
The South Eastern Freeway is a 76 kilometre controlled-access highway in South Australia. It carries traffic over the Adelaide Hills between Adelaide and the River Murray, near Murray Bridge, connecting via the Swanport Bridge to the Dukes Highway which is the main road route to Victoria. It is often referred to by South Australians simply as the Freeway, as it was the first freeway in South Australia, and is still the longest, and the only one with "Freeway" in its name rather than "Expressway" or "Highway". It is a part of the National Highway network linking the state capital cities Adelaide to Melbourne and signed as National Highway M1. The South Eastern Freeway includes 500-metre-long twin-tube tunnels in the descent towards Adelaide, the first of their kind on the National Highway. It is designated as the M1.

The O-Bahn Busway is a guided busway that is part of the bus rapid transit system servicing the northeastern suburbs of Adelaide, South Australia. The O-Bahn system was conceived by Daimler-Benz to enable buses to avoid traffic congestion by sharing tram tunnels in the German city of Essen.

Norwood is a suburb of Adelaide, about 4 km (2.5 mi) east of the Adelaide city centre. The suburb is in the City of Norwood Payneham & St Peters, whose predecessor was the oldest South Australian local government municipality.
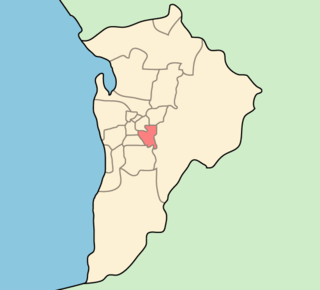
The City of Burnside is a local government area in the South Australian city of Adelaide stretching from the Adelaide Parklands into the Adelaide foothills with an area of 2,753 hectares. It was founded in August 1856 as the District Council of Burnside, the name of a property of an early settler, and was classed as a city in 1943. The LGA is bounded by Adelaide, Adelaide Hills Council, Campbelltown, Mitcham, Norwood Payneham and St Peters and Unley.

The metropolitan area of Adelaide, South Australia is served by a wide variety of transport. Being centrally located on the Australian mainland, it forms a hub for east–west and north–south routes. The road network includes major expressways such as the Southern Expressway, the South Eastern Freeway, the Port River Expressway, the Northern Expressway and the South Road Superway. The city also has a public transport system managed by Adelaide Metro, consisting of a contracted bus system including the O-Bahn Busway, six metropolitan railway lines, and the Glenelg-Adelaide-Hindmarsh Tram. According to a study conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics, Adelaide has the highest passenger vehicle travel to work (84%) and the second lowest proportion of people walking to work (2.9%)–something that is being combated by the South Australian government in an effort to increase citizen ridership and use of public transport.

The Metropolitan Adelaide Transport Study, or "MATS Plan" as it became known, was a comprehensive transport plan released in 1968 proposing a number of road and rail transport projects for the metropolitan area of Adelaide, South Australia.
Fullarton Road is a main road in the South Australian capital city of Adelaide.

The history of the City of Burnside, a local government area in the metropolitan area of Adelaide, spans three centuries. Prior to European settlement Burnside was inhabited by the Kaurna people, who lived around the creeks of the River Torrens during the winter and in the Adelaide Hills during the summer.
The Port River Expressway is a 5.5-kilometre (3.4 mi) freeway-grade road. The expressway links Port Adelaide and the LeFevre Peninsula to the northern suburbs of Adelaide and major interstate routes via Salisbury Highway (A9) to Port Wakefield Road (A1) and the Max Fatchen Northern Expressway (M2) to Perth, Darwin and Sydney.

Glen Osmond Road is a major section of the Princes Highway and state Highway 1 in the city of Adelaide, South Australia. Connecting the Adelaide city centre with the Adelaide Hills via the South Eastern Freeway; Glen Osmond Road carries half of Adelaide's freight traffic and is the major commuter route from the southern Adelaide Hills. It has intersections at Greenhill Road, Fullarton Road, Cross Road and Portrush Road.

Buses in Adelaide comprise the most extensive service of the South Australian capital's public transport system, the Adelaide Metro. A large fleet of diesel and natural gas powered buses operate services which typically terminate in the city-centre or at a suburban interchange. Buses get priority on many roads and intersections, with dedicated bus lanes and 'B'-light bus only phases at many traffic lights.
East Torrens Messenger is a weekly suburban newspaper in Adelaide, part of the Messenger Newspapers group. The East Torrens' area is bounded by Hackney Road to the west, the River Torrens Valley to the north, Magill Road to the south and the Athelstone foothills in the east.
Lower North East Road is an arterial road in the northeastern suburbs of Adelaide, South Australia. From west to east, it consists of North Terrace through Kent Town, Payneham Road and Lower North East Road proper. It links the north-eastern corner of Adelaide to Houghton in the Adelaide Hills, and is an urban alternative to North East Road.
Adelaide has two city ring routes, that loop around the Adelaide city centre and North Adelaide, known as the Inner and Outer Ring Routes.
Regency Road is a main east-west road connecting the inner northern suburbs of Adelaide, South Australia. Located approximately 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) north of the city centre, it spans from Arndale Shopping Centre, Kilkenny in the west, to Broadview in the east, continuing eastwards as Muller Road, to end at North East Road in Klemzig. Regency Road has major intersections at Torrens Road, South Road, Churchill Road, Prospect Road, Main North Road and Hampstead Road.
The East Torrens Football Association (ETFA) was an Australian rules football competition based in the eastern and north-eastern suburbs of Adelaide, South Australia until it merged with the North Adelaide District Football Association to form the Norwood-North Football Association at the end of the 1968 season. It was formed in 1916 for the purpose of “fostering junior football in the Norwood district."

The District Council of East Torrens was a local government council of South Australia from 1853 to 1997.

The City of Kensington and Norwood, originally the Corporate Town of Kensington and Norwood, was a local government area in South Australia from 1853 to 1997, centred on the inner eastern Adelaide suburbs of Kensington and Norwood. In November 1997 it amalgamated with the City of Payneham and the Town of St Peters to form the City of Norwood Payneham & St Peters.












