Related Research Articles

Franklin County is a nongovernmental county located in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Massachusetts. As of the 2020 census, the population was 71,029, which makes it the least-populous county on the Massachusetts mainland, and the third-least populous county in the state. Its traditional county seat and most populous city is Greenfield. Its largest town by area is New Salem.

Hampshire County is a historical and judicial county located in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. Following the dissolution of the county government in 1999, county affairs were managed by the Hampshire Council of Governments, which itself ceased operations in 2019, due to a "fundamentally flawed, unsustainable operational model". As of the 2020 census, the population was 162,308. Its most populous municipality is Amherst, its largest town in terms of landmass is Belchertown, and its traditional county seat is Northampton. The county is named after the county Hampshire, in England.

Suffolk County is located in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 797,936, making it the fourth-most populous county in Massachusetts. The county comprises the cities of Boston, Chelsea, Revere, and Winthrop.
In the United States, a county is an administrative or political subdivision of a state that consists of a geographic region with specific boundaries and usually some level of governmental authority. The term "county" is used in 48 U.S. states, while Louisiana and Alaska have functionally equivalent subdivisions called parishes and boroughs, respectively.

Fulton County is a county located in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of 2010, the population was 20,836. The county seat is Rochester.

Stow is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The town is located 21 miles west of Boston, in the MetroWest region of Massachusetts. The population was 7,174 at the 2020 United States Census. Stow was officially incorporated in 1683 with an area of approximately 40 square miles. Over centuries it gave up land as newer, smaller towns were created, ceding land to Harvard (1732), Shirley (1765), Boxborough (1783), Hudson (1866) and Maynard (1871). Stow now has an area of 18.1 square miles (47 km2). With the exception of factories at Assabet Village and Rock Bottom, Stow was primarily sparsely settled farm and orchard land until the 1950s.
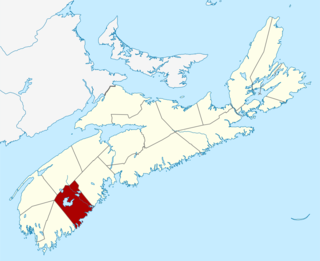
Queens County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

The demography of England has since 1801 been measured by the decennial national census, and is marked by centuries of population growth and urbanization. Due to the lack of authoritative contemporary sources, estimates of the population of England for dates prior to the first census in 1801 vary considerably.
A civil township is a widely used unit of local government in the United States that is subordinate to a county, most often in the northern and midwestern parts of the country. The term town is used in New England, New York, and Wisconsin to refer to the equivalent of the civil township in these states; Minnesota uses "town" officially but often uses it and "township" interchangeably. Specific responsibilities and the degree of autonomy vary based on each state. Civil townships are distinct from survey townships, but in states that have both, the boundaries often coincide and may completely geographically subdivide a county. The U.S. Census Bureau classifies civil townships as minor civil divisions. Currently, there are 20 states with civil townships.
During the decennial England and Wales Censuses of 1841 to 1901, the individual schedules returned from each household were transcribed and collated by the census enumerators into Census Enumerators’ Books (CEBs).
A registration county was, in Great Britain and Ireland, a statistical unit used for the registration of births, deaths and marriages and for the output of census information. In Scotland registration counties are used for land registration purposes.

Holborn was a local government district in the metropolitan area of London to the north west of the City of London from 1855 to 1900.
In the United States, an independent city is a city that is not in the territory of any county or counties and is considered a primary administrative division of its state. Independent cities are classified by the United States Census Bureau as "county equivalents" and may also have similar governmental powers to a consolidated city-county. However, in the case of a consolidated city-county, a city and a county were merged into a unified jurisdiction in which the county at least nominally exists to this day, whereas an independent city was legally separated from any county or merged with a county that simultaneously ceased to exist even in name.
John Edmund Bentley was an English sportsman who played in the first international rugby football match in 1871, representing England as a halfback.

The Grange consists of three attached, grade II listed buildings in Monmouth, Monmouthshire, Wales. It is in the historic St James Street neighbourhood, within the medieval town walls. The Grange was originally built by Captain Charles Philipps at the site of a former farm house. It was the residence of the Kane family and, later, the Windsor family. The buildings also served as a preparatory school, one of the schools of the Haberdashers' Company, until 2009. In 2011, the buildings were converted into a boarding house for students of Monmouth School, another Haberdashers' Company school.
The United Kingdom Census 1871 was a census of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland carried out on Sunday 2 April 1871. It added the categories of "lunatic" and "imbecile" to those recorded as infirm.
References
- ↑ Results of 1871 Census cited in Encyclopædia Britannica (1890), vol. 8, p.220 - Ancient county data