A halophile is an extremophile that thrives in high salt concentrations. In chemical terms, halophile refers to a Lewis acidic species that has some ability to extract halides from other chemical species.

The Korarchaeota is a proposed phylum within the Archaea. The name is derived from the Greek noun koros or kore, meaning young man or young woman, and the Greek adjective archaios which means ancient. They are also known as Xenarchaeota. The name is equivalent to Candidatus Korarchaeota, and they go by the name Xenarchaeota or Xenarchaea as well.

Acidobacteriota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. Its members are physiologically diverse and ubiquitous, especially in soils, but are under-represented in culture.

Ferroplasma is a genus of Archaea that belong to the family Ferroplasmaceae. Members of the Ferroplasma are typically acidophillic, pleomorphic, irregularly shaped cocci.

A brine pool, sometimes called an underwater lake, deepwater or brine lake, is a volume of brine collected in a seafloor depression. The pools are dense bodies of water that have a salinity that is three to eight times greater than the surrounding ocean. Brine pools are commonly found below polar sea ice and in the deep ocean. Those below sea ice form through a process called brine rejection. For deep-sea brine pools, salt is necessary to increase the salinity gradient. The salt can come from one of two processes: the dissolution of large salt deposits through salt tectonics or geothermally heated brine issued from tectonic spreading centers.

16S ribosomal RNA is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome. It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) intergenic spacer analysis (RISA) is a method of microbial community analysis that provides a means of comparing differing environments or treatment impacts without the bias imposed by culture- dependent approaches. RISA involves PCR amplification of a region of the rRNA gene operon between the small (16S) and large (23S) subunits called the intergenic spacer region ISR.

A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate, giving rise to their alkalinity. In addition, many soda lakes also contain high concentrations of sodium chloride and other dissolved salts, making them saline or hypersaline lakes as well. High pH and salinity often coincide, because of how soda lakes develop. The resulting hypersaline and highly alkalic soda lakes are considered some of the most extreme aquatic environments on Earth.
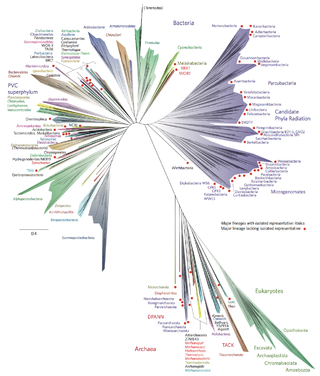
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share a pairwise sequence identity of ~75% or less with those of the members of other bacterial phyla.
Saccharibacteria, formerly known as TM7, is a major bacterial lineage. It was discovered through 16S rRNA sequencing.

The class Zetaproteobacteria is the sixth and most recently described class of the Pseudomonadota. Zetaproteobacteria can also refer to the group of organisms assigned to this class. The Zetaproteobacteria were originally represented by a single described species, Mariprofundus ferrooxydans, which is an iron-oxidizing neutrophilic chemolithoautotroph originally isolated from Kamaʻehuakanaloa Seamount in 1996 (post-eruption). Molecular cloning techniques focusing on the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene have also been used to identify a more diverse majority of the Zetaproteobacteria that have as yet been unculturable.
Community fingerprinting is a set of molecular biology techniques that can be used to quickly profile the diversity of a microbial community. Rather than directly identifying or counting individual cells in an environmental sample, these techniques show how many variants of a gene are present. In general, it is assumed that each different gene variant represents a different type of microbe. Community fingerprinting is used by microbiologists studying a variety of microbial systems to measure biodiversity or track changes in community structure over time. The method analyzes environmental samples by assaying genomic DNA. This approach offers an alternative to microbial culturing, which is important because most microbes cannot be cultured in the laboratory. Community fingerprinting does not result in identification of individual microbe species; instead, it presents an overall picture of a microbial community. These methods are now largely being replaced by high throughput sequencing, such as targeted microbiome analysis and metagenomics.
CandidatusScalindua wagneri is a Gram-negative coccoid-shaped bacterium that was first isolated from a wastewater treatment plant. This bacterium is an obligate anaerobic chemolithotroph that undergoes anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox). It can be used in the wastewater treatment industry in nitrogen reactors to remove nitrogenous wastes from wastewater without contributing to fixed nitrogen loss and greenhouse gas emission.
Sulfurimonas is a bacterial genus within the class of Campylobacterota, known for reducing nitrate, oxidizing both sulfur and hydrogen, and containing Group IV hydrogenases. This genus consists of four species: Sulfurimonas autorophica, Sulfurimonas denitrificans, Sulfurimonas gotlandica, and Sulfurimonas paralvinellae. The genus' name is derived from "sulfur" in Latin and "monas" from Greek, together meaning a “sulfur-oxidizing rod”. The size of the bacteria varies between about 1.5-2.5 μm in length and 0.5-1.0 μm in width. Members of the genus Sulfurimonas are found in a variety of different environments which include deep sea-vents, marine sediments, and terrestrial habitats. Their ability to survive in extreme conditions is attributed to multiple copies of one enzyme. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that members of the genus Sulfurimonas have limited dispersal ability and its speciation was affected by geographical isolation rather than hydrothermal composition. Deep ocean currents affect the dispersal of Sulfurimonas spp., influencing its speciation. As shown in the MLSA report of deep-sea hydrothermal vents Campylobacterota, Sulfurimonas has a higher dispersal capability compared with deep sea hydrothermal vent thermophiles, indicating allopatric speciation.
Desulfobulbus propionicus is a Gram-negative, anaerobic chemoorganotroph. Three separate strains have been identified: 1pr3T, 2pr4, and 3pr10. It is also the first pure culture example of successful disproportionation of elemental sulfur to sulfate and sulfide. Desulfobulbus propionicus has the potential to produce free energy and chemical products.

Cable bacteria are filamentous bacteria that conduct electricity across distances over 1 cm in sediment and groundwater aquifers. Cable bacteria allow for long-distance electron transport, which connects electron donors to electron acceptors, connecting previously separated oxidation and reduction reactions. Cable bacteria couple the reduction of oxygen or nitrate at the sediment's surface to the oxidation of sulfide in the deeper, anoxic, sediment layers.

Microbial oxidation of sulfur is the oxidation of sulfur by microorganisms to build their structural components. The oxidation of inorganic compounds is the strategy primarily used by chemolithotrophic microorganisms to obtain energy to survive, grow and reproduce. Some inorganic forms of reduced sulfur, mainly sulfide (H2S/HS−) and elemental sulfur (S0), can be oxidized by chemolithotrophic sulfur-oxidizing prokaryotes, usually coupled to the reduction of oxygen (O2) or nitrate (NO3−). Anaerobic sulfur oxidizers include photolithoautotrophs that obtain their energy from sunlight, hydrogen from sulfide, and carbon from carbon dioxide (CO2).
Microbial DNA barcoding is the use of DNA metabarcoding to characterize a mixture of microorganisms. DNA metabarcoding is a method of DNA barcoding that uses universal genetic markers to identify DNA of a mixture of organisms.
Modulibacteria(Moduliflexota) is a bacterial phylum formerly known as KS3B3 or GN06. It is a candidate phylum, meaning there are no cultured representatives of this group. Members of the Modulibacteria phylum are known to cause fatal filament overgrowth (bulking) in high-rate industrial anaerobic wastewater treatment bioreactors.

Zodletone Mountain is a mountain in the United States. It is located in eastern Kiowa County just west of neighboring Caddo County in the southwestern part of the state of Oklahoma. On the northern slope of the mountain is the sulfide-rich and strictly anaerobic artesian Zodletone Spring with a National Science Foundation (NSF) microbial observatory.











