Japan is an archipelagic country comprising a stratovolcanic archipelago over 3,000 km (1,900 mi) along the Pacific coast of East Asia. It consists of 14,125 islands. The four main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku. The other 14,120 islands are classified as "remote islands" by the Japanese government. The Ryukyu Islands and Nanpō Islands are south and east of the main islands.

Honshu, historically called Akitsushima, is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separates the Sea of Japan, which lies to its north and west, from the North Pacific Ocean to the south and east. It is the seventh-largest island in the world, and the second-most populous after the Indonesian island of Java.

The Chūbu region, Central region, or Central Japan is a region in the middle of Honshū, Japan's main island. In a wide, classical definition, it encompasses nine prefectures (ken): Aichi, Fukui, Gifu, Ishikawa, Nagano, Niigata, Shizuoka, Toyama, and Yamanashi.
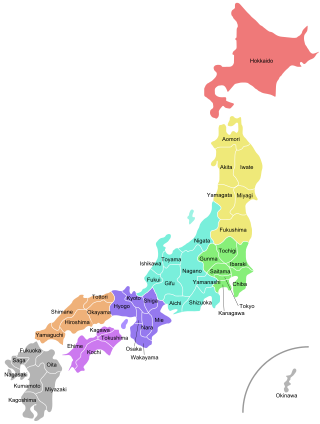
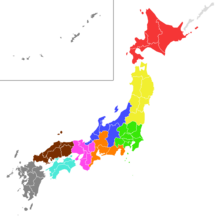
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

The dialects of the Japanese language fall into two primary clades, Eastern and Western, with the dialects of Kyushu and Hachijō Island often distinguished as additional branches, the latter perhaps the most divergent of all. The Ryukyuan languages of Okinawa Prefecture and the southern islands of Kagoshima Prefecture form a separate branch of the Japonic family, and are not Japanese dialects, although they are sometimes referred to as such.
Japan has three levels of governments: national, prefectural, and municipal. The nation is divided into 47 prefectures. Each prefecture consists of numerous municipalities, with 1,719 in total as of January 2014. There are four types of municipalities in Japan: cities, towns, villages and special wards of Tokyo. In Japanese, this system is known as shikuchōson (市区町村), where each kanji in the word represents one of the four types of municipalities. Some designated cities also have further administrative subdivisions, also known as wards. But, unlike the special wards of Tokyo, these wards are not municipalities.

The National Police Agency is the central coordinating law enforcement agency of the Japanese police system. Unlike national police in other countries, the NPA does not have any operational units of its own aside from the Imperial Guard; rather, it is responsible for supervising Japan's 47 prefectural police departments and determining their general standards and policies, though it can command police agencies under it in national emergencies or large-scale disasters. It is under the National Public Safety Commission of the Cabinet Office.

The National High School Baseball Invitational Tournament of Japan, commonly known as "Spring Kōshien" or "Senbatsu" (センバツ), is an annual high school baseball tournament.

A Roadside Station is a government-designated rest area found along roads and highways in Japan.

JR Bus collectively refers to the bus operations of Japan Railways Group companies in Japan. JR Bus is operated by eight regional companies, each owned by a JR railway company. JR Bus companies provide regional, long distance, and chartered bus services.

The list of Japanese municipal flags lists the flags of municipalities of Japan. Most municipalities of Japan have unique flags. Like prefectural flags, most of them are with a bicolor geometric highly stylized symbol (mon), often incorporating characters from Japanese writing system. However, there are three types of symbols. Therefore, the list will also discuss the emblems or logos.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Japan:

Most regions of Japan, such as Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu, belong to the temperate zone with humid subtropical climate characterized by four distinct seasons. However, its climate varies from cold humid continental climate in the north such as northern Hokkaido, to warm tropical rainforest climate in the south such as the Yaeyama Islands and Minami-Tori-shima.
The Japan Institute of Architects is a voluntary organization for architects in Japan, and an affiliated organization of the Union Internationale des Architectes (UIA). The institution was founded in May 1987 and includes round about 4,100 members today.

The District Meteorological Observatory, abbreviated to DMO, is a type of Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) weather station and a part of a local government. There are five District Meteorological Observatories in Japan. They are responsible for regional observation of the atmosphere, earthquakes, volcanos, and gathering data to make public service announcements and provide warnings in the event of a natural disaster. They also supervise Local Meteorological Observatories and other weather stations within each district area.
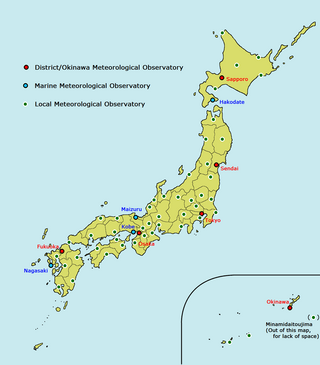
The Local Meteorological Observatory, abbreviated to the LMO, is a type of JMA weather station and a part of its local offices. JMA set up five LMOs in Hokkaido, three in Okinawa and one in another each prefecture which has neither District Meteorological Observatory nor Marine Observatory; thus Local Meteorological Observatories count 50 in Japan. They are responsible for local weather services and some of them manage local weather stations.
The 32nd annual Japanese Regional Football League Competition took place from 22 November 2008 to 30 November 2008. It took place across the prefectures of Fukuoka, Kōchi, Tottori and Okinawa. It is the tournament which decided promotion to the Japan Football League for the 2009 season. As three teams were promoted from the Japan Football League to J. League Division 2, the top three teams in this competition were promoted: Machida Zelvia, V-Varen Nagasaki and Honda Lock.