Related Research Articles
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication channel or storage in a storage medium. An early example is an invention of language, which enabled a person, through speech, to communicate what they thought, saw, heard, or felt to others. But speech limits the range of communication to the distance a voice can carry and limits the audience to those present when the speech is uttered. The invention of writing, which converted spoken language into visual symbols, extended the range of communication across space and time.

The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on June 15, 1987.

In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes".
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistical redundancy. By contrast, lossy compression permits reconstruction only of an approximation of the original data, though usually with greatly improved compression rates.
Run-length encoding (RLE) is a form of lossless data compression in which runs of data are stored as a single occurrence of that data value and a count of its consecutive occurrences, rather than as the original run. As an imaginary example of the concept, when encoding an image built up from colored dots, the sequence "green green green green green green green green green" is shortened to "green x 9". This is most efficient on data that contains many such runs, for example, simple graphic images such as icons, line drawings, games, and animations. For files that do not have many runs, encoding them with RLE could increase the file size.
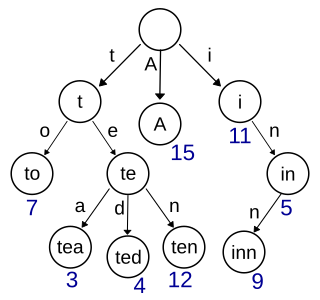
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a type of search tree: specifically, a k-ary tree data structure used for locating specific keys from within a set. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key, the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key.

zlib is a software library used for data compression as well as a data format. zlib was written by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler and is an abstraction of the DEFLATE compression algorithm used in their gzip file compression program. zlib is also a crucial component of many software platforms, including Linux, macOS, and iOS. It has also been used in gaming consoles such as the PlayStation 4, PlayStation 3, Wii U, Wii, Xbox One and Xbox 360.
The Burrows–Wheeler transform rearranges a character string into runs of similar characters. This is useful for compression, since it tends to be easy to compress a string that has runs of repeated characters by techniques such as move-to-front transform and run-length encoding. More importantly, the transformation is reversible, without needing to store any additional data except the position of the first original character. The BWT is thus a "free" method of improving the efficiency of text compression algorithms, costing only some extra computation. The Burrows–Wheeler transform is an algorithm used to prepare data for use with data compression techniques such as bzip2. It was invented by Michael Burrows and David Wheeler in 1994 while Burrows was working at DEC Systems Research Center in Palo Alto, California. It is based on a previously unpublished transformation discovered by Wheeler in 1983. The algorithm can be implemented efficiently using a suffix array thus reaching linear time complexity.
A prefix code is a type of code system distinguished by its possession of the "prefix property", which requires that there is no whole code word in the system that is a prefix of any other code word in the system. It is trivially true for fixed-length codes, so only a point of consideration for variable-length codes.

bzip2 is a free and open-source file compression program that uses the Burrows–Wheeler algorithm. It only compresses single files and is not a file archiver. It relies on separate external utilities for tasks such as handling multiple files, encryption, and archive-splitting.
Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) is a universal lossless data compression algorithm created by Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv, and Terry Welch. It was published by Welch in 1984 as an improved implementation of the LZ78 algorithm published by Lempel and Ziv in 1978. The algorithm is simple to implement and has the potential for very high throughput in hardware implementations. It is the algorithm of the Unix file compression utility compress and is used in the GIF image format.
LZ77 and LZ78 are the two lossless data compression algorithms published in papers by Abraham Lempel and Jacob Ziv in 1977 and 1978. They are also known as LZ1 and LZ2 respectively. These two algorithms form the basis for many variations including LZW, LZSS, LZMA and others. Besides their academic influence, these algorithms formed the basis of several ubiquitous compression schemes, including GIF and the DEFLATE algorithm used in PNG and ZIP.

In computer science, the Aho–Corasick algorithm is a string-searching algorithm invented by Alfred V. Aho and Margaret J. Corasick in 1975. It is a kind of dictionary-matching algorithm that locates elements of a finite set of strings within an input text. It matches all strings simultaneously. The complexity of the algorithm is linear in the length of the strings plus the length of the searched text plus the number of output matches. Note that because all matches are found, multiple matches will be returned for one string location if multiple substrings matched.
Delta encoding is a way of storing or transmitting data in the form of differences (deltas) between sequential data rather than complete files; more generally this is known as data differencing. Delta encoding is sometimes called delta compression, particularly where archival histories of changes are required.
7z is a compressed archive file format that supports several different data compression, encryption and pre-processing algorithms. The 7z format initially appeared as implemented by the 7-Zip archiver. The 7-Zip program is publicly available under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License. The LZMA SDK 4.62 was placed in the public domain in December 2008. The latest stable version of 7-Zip and LZMA SDK is version 24.08.
A dictionary coder, also sometimes known as a substitution coder, is a class of lossless data compression algorithms which operate by searching for matches between the text to be compressed and a set of strings contained in a data structure maintained by the encoder. When the encoder finds such a match, it substitutes a reference to the string's position in the data structure.
The move-to-front (MTF) transform is an encoding of data designed to improve the performance of entropy encoding techniques of compression. When efficiently implemented, it is fast enough that its benefits usually justify including it as an extra step in data compression algorithm.
PAQ is a series of lossless data compression archivers that have gone through collaborative development to top rankings on several benchmarks measuring compression ratio. Specialized versions of PAQ have won the Hutter Prize and the Calgary Challenge. PAQ is free software distributed under the GNU General Public License.

In computer science, a radix tree is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix r of the radix tree, where r = 2x for some integer x ≥ 1. Unlike regular trees, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.
Silence compression is an audio processing technique used to effectively encode silent intervals, reducing the amount of storage or bandwidth needed to transmit audio recordings.
References
- ↑ Ian H. Witten, Alistair Moffat, Timothy C. Bell. Managing Gigabytes. Second edition. Academic Press. ISBN 1-55860-570-3. Section 4.1: Accessing the lexicon, subsection Front coding, pp.159–161.