Related Research Articles
PackBits is a fast, simple lossless compression scheme for run-length encoding of data.

In information theory, the Hamming distance between two strings or vectors of equal length is the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different. In other words, it measures the minimum number of substitutions required to change one string into the other, or equivalently, the minimum number of errors that could have transformed one string into the other. In a more general context, the Hamming distance is one of several string metrics for measuring the edit distance between two sequences. It is named after the American mathematician Richard Hamming.
Elias code or Elias gamma code is a universal code encoding positive integers developed by Peter Elias. It is used most commonly when coding integers whose upper-bound cannot be determined beforehand.
Elias δ code or Elias delta code is a universal code encoding the positive integers developed by Peter Elias.
A prefix code is a type of code system distinguished by its possession of the "prefix property", which requires that there is no whole code word in the system that is a prefix of any other code word in the system. It is trivially true for fixed-length codes, so only a point of consideration for variable-length codes.

G.711 is a narrowband audio codec originally designed for use in telephony that provides toll-quality audio at 64 kbit/s. It is an ITU-T standard (Recommendation) for audio encoding, titled Pulse code modulation (PCM) of voice frequencies released for use in 1972.
Golomb coding is a lossless data compression method using a family of data compression codes invented by Solomon W. Golomb in the 1960s. Alphabets following a geometric distribution will have a Golomb code as an optimal prefix code, making Golomb coding highly suitable for situations in which the occurrence of small values in the input stream is significantly more likely than large values.

The syntax of the C programming language is the set of rules governing writing of software in C. It is designed to allow for programs that are extremely terse, have a close relationship with the resulting object code, and yet provide relatively high-level data abstraction. C was the first widely successful high-level language for portable operating-system development.
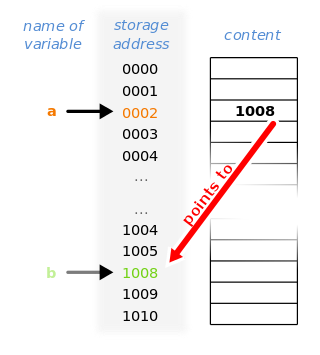
In computer science, a pointer is an object in many programming languages that stores a memory address. This can be that of another value located in computer memory, or in some cases, that of memory-mapped computer hardware. A pointer references a location in memory, and obtaining the value stored at that location is known as dereferencing the pointer. As an analogy, a page number in a book's index could be considered a pointer to the corresponding page; dereferencing such a pointer would be done by flipping to the page with the given page number and reading the text found on that page. The actual format and content of a pointer variable is dependent on the underlying computer architecture.
In computer science, a union is a value that may have any of multiple representations or formats within the same area of memory; that consists of a variable that may hold such a data structure. Some programming languages support a union type for such a data type. In other words, a union type specifies the permitted types that may be stored in its instances, e.g., float and integer. In contrast with a record, which could be defined to contain both a float and an integer; a union would hold only one at a time.
In computer programming, undefined behavior (UB) is the result of executing a program whose behavior is prescribed to be unpredictable, in the language specification of the programming language in which the source code is written. This is different from unspecified behavior, for which the language specification does not prescribe a result, and implementation-defined behavior that defers to the documentation of another component of the platform.
Elias ω coding or Elias omega coding is a universal code encoding the positive integers developed by Peter Elias. Like Elias gamma coding and Elias delta coding, it works by prefixing the positive integer with a representation of its order of magnitude in a universal code. Unlike those other two codes, however, Elias omega recursively encodes that prefix; thus, they are sometimes known as recursive Elias codes.

In data compression, a universal code for integers is a prefix code that maps the positive integers onto binary codewords, with the additional property that whatever the true probability distribution on integers, as long as the distribution is monotonic (i.e., p(i) ≥ p(i + 1) for all positive i), the expected lengths of the codewords are within a constant factor of the expected lengths that the optimal code for that probability distribution would have assigned. A universal code is asymptotically optimal if the ratio between actual and optimal expected lengths is bounded by a function of the information entropy of the code that, in addition to being bounded, approaches 1 as entropy approaches infinity.
Color BASIC is the implementation of Microsoft BASIC that is included in the ROM of the Tandy/Radio Shack TRS-80 Color Computers manufactured between 1980 and 1991. BASIC is a high level language with simple syntax that makes it easy to write simple programs. Color BASIC is interpreted, that is, decoded as it is run.
sizeof is a unary operator in the programming languages C and C++. It generates the storage size of an expression or a data type, measured in the number of char-sized units. Consequently, the construct sizeof (char) is guaranteed to be 1. The actual number of bits of type char is specified by the preprocessor macro CHAR_BIT, defined in the standard include file limits.h. On most modern computing platforms this is eight bits. The result of sizeof has an unsigned integer type that is usually denoted by size_t.
In computer science and information theory, a canonical Huffman code is a particular type of Huffman code with unique properties which allow it to be described in a very compact manner. Rather than storing the structure of the code tree explicitly, canonical Huffman codes are ordered in such a way that it suffices to only store the lengths of the codewords, which reduces the overhead of the codebook.
A negative base may be used to construct a non-standard positional numeral system. Like other place-value systems, each position holds multiples of the appropriate power of the system's base; but that base is negative—that is to say, the base b is equal to −r for some natural number r.
LEB128 or Little Endian Base 128 is a variable-length code compression used to store arbitrarily large integers in a small number of bytes. LEB128 is used in the DWARF debug file format and the WebAssembly binary encoding for all integer literals.
In the C programming language, operations can be performed on a bit level using bitwise operators.
The Hack Computer is a theoretical computer design created by Noam Nisan and Shimon Schocken and described in their book, The Elements of Computing Systems: Building a Modern Computer from First Principles. In using the term “modern”, the authors refer to a digital, binary machine that is patterned according to the von Neumann architecture model.
References
- ↑ "1968 paper by V. I. Levenshtein (in Russian)" (PDF).
- ↑ David Salomon (2007). Variable-length codes for data compression. Springer. p. 80. ISBN 978-1-84628-958-3.