
Yemen is one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Near East. Its relatively fertile land and adequate rainfall in a moister climate helped sustain a stable population, a feature recognized by the ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy, who described Yemen as Eudaimon Arabia, meaning "Fertile Arabia" or "Happy Arabia". The South Arabian alphabet was developed at latest between the 12th century BC and the 6th century AD, when Yemen was successively dominated by six civilizations that controlled the lucrative spice trade: Ma'in, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, Saba, and Himyar. With the 630 AD arrival of Islam, Yemen became part of the wider Muslim world, where it has remained.

The foreign relations of Yemen are the relationships and policies that Yemen maintains with other countries. It is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Yemen participates in the nonaligned movement. The Republic of Yemen accepted responsibility for all treaties and debts of its predecessors, the YAR and the PDRY. Additionally, Yemen acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty and has stressed the need to render the Middle East region free of nuclear and other weapons of mass destruction.

Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to the north, Oman to the northeast, the Red Sea to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south, sharing maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia across the Horn of Africa. Covering roughly 455,000 square kilometres, with a coastline of approximately 2,000 kilometres, Yemen is the second largest country on the Arabian Peninsula. Sanaa is its constitutional capital and largest city. Yemen's estimated population is 34.7 million, mostly Arab Muslims. It is a member of the Arab League, the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.

Socotra or Saqatri is an island in the Indian Ocean part of Yemen. Lying between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea and near major shipping routes, Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago, which since 2013 constitutes one of Yemen's governorates.

South Yemen, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, abbreviated to Democratic Yemen, was a state that existed from 1967 to 1990 as the only communist state in the Middle East and the Arab world. It was made up of the southern and eastern governorates of the present-day Republic of Yemen, including the island of Socotra. It was bordered by North Yemen to the north-west, Saudi Arabia to the north, and Oman to the east.

South Arabia is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'Asir, which are presently in Saudi Arabia, and Dhofar of present-day Oman.
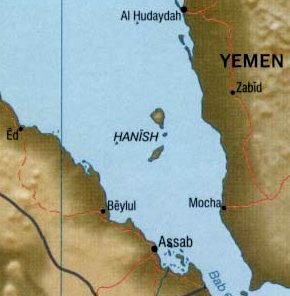
The Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that the territory belonged to Yemen.

The Yemeni unification took place on 22 May 1990, when the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen was united with the Yemen Arab Republic, forming the Republic of Yemen.

The People's Democratic Republic of Yemen became independent as the "People's Republic of Southern Yemen" in November 1967, after the British withdrawal from the Federation of South Arabia and the Protectorate of South Arabia. In May 1990, South Yemen unified with the Yemen Arab Republic to form the united Republic of Yemen. During the May–July 1994 Civil War, South Yemen seceded from the united Yemen and established the short-lived Democratic Republic of Yemen.
The People's Vanguard Party was a Ba'athist political party in Yemen. The party was established in the late 1950s. It was the Yemeni branch of the Baath Party. When the Baath Party was divided between Syrian and Iraqi factions, the Yemeni branch overwhelmingly sided with the Syrian-led Ba'ath Party. After the split, the Syrian-aligned Ba'athists 'Yemenized' their party and took the name People's Vanguard Party.

The South Yemen civil war, colloquially referred to in Yemen as the events of '86, the events of January 13, or simply as the events, was a failed coup d'etat and brief civil war which took place on January 13, 1986, in South Yemen. The civil war developed as a result of ideological differences, and later tribal tensions, between two factions of the ruling Yemeni Socialist Party (YSP), centred on Abdul Fattah Ismail's faction, at-Toghmah, and Ali Nasir Muhammad's faction, az-Zomrah, for the leadership of the YSP and South Yemen. The conflict quickly escalated into a costly civil war that lasted eleven days and resulted in thousands of casualties. Additionally, the conflict resulted in the demise of much of the Yemeni Socialist Party's most experienced socialist leadership cadre, contributing to a much weaker government and the country's eventual unification with North Yemen in 1990.
The al-Wadiah War was a military conflict which broke out on 27 November 1969 between Saudi Arabia and the People's Republic of Southern Yemen after disputes for the towns of al-Wadiah and Sharurah on the PRSY-Saudi Arabian border. The conflict ended on 6 December when Saudi forces captured al-Wadiah.

The NDF Rebellion was an uprising and civil war in the Yemen Arab Republic by the National Democratic Front, under Yahya Shami, between 1978 and 1982.
Yemeni Americans are Americans of Yemeni ancestry. According to an estimate in 2020, more than 90,000 Yemenis live in the United States.

Bangladesh–Yemen relations are the bilateral relations between Bangladesh and Yemen. In 2014 Mohammad Ashab Uddin was named Bangladeshi ambassador to Yemen.

Turkey and Yemen have very long and deep historical ties, spanned from the Ottoman Empire to the modern era. However, their relationship is mostly very complicated with both the Ottoman occupation and Yemeni rebellion against the Turks. Turkey has an embassy in Sana'a, but it closed down in 2015, after the outbreak of Yemeni Civil War. Yemen has an embassy in Ankara.

The First Yemenite War was a short military conflict between the Yemen Arab Republic and the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen.
The Military ranks of South Yemen were the military insignia used by the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen Armed Forces until its dissolution during the 1990 Yemeni unification.












