
Rhynchocephalia is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose group with high morphological and ecological diversity. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved global distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria.

Youngina is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the Late Permian Beaufort Group of the Karoo Red Beds of South Africa. This, and a few related forms, make up the family Younginidae, within the order Eosuchia. Eosuchia, having become a wastebasket taxon for many probably distantly-related primitive diapsid reptiles ranging from the Late Carboniferous to the Eocene, Romer proposed that it be replaced by Younginiformes.

Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Early Triassic, reaching their broadest abundance and a global distribution during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic.

Ericiolacerta is an extinct genus of small therocephalian therapsids from the early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. Ericiolacerta, meaning "hedgehog lizard", was named by D.M.S. Watson in 1931. The species E. parva is known from the holotype specimen which consists of a nearly complete skeleton found in the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone within the Katberg Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa, and from a partial jaw found in the Lower Triassic Fremouw Formation in Antarctica. Ericiolacerta was around 20 centimetres (7.9 in) in length, with long limbs and relatively small teeth. It probably ate insects and other small invertebrates. The therocephalians – therapsids with mammal-like heads – were abundant in Permian times, but only a few made it into the Triassic. Ericiolacerta was one of those. It is possible that they gave rise to the cynodonts, the only therapsid group to survive into post-Triassic times. Cynodonts gave rise to mammals.
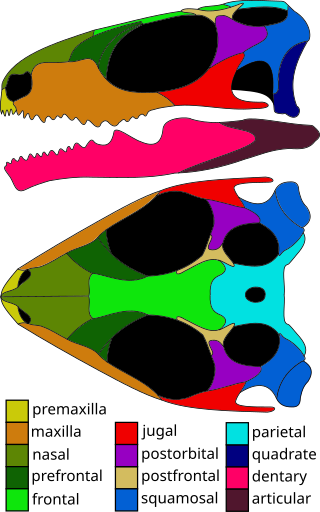
Planocephalosaurus is an extinct genus of basal rhynchocephalian. Fossils of the genus are primarily known from fissure fill deposits from the Late Triassic of southwest Britain, with fragmentary remains possibly belonging to the genus also known from the Late Triassic of Texas.

Nicrosaurus (/nɪkroʊˈsɔrəs/) is an extinct genus of phytosaur reptile existing during the Late Triassic period. Although it looked like a crocodile, it was not closely related to these creatures, instead being an example of parallel evolution. The main difference between Nicrosaurus and modern crocodiles is the position of the nostrils – Nicrosaurus's nostrils, or external nares, were placed directly in front of the forehead, whereas in crocodiles, the nostrils are positioned on the end of the snout. A 2013 study has also found that ilium of Nicrosaurus is quite distinctive from all other phytosaurs.

Dinogorgon is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name Dinogorgon is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name rubidgei is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is D. rubidgei.

Mesosuchus is an extinct genus of basal rhynchosaur from early Middle Triassic deposits of Eastern Cape, South Africa. It is known from the holotype SAM 5882, a partial skeleton, and from the paratypes SAM 6046, SAM 6536, SAM 7416 and SAM 7701 from the Aliwal North Euparkeria site. Mesosuchus is quite small, spanning around 30 cm in length. Mesosuchus was discovered and named by D. M. S. Watson in 1912.
Langobardisaurus is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph reptile, with one valid species, L. pandolfii. Its fossils have been found in Italy and Austria, and it lived during the Late Triassic period, roughly 228 to 201 million years ago. Langobardisaurus was initially described in 1994, based on fossils from the Calcare di Zorzino Formation in Northern Italy. Fossils of the genus are also known from the Forni Dolostone of Northern Italy and the Seefeld Formation of Austria.

Clevosaurus is an extinct genus of rhynchocephalian reptile from the Late Triassic and the Early Jurassic periods. Species of Clevosaurus were widespread across Pangaea, and have been found on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. Five species of Clevosaurus have been found in ancient fissure fill deposits in south-west England and Wales, alongside other sphenodontians, early mammals and dinosaurs. In regards to its Pangaean distribution, C. hadroprodon is the oldest record of a sphenodontian from Gondwana, though its affinity to Clevosaurus has been questioned.

Myosaurus is a genus of dicynodont synapsids. Myosaurus was a small, herbivorous synapsid that existed around the early Triassic period. All of the fossils found of this species were found in Antarctica and South Africa. Compared to other fossils found from species that existed during this time, the Myosaurus is not common in the fossil record. This is due to a shortage of discovered fossils that possess characteristics unique to the Myosaurus. Notably, under 130 fossil fragments have been found that have been classified as Myosauridae, and almost all have been skulls. These skulls can be classified as Myosaurus because this species, unlike other dicynodonts, do not possess tusks or postfrontal teeth. The only species identified in the family Myosauridae is the Myosaurus gracilis, or M. gracilis. It should be recognized that the Myosaurus is almost always referred to as the M. gracilis in scientific research.

Trirachodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts. Fossils have been found in the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in South Africa and the Omingonde Formation of Namibia, dating back to the Early and Middle Triassic.

Gephyrosaurus is an extinct genus of lepidosaurian reptile known from the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic of the United Kingdom. It is generally considered to be one of the most primitive members of the clade Rhynchocephalia.
Variodens is an extinct genus of trilophosaur. Fossils have been found from the Emborough Quarries in the Mendip Hills of Somerset, England. These fossils have been uncovered from a Late Triassic fissure fill within Carboniferous-age limestone. The type and only known species is V. inopinatus, named in 1957.
Theledectes is an extinct genus of theledectine procolophonid parareptile from middle Triassic deposits of Free State Province, South Africa.The type species, Theledectes perforatus, is based on the holotype BP/1/4585, a flattened skull. This skull was collected by the South African palaeontologist, James W. Kitching from Hugoskop in the Rouxville District and referred to subzone B of the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Burgersdorp Formation, Beaufort Group. The genus was first named by Sean P. Modesto and Ross J. Damiani in 2003. However, the species was initially assigned to the genus Thelegnathus by C.E. Gow in 1977, as the species Thelegnathus perforatus.
Acallosuchus is an extinct genus of reptile from the Triassic Chinle Formation of the southwestern United States. Although it was discovered in 1923, Acallosuchus was not described until 1995, when the type species A. rectori was named. The taxonomy classification of Acallosuchus is uncertain. Although it is known to be a neodiapsid reptile, it has not been assigned with confidence to any particular group of neodiapsids.

Prolacerta is a genus of archosauromorph from the lower Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. The only known species is Prolacerta broomi. Prolacerta was a small and slender reptile, with a rather long neck, low skull, and serrated teeth. It would have resembled a modern monitor lizard at a quick glance, though this is an example of convergent evolution as opposed to close affinities.

Opisthodontia is a proposed clade of sphenodontian reptiles, uniting Opisthias from the Late Jurassic-earliest Cretaceous of Europe and North America with the Eilenodontinae, a group of herbivorous sphenodontians known from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous.

Colobops is a genus of reptile from the Late Triassic of Connecticut. Only known from a tiny skull, this reptile has been interpreted to possess skull attachments for very strong jaw muscles. This may have given it a very strong bite, despite its small size. However, under some interpretations of the CT scan data, Colobops's bite force may not have been unusual compared to other reptiles. The generic name, Colobops, is a combination of κολοβός, meaning shortened, and ὤψ, meaning face. This translation, "shortened face", refers to its short and triangular skull. Colobops is known from a single species, Colobops noviportensis. The specific name, noviportensis, is a latinization of New Haven, the name of both the geological setting of its discovery as well as a nearby large city. The phylogenetic relations of Colobops are controversial. Its skull shares many features with those of the group Rhynchosauria, herbivorous archosauromorphs distantly related to crocodilians and dinosaurs. However, many of these features also resemble the skulls of the group Rhynchocephalia, an ancient order of reptiles including the modern tuatara, Sphenodon. Although rhynchosaurs and rhynchocephalians are not closely related and have many differences in the skeleton as a whole, their skulls are remarkably similar. As Colobops is only known from a skull, it is not certain which one of these groups it belonged to. Pritchard et al. (2018) interpreted it as a basal rhynchosaur, while Scheyer et al. (2020) reinterpreted it as a rhynchocephalian.
Kraterokheirodon is an extinct genus of enigmatic tetrapod, that was possibly an amniote, from the Late Triassic Chinle Formation of Arizona. The type and only species is K. colberti. Although it is known only from two large teeth, their shape is so unlike those of any other animal that Kraterokheirodon cannot definitively be classified under any known group of tetrapods. Its discovery also indicates that our understanding of Late Triassic tetrapod diversity is still incomplete, with Kraterokheirodon representing an otherwise unknown lineage of large tetrapod in western North America.



















