In knot theory, a prime knot or prime link is a knot that is, in a certain sense, indecomposable. Specifically, it is a non-trivial knot which cannot be written as the knot sum of two non-trivial knots. Knots that are not prime are said to be composite knots or composite links. It can be a nontrivial problem to determine whether a given knot is prime or not.
Contents
A family of examples of prime knots are the torus knots. These are formed by wrapping a circle around a torus p times in one direction and q times in the other, where p and q are coprime integers.
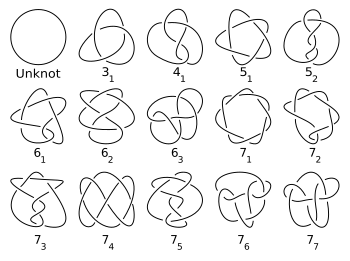
Knots are characterized by their crossing numbers. The simplest prime knot is the trefoil with three crossings. The trefoil is actually a (2, 3)-torus knot. The figure-eight knot, with four crossings, is the simplest non-torus knot. For any positive integer n, there are a finite number of prime knots with n crossings. The first few values for exclusively prime knots (sequence A002863 in the OEIS ) and for prime or composite knots (sequence A086825 in the OEIS ) are given in the following table. As of June 2025, prime knots up to 20 crossings have been fully tabulated. [1]
n 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Number of prime knots
with n crossings0 0 1 1 2 3 7 21 49 165 552 2176 9988 46972 253293 1388705 8053393 48266466 294130458 1847319428 Composite knots 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 5 ... ... ... ... ... ... Total 0 0 1 1 2 5 8 26 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Enantiomorphs are counted only once in this table and the following chart (i.e. a knot and its mirror image are considered equivalent).