This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2008) |
This is a list of historical wars or other military conflicts outside the geographic boundaries of Japan in which Japanese soldiers participated. It is not comprehensive.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2008) |
This is a list of historical wars or other military conflicts outside the geographic boundaries of Japan in which Japanese soldiers participated. It is not comprehensive.

The history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe. See History of the Middle East and Outline of South Asian history for further details.
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided between two countries at or near the 38th parallel, North Korea and South Korea. Korea consists of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. The peninsula is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan.

The Lower Paleolithic era in the Korean Peninsula and Manchuria began roughly half a million years ago. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC, and the Neolithic period began after 6000 BC, followed by the Bronze Age by 2000 BC, and the Iron Age around 700 BC.
Sino-Japanese War most often refers to:

Goguryeo, also called Goryeo, was a Korean kingdom located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of Northeast China. At its peak of power, Goguryeo controlled most of the Korean peninsula, large parts of Manchuria and parts of eastern Mongolia and Inner Mongolia.

Baekje or Paekche, also called Nambuyeo, was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BC to 660 AD. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla.

Samhan or the Three Kingdoms of Korea refers to the three kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla. Goguryeo was later known as Goryeo, from which the modern name Korea is derived. The Three Kingdoms period is defined as being from 57 BC to 668 AD.
Geunchogo of Baekje, Chogo II of Baekje was the 13th king of Baekje, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. He reigned over the apex of Baekje's powers.

Korea's military history spans thousands of years, beginning with the ancient nation of Gojoseon and continuing into the present day with the countries of North Korea and South Korea, and is notable for its many successful triumphs over invaders. Throughout its history, Korea has boasted numerous exceptional leaders who gained outstanding victories against numerically superior enemies. Famed leaders credited with defending Korea against foreign invasions include: Eulji Mundeok of Goguryeo, who defeated Sui China during the Goguryeo–Sui War; Yeon Gaesomun of Goguryeo, who defeated Emperor Taizong of Tang China during the Goguryeo–Tang War; Gang Gam-chan of Goryeo, who defeated the Khitan Empire during the Goryeo-Khitan War; Choe Yeong and Yi Seong-gye of Goryeo, who defeated the Red Turbans, who later established Ming China, during the Red Turban Invasions; and Yi Sun-shin of Joseon, who defeated the Japanese at sea during the Imjin War. Other notable leaders include: Gwanggaeto the Great of Goguryeo, who created a great empire in Northeast Asia through conquest, and subjugated the other Korean kingdoms of Baekje, Silla and Gaya to bring about a brief unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea; Geunchogo of Baekje, who captured Pyongyang and established overseas territories to control much of the Korean peninsula and dominate the seas; Munmu and Kim Yu-sin of Silla, who united the Three Kingdoms of Korea and defeated Tang China to gain complete control of the Korean peninsula; Dae Jo-yeong, who created Balhae from Goguryeo's ashes and reconquered Goguryeo lands lost during the Goguryeo-Tang War; Jang Bogo of Later Silla, who created a maritime empire and commanded a powerful fleet; Wang Geon, who united the Later Three Kingdoms of Korea and established Goryeo as the successor to Goguryeo; and Yun Gwan of Goryeo, who defeated the Jurchens and constructed nine fortresses in Manchuria.
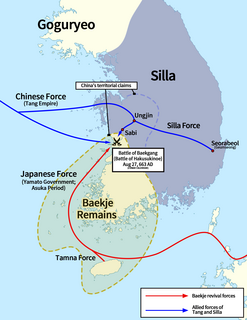
The Battle of Baekgang or Battle of Baekgang-gu, also known as Battle of Hakusukinoe in Japan, as Battle of Baijiangkou in China, was a battle between Baekje restoration forces and their ally, Yamato Japan, against the allied forces of Silla and Tang China. The battle took place in the Baengma River or Baek River, which is the lower reach of the Geum River in Jeollabuk-do province, Korea. The Silla-Tang forces won a decisive victory, compelling Yamato Japan to withdraw completely from Korean affairs and crushing the Baekje restoration movement.

For over 15 centuries, the relationship between Japan and Korea was characterized by cultural exchanges, economic trade, political contact and military confrontations, all of which underlie their relations even today. During the ancient era, exchanges of cultures and ideas between Japan and mainland Asia were common through migration via the Korean Peninsula, and diplomatic contact and trade between the two.

This is a timeline of the history of Korea. Some dates prior to the 5th century are speculative or approximate.

The Soviet–Japanese War, known in Mongolia as the Liberation War of 1945, was a military conflict within the Second World War beginning soon after midnight on 9 August 1945, with the Soviet invasion of the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo. The Soviets and Mongolians ended Japanese control of Manchukuo, Mengjiang, northern Korea, Karafuto, and the Chishima Islands. The defeat of Japan's Kwantung Army helped bring about the Japanese surrender and the termination of World War II. The Soviet entry into the war was a significant factor in the Japanese government's decision to surrender unconditionally, as it was made apparent that the Soviet Union was not willing to act as a third party in negotiating an end to hostilities on conditional terms.

The naval history of Korea dates back thousands of years since the prehistoric times when simple fishing ships were used. Military naval history dates back to the Three Kingdoms period and Unified Silla dynasties of Korea in the 7th century. Because of the constant coastal attacks by the Wa Japanese and other barbarian tribes, Korean shipbuilding excelled to counter these threats as a result. During the Unified Silla period, Jang Bogo, a merchant, rose as an admiral and created the first maritime trading within East Asian countries. During the Goryeo dynasty, sturdy wooden ships were built and used to fight pirates. Korean shipbuilding again excelled during the Imjin war, when Admiral Yi defeated the advancing Japanese fleets.

The Goguryeo–Tang War occurred from 645 to 668 and was fought between Goguryeo and the Tang dynasty. During the course of the war, the two sides allied with various other states. Goguryeo successfully repulsed the invading Tang armies during the first Tang invasions of 645–648. After conquering Baekje in 660, Tang and Silla armies invaded Goguryeo from the north and south in 661, but were forced to withdraw in 662. In 666, Yeon Gaesomun died and Goguryeo became plagued by violent dissension, numerous defections, and widespread demoralization. The Tang–Silla alliance mounted a fresh invasion in the following year, aided by the defector Yeon Namsaeng. In late 668, exhausted from numerous military attacks and suffering from internal political chaos, Goguryeo and the remnants of Baekje army succumbed to the numerically superior armies of the Tang dynasty and Silla.

The Silla–Tang War (670–676) occurred between the Korean Silla kingdom with the remnant forces from Goguryeo and Baekje, and the Chinese Tang Empire. It began in the geopolitical context immediately following the conquest of Goguryeo and Baekje by Silla and Tang. The conflict ended with a truce between Tang and Silla due to the internal political situation in both states, with the dividing territorial line at the Taedong River basin.

The territorial conquests of the Empire of Japan in the Western Pacific and East Asia regions began in 1895 with its victory over Qing China in the First Sino-Japanese War. Subsequent victories over the Russian Empire and German Empire expanded Japanese rule to Taiwan, Korea, Micronesia, southern Sakhalin, several concessions in China, and the South Manchuria Railway. In 1931, Japan invaded Manchuria, resulting in the establishment of the puppet state of Manchukuo the following year; thereafter, Japan adopted a policy of founding and supporting puppet states in conquered regions. These conquered territories became the basis for the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere in 1940.

The evacuation of Karafuto (Sakhalin) and the Kuriles refers to the events that took place during the Pacific theater of World War II as the Japanese population left these areas, to August 1945 in the northwest of the main islands of Japan.

The history of China–Japan relations share a long history dating back thousands of years through trade, cultural exchanges, friendships, and conflicts. Japan has deep historical and cultural ties with China; cultural contacts throughout its history has strongly influenced the nation – including its writing system architecture, cuisine, culture, literature, religion, philosophy, and law.

The Baekje–Tang War was fought between Baekje and the allied forces of Tang China and Silla between 660 and 663. It was in some respect a spillover of the, at the time, ongoing Goguryeo–Tang War. After numerous attacks and raids by the combined forces of Baekje and Goguryeo, King Muyeol of Silla sought help from Emperor Gaozong of Tang to aid his exhausted kingdom. Emperor Gaozong granted his request and launched the invasion of Baekje in 660. After the conquest of Baekje later that year, loyalist forces from Baekje with the aid of Yamato allies attempted to resist the occupation of their kingdom until the two allied forces were destroyed in 663.