
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also known as bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is a type of chronic pain that affects the bladder and pelvic floor. Together with CP/CPPS, it makes up urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome (UCPPS). Symptoms include feeling the need to urinate right away, needing to urinate often, and pain with sex. IC/BPS is associated with depression and lower quality of life. Many of those affected also have irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia.
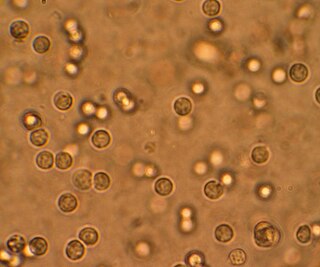
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific.

The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow muscular organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a hollow distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. The typical human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.
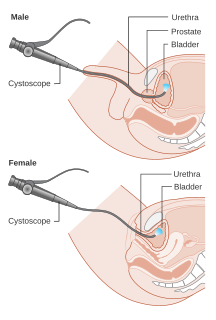
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.

Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. It can be classified according to the quantity, the anatomical origin of bleeding and the occurrence during bleeding.
Glomerulation refers to bladder hemorrhages which are thought to be associated with some types of interstitial cystitis (IC).
Dysuria refers to painful or difficult urination.

Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections.

Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications may include pus around the kidney, sepsis, or kidney failure.
Hemorrhagic cystitis or haemorrhagic cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder defined by lower urinary tract symptoms that include dysuria, hematuria, and hemorrhage. The disease can occur as a complication of cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide and radiation therapy. In addition to hemorrhagic cystitis, temporary hematuria can also be seen in bladder infection or in children as a result of viral infection.

The abdominopelvic cavity is a body cavity that consists of the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity. It contains the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, and most of the small and large intestines. It also contains the urinary bladder and internal reproductive organs. The abdominal pelvic cavity is a little pocket sac that lies way low in the base of the abdominal pelvis cavity. There's no membrane that separates out the abdominal cavity from the pelvic cavity so it is sometimes referred to as the abdominal pelvis or the peritoneal cavity. There are many diseases and disorders associated with the organs of the abdominopelvic cavity.

Michaelis–Gutmann bodies, (M-G bodies) are concentrically layered basophilic inclusions found in Hansemann cells in the urinary tract. They are 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are thought to represent remnants of phagosomes mineralized by iron and calcium deposits.

Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. Escherichia coli is the most common bacterium found. People without symptoms should generally not be tested for the condition. Differential diagnosis include contamination.

Urinary bladder disease includes urinary bladder inflammation such as cystitis, bladder rupture and bladder obstruction (tamponade). Cystitis is common, sometimes referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacteria, bladder rupture occurs when the bladder is overfilled and not emptied while bladder tamponade is a result of blood clot formation near the bladder outlet.
Urologic diseases or conditions include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, bladder control problems, and prostate problems, among others. Some urologic conditions do not affect a person for that long and some are lifetime conditions. Kidney diseases are normally investigated and treated by nephrologists, while the specialty of urology deals with problems in the other organs. Gynecologists may deal with problems of incontinence in women.
Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC) or feline interstitial cystitis or cystitis in cats, is one of the most frequently observed forms of feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD). Feline cystitis means "inflammation of the bladder in cats". The term idiopathic means unknown cause; however, certain behaviours have been known to aggravate the illness once it has been initiated. It can affect both males and females of any breed of cat. It is more commonly found in female cats; however, when males do exhibit cystitis, it is usually more dangerous.
David Paul von Hansemann was a German pathologist born in Eupen. He is remembered for his work in the field of oncology, in particular, his concept pertaining to anaplasia of cancer cells.

Cystitis glandularis is the transformation of mucosal cells lining the urinary bladder. They undergo glandular metaplasia, a process in which irritated tissues take on a different form, in this case that of a gland. The main importance is in the findings of test results, in this case histopathology. They must distinguish a benign metaplastic change from the cancerous condition urothelial cell carcinoma. It is a very common finding in bladder biopsies and cystectomies, and most often found in the trigone area. Cystitis glandularis lesions are usually present as small microscopic foci; however, occasionally it can form raised intramucosal or polypoid lesions. The cystitis glandularis lesions are within the submucosa.
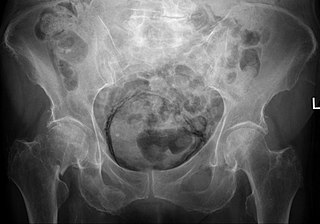
Emphysematous cystitis is a rare type of infection of the bladder wall by gas-forming bacteria or fungi. The most frequent offending organism is E. coli. Other gram negative bacteria, including Klebsiella and Proteus are also commonly isolated. Fungi, such as Candida, have also been reported as causative organisms. Citrobacter and Enterococci have also been found to cause emphysematous cystitis. Although it is a rare type of bladder infection, it is the most common type of all gas-forming bladder infections. The condition is characterized by the formation of air bubbles in and around the bladder wall. The gas found in the bladder consists of nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. The disease most commonly affects elderly diabetic and immunocompromised patients. The first case was identified in a post-mortem examination in 1888.
A urethral diverticulum is a condition where the urethra or the periurethral glands push into the connective tissue layers (fascia) that surround it.













