Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a potent opioid mainly used as a recreational drug for its euphoric effects. Medical grade diamorphine is used as a pure hydrochloride salt. Various white and brown powders sold illegally around the world as heroin are routinely diluted with cutting agents. Black tar heroin is a variable admixture of morphine derivatives—predominantly 6-MAM (6-monoacetylmorphine), which is the result of crude acetylation during clandestine production of street heroin. Heroin is used medically in several countries to relieve pain, such as during childbirth or a heart attack, as well as in opioid replacement therapy.
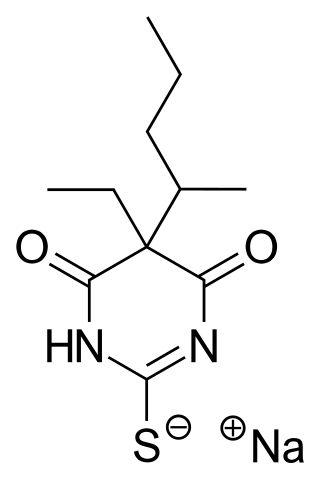
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal, thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal, is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was previously the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States, but the US manufacturer Hospira stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011 and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare.

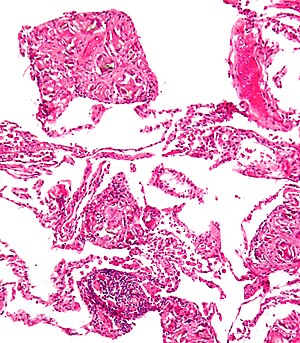
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant. It is an ingredient in ceramics, paints, and roofing material. It is a main ingredient in many cosmetics. It occurs as foliated to fibrous masses, and in an exceptionally rare crystal form. It has a perfect basal cleavage and an uneven flat fracture, and it is foliated with a two-dimensional platy form.

Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but the term may also be applied in a broader sense to include euthanasia and other forms of suicide. The drugs cause the person to become unconscious, stops their breathing, and causes a heart arrhythmia, in that order.
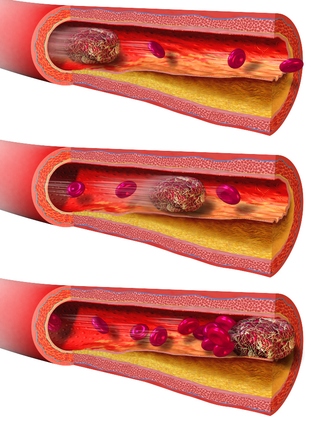
An embolus is an unattached mass that travels through the bloodstream and is capable of creating blockages. When an embolus occludes a blood vessel, it is called an embolism or embolic event. There are a number of different types of emboli, including blood clots, cholesterol plaque or crystals, fat globules, gas bubbles, and foreign bodies, which can result in different types of embolisms.

Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding.

Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mouth. When taken by mouth, it typically begins working within an hour, while intravenously, it typically begins working within five minutes.

Bleomycin is a medication used to treat cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, and cervical cancer among others. Typically used with other cancer medications, it can be given intravenously, by injection into a muscle or under the skin. It may also be administered inside the chest to help prevent the recurrence of a fluid around the lung due to cancer; however talc is better for this.
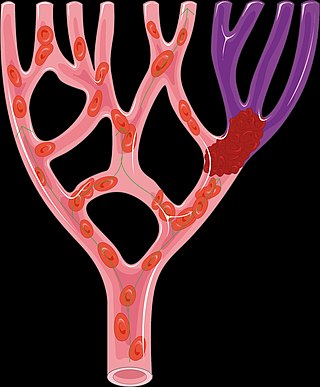
Alteplase, sold under the brand name Activase among others, is a biosynthetic form of human tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA). It is a thrombolytic medication used to treat acute ischemic stroke, acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism associated with low blood pressure, and blocked central venous catheter. It is given by injection into a vein or artery. Alteplase is the same as the normal human plasminogen activator produced in vascular endothelial cells and is synthesized via recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO). Alteplase causes the breakdown of a clot by inducing fibrinolysis.

Xylazine is a pharmaceutical drug used for sedation, anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and analgesia in animals such as horses, cattle, and other non-human mammals. Veterinarians also use xylazine as an emetic, especially in cats. It is an analog of clonidine and an agonist at the α2 class of adrenergic receptor.
Wooden chest syndrome is a rigidity of the chest following the administration of high doses of opioids during anaesthesia.

Black tar heroin is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be dark orange or dark brown in appearance.
Intracardiac injections are injections that are given directly into the heart muscles or ventricles. They can be used in emergencies, although they are rarely used in modern practice.

"Chasing the dragon" (CTD), or "foily" in Australian English, refers to inhaling the vapor from a heated solution of a powdered psychoactive drug on a sheet of aluminum foil. The moving vapor is chased after with a tube through which the user inhales. The "chasing" occurs as the user gingerly keeps the liquid moving in order to keep it from overheating and burning up too quickly, on a heat conducting material such as aluminium foil.

Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body. Intravenous therapy, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. As of 2004, there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries.
Dosage forms are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components (excipients), in a particular configuration, and apportioned into a particular dose. For example, two products may both be amoxicillin, but one is in 500 mg capsules and another is in 250 mg chewable tablets. The term unit dose can also sometimes encompass non-reusable packaging as well, although the FDA distinguishes that by unit-dose "packaging" or "dispensing". Depending on the context, multi(ple) unit dose can refer to distinct drug products packaged together, or to a single drug product containing multiple drugs and/or doses. The term dosage form can also sometimes refer only to the pharmaceutical formulation of a drug product's constituent drug substance(s) and any blends involved, without considering matters beyond that. Because of the somewhat vague boundaries and unclear overlap of these terms and certain variants and qualifiers within the pharmaceutical industry, caution is often advisable when conversing with someone who may be unfamiliar with another person's use of the term.

Computed tomography angiography is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, images are created to look for blockages, aneurysms, dissections, and stenosis. CTA can be used to visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta and other large blood vessels, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs. CTA can also be used to localise arterial or venous bleed of the gastrointestinal system.
In medicine, a bolus is the administration of a discrete amount of medication, drug, or other compound within a specific time, generally 1–30 minutes, to raise its concentration in blood to an effective level. The administration can be given by injection: intravenously, intramuscularly, intrathecally, subcutaneously, or by inhalation. The article on routes of administration provides more information, as the preceding list of ROAs is not exhaustive.

Intravenous sodium bicarbonate, also known as sodium hydrogen carbonate, is a medication primarily used to treat severe metabolic acidosis. For this purpose it is generally only used when the pH is less than 7.1 and when the underlying cause is either diarrhea, vomiting, or the kidneys. Other uses include high blood potassium, tricyclic antidepressant overdose, and cocaine toxicity as well as a number of other poisonings. It is given by injection into a vein.

Emphysema, or pulmonary emphysema, is a lower respiratory tract disease, characterised by air-filled spaces (pneumatoses) in the lungs, that can vary in size and may be very large. The spaces are caused by the breakdown of the walls of the alveoli and they replace the spongy lung parenchyma. This reduces the total alveolar surface available for gas exchange leading to a reduction in oxygen supply for the blood. Emphysema usually affects the middle aged or older population because it takes time to develop with the effects of tobacco smoking, and other risk factors. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a genetic risk factor that may lead to the condition presenting earlier.