Mycobacterium marinum is a slow growing mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus Mycobacterium and the phylum Actinobacteria. The strain marinum was first identified by Aronson in 1926 and it is observed as a pathogenic mycobacterium. For example, tuberculosis-like infections in fish (mycobacteriosis) and skin lesions in humans.
Mycolicibacter arupensis is a slowly growing mycobacterium first isolated from soil and human sputum samples in Spain. Etymology: arupense, pertaining to the ARUP Institute for Clinical and Experimental Pathology, where the type strain was characterized.
Mycolicibacter kumamotonensis is a species of bacteria.
Etymology: kumamotonensis, pertaining to Kumamoto Prefecture in Japan, where the type strain was isolated.
Mycolicibacter nonchromogenicus is an infectious species of bacteria.
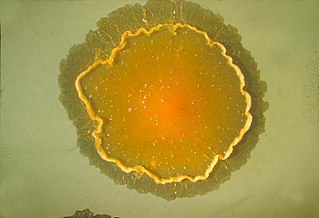
Mycolicibacter terrae is a slow-growing species of mycobacteria. It is an ungrouped member of the third Runyon. It is known to cause serious skin infections, which are "relatively resistant to antibiotic therapy".
Christensenella hongkongensis is a species of clinically relevant gram-positive coccobacilli, first isolated from patients in Hong Kong and Canada in 2006. Although the species remains relatively rare, it has a high mortality rate of up to 50%. Christensenella is thought to be broadly distributed globally, as it has been isolated from patient blood cultures around the world including Hong Kong, South Korea, New Zealand, Canada, Sweden, France and Italy. Fewer than 15 cases of C. hongkongensis have been observed worldwide.
Mycolicibacter is a genus of Gram-Positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae from the order Mycobacteriales.
Mycobacteroides is a genus of Gram-Positive rod-shaped bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae from the order Mycobacteriales.
Mycolicibacillus koreensis is a slow-growing, non-chromogenic species of Mycolicibacillus originally isolated from the sputum of a human patient. It grows at temperatures from 25–37 °C and is susceptible to quinolones. The genome of M. koreensis contains a tRNA array that contains a long non-coding RNA called GOLDD.
Mycobacteroides franklinii is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides. Most of the original strains were isolated from clinical specimens in Pennsylvania, but some have been found in conduit water in the Netherlands. In general, human M. franklinii infections present with symptoms similar to an infection with Mycobacteroides abscessus, but it can also be associated with tattoo infections. M. franklinii is also associated with outbreaks of mycobacteriosis in farmed fish. M. fanklinii is susceptible to cefoxitin and bedaquiline.
Mycobacteroides salmoniphilum is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides. It was first identified as the causative agent of mycobacteriosis in chinook salmon and steelhead trout, but has since been found to cause disease in Atlantic cod, Atlantic salmon, burbot, coho salmon, freshwater ornamental fish, and Russian sturgeon. It has also been isolated from tap water. It is not known to infect humans. M. salmoniphilum is susceptible to amikacin.
Mycobacteroides saopaulense is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota belonging to the genus Mycobacteroides that was first isolated from a human patient undergoing LASIK surgery. It has also been isolated from turtles and cows. A strain isolated from mangroves has been demonstrated to produce clavulanic acid and streptomycin. The genome of M. saopaulense contains a tRNA array that contains a long non-coding RNA called GOLDD. M. saopaulense is susceptible to amikacin, kanamycin, and clarithromycin.
Mycolicibacter algericus is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota that was first isolated from the lung lesion of a goat. It is non-pigmented and grows slowly at 25–42 °C on Löwenstein–Jensen medium. It has also been isolated from freshwater fish, fresh produce, water treatment plant sludge, and a natural cave.
Mycolicibacter engbaekii is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota. It is susceptible to amikacin, clarithromycin, ethambutol, linezolid, and rifabutin. It has also been recovered from African tuberculosis patients, water treatment plant sludge, and dairy cattle.
Mycolicibacter heraklionensis is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota. It is susceptible to clarithromycin. It is known to cause tenosynovitis in humans, but has also been isolated from sputum, urine, and a soft-tissue ankle mass.
Mycolicibacter longobardus is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota. It is susceptible to sulfamethoxazole and clarithromycin. It has been associated with cases of osteomyelitis and an epidermal inclusion cyst of the hand,
"Mycolicibacter icosiumassiliensis" is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota.
Mycolicibacter minnesotensis is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota that was first isolated from a sphagnum peat bog. It is pink-pigmented and grows at 27–34 °C. It has also been isolated from fresh produce and water treatment plant sludge.
Mycolicibacter senuensis is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota that was first isolated from the sputum of a patient with an unspecified pulmonary infection. It is non-pigmented and grows slowly at 25–37 °C. It has also been isolated from swine.
Mycolicibacter paraterrae is a species of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota that was first isolated from the sputum of a patient with an unspecified pulmonary infection. It forms orange colonies when grown in the dark and grows slowly at 25–37 °C. It has also been isolated from
