
The demographics of Malaysia are represented by the multiple ethnic groups that exist in the country. Malaysia's population, according to the 2010 census, is 28,334,000 including non-citizens, which makes it the 42nd most populated country in the world. Of these, 5.72 million live in East Malaysia and 22.5 million live in Peninsular Malaysia. The population distribution is uneven, with some 79% of its citizens concentrated in Peninsular Malaysia, which has an area of 131,598 square kilometres (50,810.27 sq mi), constituting under 40% of the total area of Malaysia.
Malayalam is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India and is spoken by 2.88% of Indians. Malayalam was designated a "Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé), and is spoken by 34 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Nilgiris and Kanyakumari, districts of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali Diaspora worldwide, especially in the Persian Gulf countries, due to large populations of Malayali expatriates there.

Onam is an annual Hindu harvest festival celebrated in the Indian state of Kerala. A major annual event for Keralites, it is the official festival of the state and includes a spectrum of cultural events. Drawing from Hindu mythology, Onam commemorates King Mahabali and Vamana.
The Malayali people are a Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala in India, occupying its southwestern Malabar coast. They are predominantly native speakers of the Malayalam language, one of the six Classical languages in India. The state of Kerala was created in 1956 through the States Reorganisation Act. Prior to that, since the 1800s existed the Kingdom of Cochin, the Kingdom of Travancore, Malabar District, and South Canara of the British India. The Malabar District was annexed by the British through the Third Mysore War (1790–92) from Tipu Sultan. Before that, the Malabar District was under various kingdoms including the Zamorins of Calicut, Kingdom of Tanur, Arakkal kingdom, Kolathunadu, Valluvanad, and Palakkad Rajas.

Mappila Muslim, often shortened to Mappila, formerly anglicized as Moplah/Mopla and historically known as Jonaka/Chonaka Mappila or Moors Mopulars/Mouros da Terra and Mouros Malabares, in general, is a member of the Muslim community of same name found predominantly in Kerala and Lakshadweep Islands, in southern India. Muslims of Kerala make up 26.56% of the population of the state (2011), and as a religious group they are the second largest group after Hindus (54.73%). Mappilas share the common language of Malayalam with the other religious communities of Kerala.

The culture of Kerala has developed over the past millennia, influences from other parts of India and abroad. It is defined by its antiquity and the organic continuity sustained by the Malayali people. Modern Kerala society took shape owing to migrations from different parts of India and abroad throughout Classical Antiquity.
Marakkar/Maricar/Marecar/Marikkar/Marican/Marecan (Sinhalese: Marakkala), is a South Asian Muslim community found in parts of Indian states of Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and in Sri Lanka. The Marakkars speak Malayalam in Kerala and Tamil in Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka. The community trace their ancestry to marriages between early Arab Muslim traders of the high seas and indigenous Mukkuvar coastal women. Arab traders have also married with other non-Mukkuvar South Asian women in Sri Lanka and India, but their descendants are not necessarily members of the Marakkar community.

Islam arrived in Kerala, the Malayalam-speaking region in the south-western tip of India, through Middle Eastern merchants. The Indian coast has an ancient relation with West Asia and the Middle East, even during the pre-Islamic period.
Arabi Malayalam script, also known as Ponnani script, is a writing system - a variant form of the Arabic script with special orthographic features - for writing Arabi Malayalam, a Dravidian language in southern India. Though the script originated and developed in Kerala, today it is predominantly used in Malaysia and Singapore by the migrant Muslim community.

Tamil Malaysians, also known as Malaysian Tamilar, are people of full or partial Tamil descent who were born in or immigrated to Malaysia from Tamil Nadu, India and the Tamil regions of north-east Sri Lanka. The Majority of 1.8 - 2 million people 80% of the Malaysian Indian populations in Malaysia were from Indian Tamil ethnic groups from Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka. The bulk of Tamil Malaysian migration began during the British Raj, when Britain facilitated the migration of Indian workers to work in plantations. There are also, however, some established Tamil communities spanning a millennium.
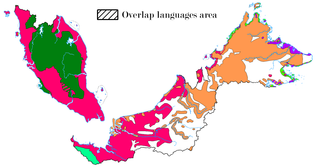
The indigenous languages of Malaysia belong to the Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian families. The national, or official, language is Malay which is the mother tongue of the majority Malay ethnic group. The main ethnic groups within Malaysia are the Malays, Chinese and Indians, with many other ethnic groups represented in smaller numbers, each with its own languages. The largest native languages spoken in East Malaysia are the Iban, Dusunic, and Kadazan languages. English is widely understood and spoken in service industries and is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary school. It is also the main language spoken in most private colleges and universities. English may take precedence over Malay in certain official contexts as provided for by the National Language Act, especially in the states of Sabah and Sarawak, where it may be the official working language.

The population of Kerala, India is a heterogenous group that comprises many ethnic groups that originated in other parts of India as well as the world, with distinctive cultural and religious traditions. While the majority of Keralites speak the Malayalam language, various ethnic groups may speak other languages as well.

Peninsular Malaysia (Malay: Semenanjung Malaysia), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, formerly known as Malaya, is the part of Malaysia which occupies the southern half of the Malay Peninsula in Southeast Asia and the nearby islands. Its area totals 132,265 km2 (51,068 sq mi), which is nearly 40% of the total area of the country; the other 60% is East Malaysia. For comparison, it is slightly larger than England (130,395 Km2). It shares a land border with Thailand to the north.
Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act. Karnataka is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the north-west, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the south-east, and Kerala to the south-west. The state covers an area of 74,122 sq mi (191,976 km2), or 5.83% of the total geographical area of India. It comprises 30 districts. Kannada is the official language of Karnataka and is spoken by 72% of the population. Various ethnic groups with origins in other parts of India have unique customs and use languages at home other than Kannada, adding to the cultural diversity of the state. Other ethnic minorities in the state in 1991 were Urdu speakers (8%), Telugu people (6%), Tamil people (3.45%), Marathi people (3.29%), Tuluvas (3.18%),Lambani(2.1%),Hindi (1.47%), Konkani people (1.78%), Malayalis (1.69%), Kodavas (0.25%), and Gujarati people (0.10%).
The Malaysian Telugus or Telugu Malaysians, consists of people of full or partial Telugu descent who were born in or immigrated to Malaysia. Most of Malaysian Telugus today are 5th or 6th generation who migrated during the colonial period. While most of current Malaysian Telugu ancestors originated from what is now Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, substantial number of them originated from area of Orissa and Bengal state. While most Telugus come to Malaysia as labourers, some were professionals and traders who arrived as refugees. In 1930s, anti-Indian riots in Burma results in large number of ethnic Telugus fleeing from Burma either back to India, Thailand or Malaya. Another wave of Telugu migration from Burma occurs during world war two, when Japanese invaded Burma.

The Evangelical Lutheran Church in Malaysia or ELCM is one of the four Lutheran bodies in Malaysia. It currently has 21 congregations nationwide with a total of 3,650 members.

Malaysian Indians or Indian Malaysians are Malaysian citizens of Indian or South Asian ancestry. Today, they form the third-largest group in Malaysia after the Malays and the Chinese. Most are descendants of those who migrated from India to Malaysia during the British colonisation of Malaya.

Penangite Indians, also known as Chulias, are Malaysian Indians that live primarily in the state of Penang, Malaysia. Most are the descendants from those who migrated from India during the British colonisation of Malaya. However, historical sources prove that the ancient Indians arrived in Penang during the Chola dynasty. Penangite Indians forms a large percentage of the state's professional community such as business, law and medicine as well as politics, it can be proven by the appointment of Dr. P. Ramasamy as deputy chief minister of Penang. It made him the first Malaysian of Indian origin to hold the post of deputy chief minister in any state of Malaysia. In addition, first Tamil Vernacular School in Malaysia was established in Penang.
N.K Menon (1895-1979) is Malaysian politician and doctor of Indian Origin. He had serve as assemblyman for Jelutong in year 1954. He is well known for criticizing the exploitation of Indian labour by British capitalist. He also well known as the founder of Radical Party.
The Malayali Diaspora refers to Malayali who live outside their homeland of Indian states of Kerala and Union Territories of Mahé, India and Lakshadweep. They are predominantly found in Gulf, North America, Europe, Australia, Caribbean, Africa and other regions around the world.





















