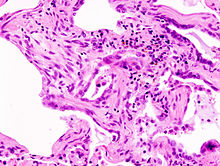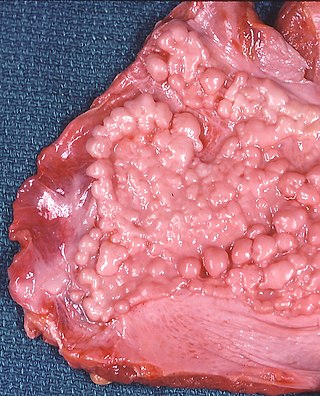
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart disease.
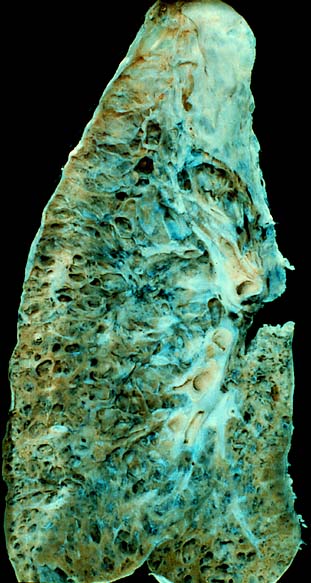
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare, progressive and systemic disease that typically results in cystic lung destruction. It predominantly affects women, especially during childbearing years. The term sporadic LAM is used for patients with LAM not associated with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), while TSC-LAM refers to LAM that is associated with TSC.

Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.

Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
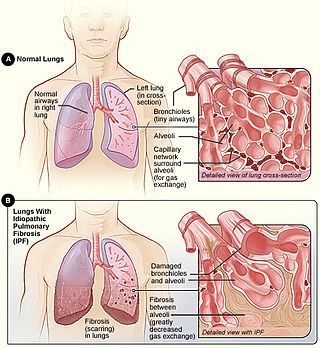
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) synonymous with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic pulmonary fibrosis characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function.

Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.
Ventilator-associated lung injury (VALI) is an acute lung injury that develops during mechanical ventilation and is termed ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) if it can be proven that the mechanical ventilation caused the acute lung injury. In contrast, ventilator-associated lung injury (VALI) exists if the cause cannot be proven. VALI is the appropriate term in most situations because it is virtually impossible to prove what actually caused the lung injury in the hospital.
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness is a state characterised by easily triggered bronchospasm.
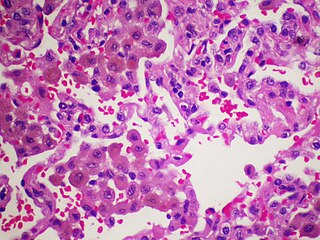
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia featuring elevated numbers of macrophages within the alveoli of the lung. The alveolar macrophages have a characteristic light brown pigmentation and accumulate in the alveolar lumen and septa regions of the lower lobes of the lungs. The typical effects of the macrophage accumulation are inflammation and later fibrosis of the lung tissue.

Respiratory bronchiolitis is a lung disease associated with tobacco smoking. In pathology, it is defined by the presence of "smoker's macrophages". When manifesting significant clinical symptoms it is referred to as respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD).
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite standard medical treatment. It is a broad therapeutic concept. It is defined by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society as an evidence-based, multidisciplinary, and comprehensive intervention for patients with chronic respiratory diseases who are symptomatic and often have decreased daily life activities. In general, pulmonary rehabilitation refers to a series of services that are administered to patients of respiratory disease and their families, typically to attempt to improve the quality of life for the patient. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be carried out in a variety of settings, depending on the patient's needs, and may or may not include pharmacologic intervention.
Ciclosporin is a cyclic polypeptide that has been used widely as an orally-available immunosuppressant. It was originally used to prevent transplant rejection of solid organs but has also found use as an orally administered agent to treat psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, dry eye and other auto-immune related conditions. A variety of pre-clinical and clinical studies have been and are investigating its use to treat lung-related disorders via inhalation.
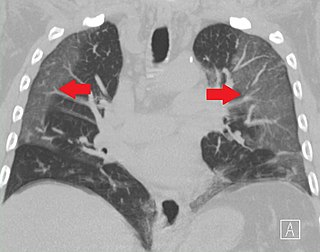
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.

Flock worker's lung is an occupational lung disease caused by exposure to flock, small fibers that are glued to a backing in order to create a specific texture. People who work in flocking are at risk of inhaling small pieces of the flock fibers, which causes interstitial lung disease. The disease was initially described in 1998, when a group of workers at a flocking plant developed interstitial lung disease of unknown cause.

William N. Rom is the Sol and Judith Bergstein Professor of Medicine and Environmental Medicine, Emeritus at New York University School of Medicine and former Director of the Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at New York University and Chief of the Chest Service at Bellevue Hospital Center, 1989–2014. He is Research Scientist at the School of Global Public Health at New York University and Adjunct Professor at the NYU Robert F. Wagner Graduate School of Public Service. He teaches Climate Change and Global Public Health and Environmental Health in a Global World.
Averill Abraham Liebow was an international leader on the pathology of the lung. He is credited with the development of a classification system for lung disease. His observations resulted in the discovery of new diseases. Liebow was among the first scientists to enter Hiroshima, Japan, after the atomic bomb was dropped in 1945. Accounts of that experience were published in "Encounter With Disaster: A Medical Diary of Hiroshima" and "Medical Effects of the Atomic Bomb in Japan."