
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare lung disorder characterized by an abnormal accumulation of surfactant-derived lipoprotein compounds within the alveoli of the lung. The accumulated substances interfere with the normal gas exchange and expansion of the lungs, ultimately leading to difficulty breathing and a predisposition to developing lung infections. The causes of PAP may be grouped into primary, secondary, and congenital causes, although the most common cause is a primary autoimmune condition in an individual.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

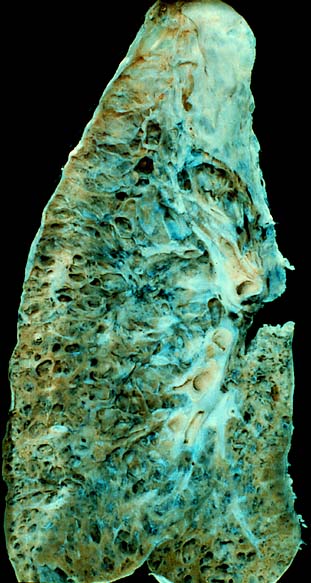
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.

Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris, aspiration, herbicides or fluorocarbons and some systemic diseases. If unresolved, continued inflammation can result in irreparable damage such as pulmonary fibrosis.

Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.

Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease.

Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), also known as obliterative bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis and popcorn lung, is a disease that results in obstruction of the smallest airways of the lungs (bronchioles) due to inflammation. Symptoms include a dry cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and feeling tired. These symptoms generally get worse over weeks to months. It is not related to cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, previously known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia.

Alveolar lung diseases, are a group of diseases that mainly affect the alveoli of the lungs.
Occupational lung diseases comprise a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiolitis obliterans, inhalation injury, interstitial lung diseases, infections, lung cancer and mesothelioma. These can be caused directly or due to immunological response to an exposure to a variety of dusts, chemicals, proteins or organisms. Occupational cases of interstitial lung disease may be misdiagnosed as COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or a myriad of other diseases; leading to a delay in identification of the causative agent.
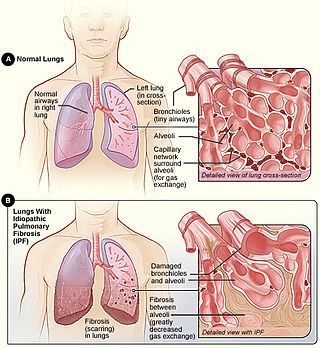
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) synonymous with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic pulmonary fibrosis characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function.

Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.

Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways. There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.

Respiratory bronchiolitis is a lung disease associated with tobacco smoking. In pathology, it is defined by the presence of "smoker's macrophages". When manifesting significant clinical symptoms it is referred to as respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD).
Rheumatoid lung disease is a disease of the lung associated with RA, rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid lung disease is characterized by pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis, lung nodules and pulmonary hypertension. Common symptoms associated with the disease include shortness of breath, cough, chest pain and fever. It is estimated that about one quarter of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop this disease, which are more likely to develop among elderly men with a history of smoking.
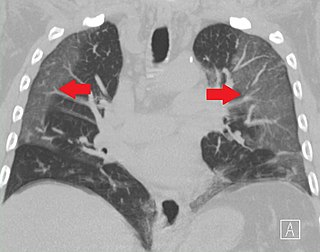
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.

Antisynthetase syndrome (ASS) is a multisystematic autoimmune disease associated with inflammatory myositis, interstitial lung disease, and antibodies directed against various synthetases of aminoacyl-transfer RNA. Other common symptoms include mechanic's hands, Raynaud's phenomenon, arthritis, and fever.

Flock worker's lung is an occupational lung disease caused by exposure to flock, small fibers that are glued to a backing in order to create a specific texture. People who work in flocking are at risk of inhaling small pieces of the flock fibers, which causes interstitial lung disease. The disease was initially described in 1998, when a group of workers at a flocking plant developed interstitial lung disease of unknown cause.
Averill Abraham Liebow was an international leader on the pathology of the lung. He is credited with the development of a classification system for lung disease. His observations resulted in the discovery of new diseases. Liebow was among the first scientists to enter Hiroshima, Japan, after the atomic bomb was dropped in 1945. Accounts of that experience were published in "Encounter With Disaster: A Medical Diary of Hiroshima" and "Medical Effects of the Atomic Bomb in Japan."

















