| Thermodynamics |
|---|
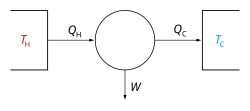 |
The pseudo Stirling cycle, also known as the adiabatic Stirling cycle, is a thermodynamic cycle with an adiabatic working volume and isothermal heater and cooler, in contrast to the ideal Stirling cycle with an isothermal working space. [1] The working fluid has no bearing on the maximum thermal efficiencies of the pseudo Stirling cycle. [2]
Contents
Practical Stirling engines usually use a adiabatic Stirling cycle as the ideal Stirling cycle can not be practically implemented. Nomenclature (practical engines and ideal cycle are both named Stirling) [3] and lack in specificity (omitting ideal or adiabatic Stirling cycle) can cause confusion.














