Blacktown is a suburb in the City of Blacktown local government area, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Blacktown is located 34 km (21 mi) west of the Sydney central business district. It is one of the most multicultural places within Greater Sydney.

Doonside is a suburb in the metropolis of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Doonside is located 40 kilometres (25 mi) west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Blacktown and is part of the Greater Western Sydney region. Featherdale Wildlife Park and the Nurragingy Nature Reserve are popular local tourist attractions.

Greater Western Sydney (GWS) is a large region of the metropolitan area of Greater Sydney, New South Wales (NSW), Australia that generally embraces the north-west, south-west, central-west, far western and the Blue Mountains sub-regions within Sydney's metropolitan area and encompasses 11 local government areas: Blacktown, Blue Mountains, Camden, Campbelltown, Cumberland, Fairfield, Hawkesbury, Liverpool, Parramatta, Penrith and Wollondilly. It includes Western Sydney, which has a number of different definitions, although the one consistently used is the region composed of ten local government authorities, most of which are members of the Western Sydney Regional Organisation of Councils (WSROC). The NSW Government's Office of Western Sydney calls the region "Greater Western Sydney".

Colebee is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Colebee is located 47 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Blacktown and is part of the Western Sydney region.

Sydney Olympic Park is a suburb of Greater Western Sydney, located 13 kilometres west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Parramatta Council. It is commonly known as Olympic Park but officially named Sydney Olympic Park. The area was part of the suburb of Lidcombe and known as "North Lidcombe", but between 1989 and 2009 was named "Homebush Bay". The names "Homebush Bay" and, sometimes, "Homebush" are still used colloquially as a metonym for Stadium Australia as well as the Olympic Park precinct as a whole, but Homebush is an older, separate suburb to the southeast, in the Municipality of Strathfield.

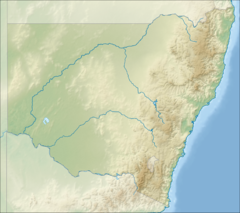
The Cumberland Plain, also known as Cumberland Basin, is a relatively flat region lying to the west of Sydney CBD in New South Wales, Australia. An IBRA biogeographic region, Cumberland Basin is the preferred physiographic and geological term for the low-lying plain of the Permian-Triassic Sydney Basin found between Sydney and the Blue Mountains, and it is a structural sub-basin of the Sydney Basin.

The Sydney Turpentine-Ironbark Forest (STIF) is a wet sclerophyll forest community of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, that is typically found in the Inner West and Northern region of Sydney. It is also among the three of these plant communities which have been classified as Endangered, under the New South Wales government's Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995, with only around 0.5% of its original pre-settlement range remaining.

Centennial Parklands is the name given to a group of three urban parklands located in the eastern suburbs of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Comprising approximately 360 hectares, the lands encompass Centennial Park, Moore Park and Queens Park. The Parklands are listed on the New South Wales Heritage Register, with various components of national, state or local heritage significance. The parks are contained within the local government areas of City of Randwick, Waverley Municipal Council, and City of Sydney.

The Auburn Botanic Gardens are a botanical garden located in Auburn, New South Wales, Australia. It was established in 1977 and covers an area of 9.7 hectares. There are two lakes, a waterfall and bridges. Duck River winds through the garden. The garden is maintained by Cumberland Council. It is open daily, and there is a small entry fee on weekends. The Japanese gardens, which have hosted couples from overseas, are one of the main attractions.

Chipping Norton Lake is a 49-hectare (120-acre) artificial lake and regional park located in the Sydney suburb of Chipping Norton, New South Wales, Australia. It is a part of the Georges River system. Chipping Norton Lake is managed by Liverpool City Council. The lake is an important recreational area for Liverpool, City of Canterbury-Bankstown and Fairfield City Council.

The Balls Head Reserve is a forested headland nature reserve situated on Balls Head in Sydney. The headland is in Port Jackson, 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) west of the Sydney Harbour Bridge, between Berrys Bay to the east and Balls Head Bay to the west. It is named after Lieutenant Henry Lidgbird Ball, a Royal Naval officer who commanded HMS Supply on the First Fleet. The park is accessed via Balls Head Drive, Waverton, New South Wales, Australia.

The Western Sydney Parklands is an urban park system and a nature reserve located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The NSW government has spent around $400 million for the park. The park is governed by the NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service and is listed under the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1974. The Parklands begin in the north in the City of Blacktown, cross the City of Fairfield, and end in the City of Liverpool.

Western Sydney Regional Park is a large urban park and a nature reserve situated in Western Sydney, Australia within the suburbs of Horsley Park and Abbotsbury. A precinct of Western Sydney Parklands, and situated within the heart of the Cumberland Plain Woodland, the regional park features several picnic areas, recreational facilities, equestrian trails, and walking paths within the Australian bush.

The Central Gardens Nature Reserve, also called Central Gardens, is a protected nature reserve and urban park located in the western suburbs of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Established in 1976, the 12-hectare (30-acre) reserve, garden and fauna and wildlife park is situated in the suburb of Merrylands and is managed by Cumberland Council. The park is regionally important and it attracts visitors outside the Cumberland local government area. The bushland contains remnants of Cumberland Plain Woodland and is approximately 3.5 hectares.

The Cumberland Plain Woodland, also known as Cumberland Plain Bushland and Western Sydney woodland, is a grassy woodland community found predominantly in Western Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, that comprises an open tree canopy, a groundcover with grasses and herbs, usually with layers of shrubs and/or small trees.

Colebee and Nurragingy Land Grant is a heritage-listed former farm at Richmond Road, Colebee, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. It is also known as Colebee and Nurragingy's Land Grant, Colebee Release Area, 773, 777 and 783 Richmond Road. The property is owned by Transport for NSW.

The Blacktown Native Institution Site is the heritage-listed site of a former residential institution for Aboriginal and Māori children in the City of Blacktown, part of the Greater Sydney metropolitan area in Australia. The site is located at Richmond Road, Oakhurst, New South Wales. It was built from 1822. The site has also been known as Parramatta Native Institute, Blacktown Institute, The Blacktown Site, Lloydhurst, BNI, Epping Estate, Epping Forest Estate and Native Institution Centre. The property was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 18 November 2011.

Prospect Nature Reserve is a nature reserve and recreational area that is situated in the western suburbs of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, which incorporates the Prospect Reservoir, and also features picnic spots, lookouts, walking tracks and BBQ areas within the Australian bush. It is located within the Blacktown City local government area, but is also close to the boundaries of Cumberland Council and the City of Fairfield.

The ecology of Sydney, located in the state of New South Wales, Australia, is diverse for its size, where it would mainly feature biomes such as grassy woodlands or savannas and some sclerophyll forests, with some pockets of mallee shrublands, riparian forests, heathlands, and wetlands, in addition to small temperate and subtropical rainforest fragments.
Colebee was a Boorooberongal man of the Dharug people, an Aboriginal Australian people from present-day New South Wales. Colebee and fellow Dharug man Nurragingy received land grants in recognition of their assistance in guiding British military forces in punitive expeditions against insurgent Gandangara and Darkinjung people in 1816.