Boers are the descendants of the proto Afrikaans-speaking Free Burghers of the eastern Cape frontier in Southern Africa during the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. From 1652 to 1795, the Dutch East India Company controlled Dutch Cape Colony, but the United Kingdom incorporated it into the British Empire in 1806. The name of the group is derived from Trekboer then later "boer", which means "farmer" in Dutch and Afrikaans.
The written history of the Cape Colony in what is now South Africa began when Portuguese navigator Bartolomeu Dias became the first modern European to round the Cape of Good Hope in 1488. In 1497, Vasco da Gama sailed along the whole coast of South Africa on his way to India, landed at St Helena Bay for 8 days, and made a detailed description of the area. The Portuguese, attracted by the riches of Asia, made no permanent settlement at the Cape Colony. However, the Dutch East India Company (VOC) settled the area as a location where vessels could restock water and provisions.

The history of the Cape Colony from 1806 to 1870 spans the period of the history of the Cape Colony during the Cape Frontier Wars, which lasted from 1779 to 1879. The wars were fought between the European colonists and the native Xhosa who, defending their land, fought against European rule.

Khoekhoe are the traditionally nomadic pastoralist indigenous population of South Africa. They are often grouped with the hunter-gatherer San peoples. The designation "Khoekhoe" is actually a kare or praise address, not an ethnic endonym, but it has been used in the literature as an ethnic term for Khoe-speaking peoples of Southern Africa, particularly pastoralist groups, such as the Griqua, Gona, Nama, Khoemana and Damara nations. The Khoekhoe were once known as Hottentots, a term now considered offensive.

Paarl is a town with 285,574 inhabitants in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is the largest town in the Cape Winelands. Due to the growth of the Mbekweni township, it is now a de facto urban unit with Wellington. It is situated about 60 kilometres (37 mi) northeast of Cape Town in the Western Cape Province and is known for its scenic environment and viticulture and fruit-growing heritage.

The Griquas are a subgroup of mixed-race heterogeneous formerly Xiri-speaking nations in South Africa with a unique origin in the early history of the Dutch Cape Colony. Like the Boers they migrated inland from the Cape and in the 19th century established several states in what is now South Africa and Namibia. The Griqua consider themselves as being South Africa’s first multiracial nation with people descended directly from Dutch settlers in the Cape, and local peoples.

District Six is a former inner-city residential area in Cape Town, South Africa. In 1966, the apartheid government announced that the area would be razed and rebuilt as a "whites only" neighbourhood under the Group Areas Act. Over the course of a decade, over 60,000 of its inhabitants were forcibly removed and in 1970 the area was renamed Zonnebloem, a name that makes reference to an 18th century colonial farm. At the time of the proclamation, 56% of the district’s property was White-owned, 26% Coloured-owned and 18% Indian-owned. Most of the residents were Cape Coloureds and they were resettled in the Cape Flats. The vision of a new white neighbourhood was not realised and the land has mostly remained barren and unoccupied. The original area of District Six is now partly divided between the suburbs of Walmer Estate, Zonnebloem, and Lower Vrede, while the rest is generally undeveloped land.

Paradesi Jews refer to Jewish immigrants to the Indian subcontinent during the 15th and 16th centuries following the expulsion of Jews from Spain and Portugal. Paradesi means foreign in Malayalam and Tamil. These Sephardic immigrants fled persecution and death by burning in the wake of the 1492 Alhambra Decree and King Manuel's 1496 decree expelling Jews from Portugal. They are sometimes referred to as "White Jews", although that usage is generally considered pejorative or discriminatory and refers to relatively recent Jewish immigrants, predominantly Sephardim.
South African Jews, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion, form the twelfth largest Jewish community in the world, and the largest on the African continent. As of 2020, the Kaplan Centre at the University of Cape Town estimates 52,300 Jews in the country. The South African Jewish Board of Deputies estimates that the figure is closer to 75,000.

Muizenberg is a beach-side town in the Western Cape, South Africa. It is situated where the shore of the Cape Peninsula curves round to the east on the False Bay coast. It is considered to be the main surfing spot in Cape Town and is currently home to a surfing community, centered on the popular 'Surfer's Corner'.

Vredehoek is a residential suburb of Cape Town, South Africa, located at the foot of Table Mountain and Devil's Peak. It is sandwiched between the two neighbouring suburbs of Oranjezicht and Devil's Peak Estate, the latter of which is often considered a sub-suburb of Vredehoek as they both fall under the neighbourhood watch community called DPV - Devil's Peak & Vredehoek.

Melkbosstrand is a coastal town located on the South West Coast of South Africa, 30 km north of Cape Town. It forms part of the City of Cape Town Metropolitan Municipality, the municipality governing Cape Town and its greater metropolitan area.

Caledon, originally named Swartberg, is a town in the Overberg region in the Western Cape province of South Africa, located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) east of Cape Town next to mineral-rich hot springs. As of 2011 it had a population of 13,020. It is located in, and the seat of, the Theewaterskloof Local Municipality.

The Khoikhoi–Dutch Wars refers to a series of armed conflicts that took place in the latter half of the 17th century in what was then known as the Cape of Good Hope, in the area of present-day Cape Town, South Africa, fought primarily between Dutch colonisers, who came mostly from the Dutch Republic and the local African people, the indigenous Khoikhoi.

Gardens is an affluent inner-city suburb of Cape Town located just to the south of the city centre located in the higher elevations of the "City Bowl" and directly beneath Table Mountain and Lion's Head. It is home to several national museums such as Iziko South African National Gallery and the Iziko South African Museum. The University of Cape Town also houses its Fine Arts department in the suburb, at Michaelis School of Fine Art. Company's Garden, South Africa's oldest garden, a public park and heritage site is a focal point of the suburb. The area is also home to the oldest synagogue in Southern Africa, the Old Shul and its successor, the Gardens Shul, "The Mother Synagogue of South Africa."
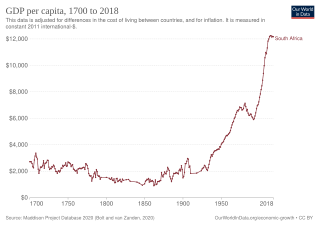
Prior to the arrival of the European settlers in the 17th century the economy of what was to become South Africa was dominated by subsistence agriculture and hunting.

The Gardens Shul, formally the Cape Town Hebrew Congregation (CTHC), also called the Great Synagogue, is a Modern Orthodox Jewish congregation and synagogue, located in the Company Gardens, in the Gardens neighborhood of Cape Town, South Africa. The congregation was established in 1841, making it the oldest Jewish congregation in South Africa.

Saint Helena Bay is a settlement in West Coast District Municipality in the Western Cape province of South Africa.

The South African Union for Progressive Judaism (SAUPJ) is an affiliate of the World Union for Progressive Judaism and supports 11 progressive congregations. Rabbi Moses Cyrus Weiler, a founder of Reform Judaism in the country, led the country's first Reform synagogue, Temple Israel in Hillbrow, Johannesburg. Weiler is credited with growing the movement, to represent 15-17% of South African Jewry and establishing 25 congregations in the country. A 2020 joint study by the Institute for Jewish Policy Research and the University of Cape Town showed that 12% of Jews identified as Progressive and that in relative terms the progressive strands are increasing after falling to 7% in 1998 and 2005 studies. In Johannesburg, the community accounts for 7% of the city's Jewry, rising to 18% in Cape Town and 25% in Durban.

The Piketberg Mountain Range is a mountain range located in the Swartland region of the Western Cape in South Africa.