
The Falkland Islands are located in the South Atlantic Ocean between 51°S and 53°S on a projection of the Patagonian Shelf, part of the South American continental shelf. In ancient geological time this shelf was part of Gondwana, and around 400 million years ago split from what is now Africa and drifted westwards from it. Today the islands are subjected to the Roaring Forties, winds that shape both their geography and climate.

Mount Usborne is a mountain on East Falkland. At 2,313 feet (705 m) above sea level, it is the highest point in the Falkland Islands.

East Falkland is the largest island of the Falklands in the South Atlantic, having an area of 6,605 km2 or 54% of the total area of the Falklands. The island consists of two main land masses, of which the more southerly is known as Lafonia; it is joined by a narrow isthmus that was the scene of the Battle of Goose Green during the Falklands War.

Weddell Island is one of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic, lying off the southwest extremity of West Falkland. It is situated 1,545 km (960 mi) west-northwest of South Georgia Island, 1,165 km (724 mi) north of Livingston Island, 606 km (377 mi) northeast of Cape Horn, 358 km (222 mi) northeast of Isla de los Estados, and 510 km (320 mi) east of the Atlantic entrance to Magellan Strait.
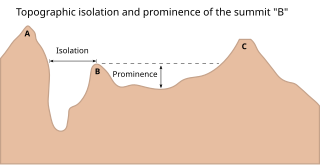
In topography, prominence measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling it but containing no higher summit within it. It is a measure of the independence of a summit. A peak's key col is a unique point on this contour line and the parent peak is some higher mountain, selected according to various criteria.

The Taconic Mountains or Taconic Range are a physiographic section of the larger New England province and part of the Appalachian Mountains, running along the eastern border of New York State and adjacent New England from northwest Connecticut to western Massachusetts, north to central western Vermont. The range includes notable summits such as Mount Equinox and Mount Greylock, the highest point in Massachusetts. Currently local residents, consistent with the prominent 19th century geologist, T. Nelson Dale, consider the Mount Greylock Massif as a subsidiary of the main Taconic Range to the west.

Mount Brandon or Brandon, at 952 metres (3,123 ft), is the 8th–highest peak in Ireland on the Arderin list, and the 9th–highest according to the Vandeleur-Lynam list. Brandon is the highest Irish mountain outside of the MacGillycuddy's Reeks range, and has the greatest prominence of any Irish peak except Carrauntoohil, Ireland's highest mountain. Brandon is named after Saint Brendan and is the end of a Christian pilgrimage trail known as Cosán na Naomh. Brandon is at the centre of the Brandon Group of mountains in the Dingle Peninsula in Kerry.

Mount Maria is a mountain of the Hornby Mountains, adjacent to Port Howard, on West Falkland island. It reaches a height of approximately 2,160 feet (660 m).

Mount Frissell, 2,454 feet (748 m), located on the border of southwest Massachusetts and northwest Connecticut, is a prominent peak of the Taconic Range.

Hill Cove is the third largest settlement on West Falkland, in the Falkland Islands, in the north-west. It is on the north coast, on the shore of Byron Sound, and overlooks Port Egmont on Saunders Island, the first British settlement in the islands. Behind the settlement is Mount Adam, which shelters it from southerly winds.
Storm Mountain is on West Falkland in the Falkland Islands. It is 1,709 feet (521 m) high. Because of its location on a narrow peninsula jutting out into the South Atlantic, between Byron Sound and King George Bay, it is highly exposed, whence its name.
Mount Moody is a hill in the Hornby Mountains on West Falkland, in the Falkland Islands. At 554 metres (1,816 ft), it is the second highest of the Hornby Mountains, after Mount Maria, and the third highest on West Falkland, after Mount Maria and Mount Adam. Like the other Hornby Mountains, Mount Moody consists of a ridge running south-south-west to north-north-west in parallel to the Falkland Sound.

Port William is a large inlet on the east coast of East Falkland island. A strait called "the Narrows" leads into Stanley Harbour.

Binn idir an dá Log at 702 metres (2,303 ft), is the 87th–highest peak in Ireland on the Arderin scale, and the 108th–highest peak on the Vandeleur-Lynam scale. Binn idir an dá Log is situated at the centre of the long north-west to south-east cental spine of the Maumturks mountain range in the Connemara National Park in Galway, Ireland. Binn idir an dá Log is the tallest mountain in the range.
Mount Edgeworth is a mountain on West Falkland, Falkland Islands. It is north east of Mount Adam and east of Hill Cove.

Kawaikini is the highest point on the Hawaiian Island of Kauai and in Kauai County and measures 5,243 feet (1,598 m) in elevation. It is the summit of the island's inactive central shield volcano, Mount Waialeale. Other peaks on Kauai include: Waialeale, Namolokama Mountain, Kalalau Lookout, Keanapuka Mountain, Haupu and Nounou.
Hills in the Puget Lowland, between the Cascades and the Olympic Mountains, including the entire Seattle metropolitan area, are generally between 350–450 feet (110–140 m) and rarely more than 500 feet (150 m) above sea level. Hills are often notable geologically and for social reasons, such as the seven hills of Seattle.

Mount Weddell is the summit of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. The mountain rises to 383 metres (1,257 ft) and is situated 8 km northeast of Race Point, 9.8 km east of Pillar Bluff, 4.35 km southwest of Weddell Settlement and 4.6 km west-northwest of Circum Point.

Circum Peak is a mountain rising to 198 m (650 ft) in the southeast part of Weddell Island in the Falkland Islands. It is located at 51°55′45″S60°55′27″W, which is 2.12 km (1.32 mi) southeast of Mount Weddell, and surmounts New Year Cove to the southeast and Gull Harbour to the northeast.

















