The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands and the first independent Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against Spanish rule, forming a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 and declaring their independence in 1581. The seven provinces it comprised were Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland, and Zeeland. It was officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands.

The Anglo–Dutch Wars were mainly fought between the Dutch Republic and the Kingdom of England (England) in the mid-17th and late 18th century. The first three wars occurred in the second half of the 17th century over trade and overseas colonies, while the fourth conflict was fought a century later. Almost all the battles were naval engagements.
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, also known as the Treaty of London, was a treaty signed between the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 17 March 1824. The treaty was to resolve disputes arising from the execution of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814. For the Dutch, it was signed by Hendrik Fagel and Anton Reinhard Falck, and for the British, George Canning and Charles Williams-Wynn.

Japan–United Kingdom relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between Japan and the United Kingdom.
The historical ties between France and the United Kingdom, and the countries preceding them, are long and complex, including conquest, wars, and alliances at various points in history. The Roman era saw both areas largely conquered by Rome, whose fortifications largely remain in both countries to this day. The Norman conquest of England in 1066, followed by the long domination of the Plantagenet dynasty of French origin, decisively shaped the English language and led to early conflict between the two nations.

The bilateral relations between the Italian Republic and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland are warm and exceptionally strong. Both nations are members of the United Nations, NATO, Council of Europe, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, G7 and G20 major economies, World Trade Organization, and among others.
British–Portuguese relations are foreign relations between Portugal and the United Kingdom. The relationship, largely driven by the nations' common interests as maritime countries on the edge of Europe and close to larger continental neighbours, dates back to the Middle Ages in 1373 with the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. The two countries presently and have historically enjoyed a friendly and close relationship. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe and NATO. Portugal is a European Union member and the United Kingdom is a former European Union member.
Belgium–United Kingdom relations are foreign relations between Belgium and the United Kingdom. Belgium has an embassy in London and 8 honorary consulates. The United Kingdom has an embassy in Brussels.

Greek–British relations are foreign relations between Greece and the United Kingdom. Greece and the United Kingdom maintain excellent and cordial relations and consider each other an ally with the Greek Prime Minister, Kyriakos Mitsotakis, paying an official visit to London in 2021. Greece and the United Kingdom are both members of the United Nations, NATO and the Council of Europe.

British–Polish relations are the bilateral relations between the countries of United Kingdom and Poland. Exchanges between the two countries date back to medieval times, when Britain and Poland, then one of Europe's largest countries, were linked by trade and diplomacy. As a result of the 18th-century Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by its neighbours, the number of Polish immigrants to Britain increased in the aftermath of two 19th-century uprisings which forced much of Poland's social and political elite into exile. A number of Polish exiles fought in the Crimean War on the British side.

British–Romanian relations are bilateral foreign relations between United Kingdom and Romania. Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 February 1880 when the United Kingdom recognized Romania's independence. Both countries are members of NATO. The United Kingdom has an embassy in Bucharest and Romania has an embassy in London. Romania also has two consulates general in Edinburgh and Manchester. Romania also has five honorary consulates based in Leeds, Newcastle, Inverness, Liverpool and Bristol. Romania has a cultural institute in London. The United Kingdom gave full support to Romania's applications for membership in the European Union and NATO.
Albania–United Kingdom relations are the bilateral relations between Albania and the United Kingdom. Albania has an embassy in London, and the United Kingdom has an embassy in Tirana.

Czech Republic–United Kingdom relations are foreign relations between the Czech Republic and the United Kingdom. The Czech Republic has an embassy in London and four honorary consulates. The United Kingdom has an embassy in Prague.

Morocco–United Kingdom relations are the bilateral relations that exist between the Kingdom of Morocco and the United Kingdom.

Spain–United Kingdom relations, also called Spanish–British relations, are the bilateral international relations between Spain and the United Kingdom. Both countries are members of the Council of Europe and NATO. Spain is a European Union member and the United Kingdom is a former European Union member.

This timeline covers the main points of British foreign policy from 1485 to the early 21st century.
Brazil–United Kingdom relations are the diplomatic relations between Brazil and the United Kingdom. Both nations are members of the G20, United Nations and the World Trade Organization.
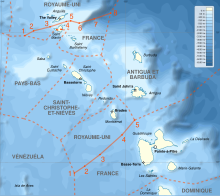
France–Netherlands relations are the interstate and bilateral relations between France and the Netherlands. The two countries notably share a border division in the Caribbean island of Saint Martin, to which the northern part of the island is a French overseas collectivity known as the Collectivity of Saint Martin, while the southern part of the island is a Dutch constituent country known as Sint Maarten. Relations between the two countries date back to the 17th and 18th centuries when a conflict led to the transformation of the Dutch Republic to the Batavian Republic and eventually the Kingdom of Holland. The two countries currently enjoy close cultural and economic relations. Both nations are members of the OECD and Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, as well as founding members of the European Union, NATO, and the United Nations.
The history of the foreign relations of the United Kingdom covers English, British, and United Kingdom's foreign policy from about 1500 to 2000. For the current situation since 2000 see foreign relations of the United Kingdom.