transition metals iron, manganese and zinc via chelation. This metal sequestration affords the complex antimicrobial properties. Calprotectin is the only known antimicrobial manganese sequestration protein complex. Calprotectin comprises as much as 60% of the soluble protein content of the cytosol of a neutrophil, and it is secreted by an unknown mechanism during inflammation. Faecal calprotectin has been used to detect intestinal inflammation and can serve as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel diseases. Blood based calprotectin is used in diagnostics of multiple inflammatory diseases, including autoimmune diseases, like arthritis, and severe infections including sepsis.

Alicaforsen is an antisense oligonucleotide therapeutic that targets the messenger RNA for the production of human ICAM-1 receptor and is being developed for the treatment of acute disease flares in moderate to severe Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).

Segmental colitis associated with diverticulosis (SCAD) is a condition characterized by localized inflammation in the colon, which spares the rectum and is associated with multiple sac-like protrusions or pouches in the wall of the colon (diverticulosis). Unlike diverticulitis, SCAD involves inflammation of the colon between diverticula, while sparing the diverticular orifices. SCAD may lead to abdominal pain, especially in the left lower quadrant, intermittent rectal bleeding and chronic diarrhea.
Shomron Ben-Horin is an Israeli physician, a co-founder & Chief Medical Officer of Evinature, and professor of medicine at the Tel-Aviv University.
Integrin α4β7 is an integrin heterodimer composed of CD49d (alpha-4) subunit and beta-7 subunit noncovalently linked. LPAM-1 is expressed on the cell surface of leukocytes. This receptor is involved in lymphocyte trafficking pathway to site of inflammation in intestinal tissues.
References
- ↑ "Global Medical Device Network". Archived from the original on 2014-08-15.
- ↑ Hanai H.; et al. (January 2011). "The mode of actions of the Adacolumn therapeutic leucocytapheresis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a concise review". Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 163 (1): 50–58. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04279.x. PMC 3010911 . PMID 21078086.
- ↑ Nikolaus S., Schreiber S.; et al. (April 1998). "Increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by circulating polymorphonuclear neutrophils and regulation by interleukin 10 during intestinal inflammation". Gut. 42 (4): 470–476. doi:10.1136/gut.42.4.470. PMC 1727082 . PMID 9616306.
- ↑ Muratov V.; et al. (2008). "Decreased numbers of FoxP3-positive and TLR-2-positive cells in intestinal mucosa are associated with improvement in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease following selective leukocyte apheresis". Journal of Gastroenterology. 43 (4): 277–282. doi:10.1007/s00535-007-2156-3. PMID 18458843. S2CID 23733856.
- ↑ Dignass A.; et al. (2015). "P511 Efficacy and safety of granulocyte/monocyte adsorptive apheresis in steroid-dependent Active Ulcerative Colitis with insufficient response or intolerance to immunosuppressants and/or biological therapies (the ART trial): Results at 24 and 48 weeks". ecco-ibd.eu. The European Crohn's and Colitis Organisation (ECCO).