Related Research Articles

Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Wheezing and nail clubbing may also occur. Those with the disease often get lung infections.
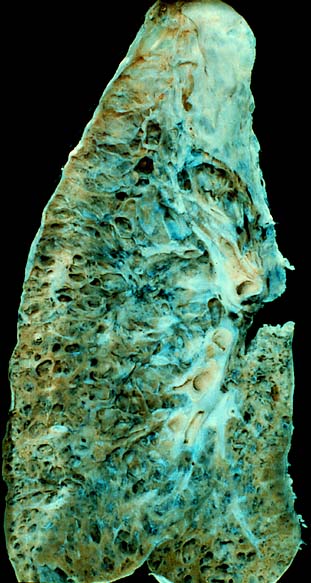
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.

Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris, aspiration, herbicides or fluorocarbons and some systemic diseases. If unresolved, continued inflammation can result in irreparable damage such as pulmonary fibrosis.
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a disease in which an eosinophil, a type of white blood cell, accumulates in the lungs. These cells cause disruption of the normal air spaces (alveoli) where oxygen is extracted from the atmosphere. Several different kinds of eosinophilic pneumonia exist and can occur in any age group. The most common symptoms include cough, fever, difficulty breathing, and sweating at night. Eosinophilic pneumonia is diagnosed by a combination of characteristic symptoms, findings on a physical examination by a health provider, and the results of blood tests and X-rays. Prognosis is excellent once most eosinophilic pneumonia is recognized and treatment with corticosteroids is begun.

Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles (bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amount of fluid introduced and then collected for examination. This method is typically performed to diagnose pathogenic infections of the lower respiratory airways, though it also has been shown to have utility in diagnosing interstitial lung disease. Bronchoalveolar lavage can be a more sensitive method of detection than nasal swabs in respiratory molecular diagnostics, as has been the case with SARS-CoV-2 where bronchoalveolar lavage samples detect copies of viral RNA after negative nasal swab testing.

Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO), also known as obliterative bronchiolitis, constrictive bronchiolitis and popcorn lung, is a disease that results in obstruction of the smallest airways of the lungs (bronchioles) due to inflammation. Symptoms include a dry cough, shortness of breath, wheezing and feeling tired. These symptoms generally get worse over weeks to months. It is not related to cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, previously known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia.
Occupational lung diseases are work-related, lung conditions that have been caused or made worse by the materials a person is exposed to within the workplace. It includes a broad group of diseases, including occupational asthma, industrial bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiolitis obliterans, inhalation injury, interstitial lung diseases, infections, lung cancer and mesothelioma. These diseases can be caused directly or due to immunological response to an exposure to a variety of dusts, chemicals, proteins or organisms.
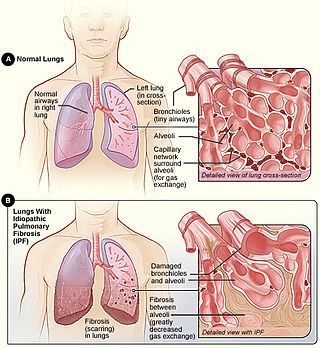
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic scarring lung disease characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism.

Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium. UIP is thus classified as a form of interstitial lung disease.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.

Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways. There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.

Fibrothorax is a medical condition characterised by severe scarring (fibrosis) and fusion of the layers of the pleural space surrounding the lungs resulting in decreased movement of the lung and ribcage. The main symptom of fibrothorax is shortness of breath. There also may be recurrent fluid collections surrounding the lungs. Fibrothorax may occur as a complication of many diseases, including infection of the pleural space known as an empyema or bleeding into the pleural space known as a haemothorax.
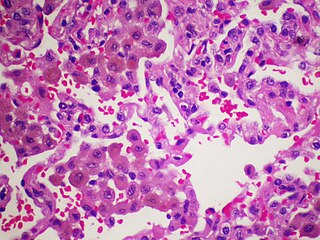
Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia featuring elevated numbers of macrophages within the alveoli of the lung. The alveolar macrophages have a characteristic light brown pigmentation and accumulate in the alveolar lumen and septa regions of the lower lobes of the lungs. The typical effects of the macrophage accumulation are inflammation and later fibrosis of the lung tissue.
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite standard medical treatment. It is a broad therapeutic concept. It is defined by the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society as an evidence-based, multidisciplinary, and comprehensive intervention for patients with chronic respiratory diseases who are symptomatic and often have decreased daily life activities. In general, pulmonary rehabilitation refers to a series of services that are administered to patients of respiratory disease and their families, typically to attempt to improve the quality of life for the patient. Pulmonary rehabilitation may be carried out in a variety of settings, depending on the patient's needs, and may or may not include pharmacologic intervention.
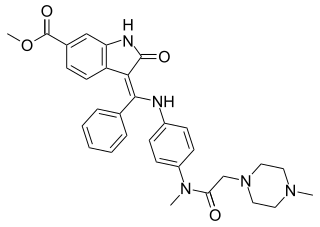
Nintedanib, sold under the brand names Ofev and Vargatef, is an oral medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and along with other medications for some types of non-small-cell lung cancer.
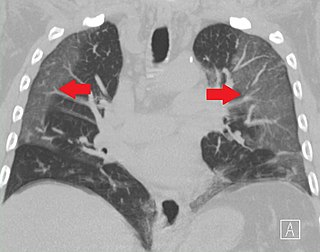
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.
Galecto Biotech is a biotechnology company that develops small molecules for the treatment of severe diseases, including fibrosis, cancer and inflammation. The company was founded in 2011 by leading galectin scientists and biotech executives from Sweden, United Kingdom, and Denmark. The company today is incorporated in the U.S., and has its operating headquarters in Copenhagen, Denmark.
References
- ↑ Cottin, V; Donsbeck, AV; Revel, D; Loire, R; Cordier, JF (October 1998). "Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Individualization of a clinicopathologic entity in a series of 12 patients". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 158 (4): 1286–93. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.158.4.9802119. PMID 9769293.
- ↑ Kinder, Brent W.; Collard, Harold R.; Koth, Laura; Daikh, David I.; Wolters, Paul J.; Elicker, Brett; Jones, Kirk D.; King, Talmadge E. (October 2007). "Idiopathic Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 176 (7): 691–697. doi:10.1164/rccm.200702-220OC. PMC 1994238 . PMID 17556720.
- ↑ Travis, William D.; Hunninghake, Gary; King, Talmadge E.; Lynch, David A.; Colby, Thomas V.; Galvin, Jeffrey R.; Brown, Kevin K.; Chung, Man Pyo; Cordier, Jean-François; du Bois, Roland M.; Flaherty, Kevin R.; Franks, Teri J.; Hansell, David M.; Hartman, Thomas E.; Kazerooni, Ella A.; Kim, Dong Soon; Kitaichi, Masanori; Koyama, Takashi; Martinez, Fernando J.; Nagai, Sonoko; Midthun, David E.; Müller, Nestor L.; Nicholson, Andrew G.; Raghu, Ganesh; Selman, Moisés; Wells, Athol (15 June 2008). "Idiopathic Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 177 (12): 1338–1347. doi:10.1164/rccm.200611-1685OC. PMID 18388353.
- ↑ Travis, William D.; Matsui, Kazuhiro; Moss, Joel; Ferrans, Victor J. (January 2000). "Idiopathic Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: Prognostic Significance of Cellular and Fibrosing Patterns". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 24 (1): 19–33. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200001000-00003 . PMID 10632484.